Product Description
G3 series helical geared motor,
1. Two types of housing: Aluminum alloy and cast iron; Two kinds of frames: foot mounting and flange mounting. They are good-looking in appearance, suitable for universal mounting.
2. Helical gear with the high-10sile alloy material makes the construction more compact, housing smaller, efficiency higher, output torque larger.
3.Hardened facing & well finished transmission gear has the advantages : seldom distortion, high precision,stable transmission, lower noise, possible for continuous work under the dreadful conditions.
4.With 6 specification for the diameter of output shaft: Ø18,Ø22,Ø28,Ø32,Ø40,Ø50.
5.Two or three-stage transmission, large in ratio range, each single frame size with 14 ratios from 5:1 to 200:1.
6.Using high quality bearing prolongs the use life.
7.High-performance oil seal prevents the lubricant from leaki
ng back to the inner of motor.
8.Three-phase motor combined the standard and full-enclosed aluminum motor, which is good in waterproof, easy in heat dissipation, high in running efficiency.
9.Modular combination extends the transmission ratio from i=5:1 to 1400:1.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor |
|---|---|
| Function: | Speed Reduction |
| Layout: | Coaxial |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Vertical Type |
| Step: | Single-Step |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Where can individuals find reliable resources for learning more about gear motors and their applications?
Individuals seeking to learn more about gear motors and their applications have access to various reliable resources that provide valuable information and insights. Here are some sources where individuals can find reliable information about gear motors:
1. Manufacturer Websites:
Manufacturer websites are a primary source of information about gear motors. Gear motor manufacturers often provide detailed product specifications, application guides, technical documentation, and educational materials on their websites. These resources offer insights into different gear motor types, features, performance characteristics, and application considerations. Manufacturer websites are a reliable and convenient starting point for learning about gear motors.
2. Industry Associations and Organizations:
Industry associations and organizations related to mechanical engineering, automation, and motion control often have resources and publications dedicated to gear motors. These organizations provide technical articles, whitepapers, industry standards, and guidelines related to gear motor design, selection, and application. Examples of such associations include the American Gear Manufacturers Association (AGMA), International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), and Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
3. Technical Publications and Journals:
Technical publications and journals focused on engineering, robotics, and motion control are valuable sources of in-depth knowledge about gear motors. Publications like IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, Mechanical Engineering magazine, or Motion System Design magazine often feature articles, case studies, and research papers on gear motor technology, advancements, and applications. These publications provide authoritative and up-to-date information from industry experts and researchers.
4. Online Forums and Communities:
Online forums and communities dedicated to engineering, robotics, and automation can be excellent resources for discussions, insights, and practical experiences related to gear motors. Websites like Stack Exchange, engineering-focused subreddits, or specialized forums provide platforms for individuals to ask questions, share knowledge, and engage in discussions with professionals and enthusiasts in the field. Participating in these communities allows individuals to learn from real-world experiences and gain practical insights.
5. Educational Institutions and Courses:
Technical colleges, universities, and vocational training centers often offer courses or programs in mechanical engineering, mechatronics, or automation that cover gear motor fundamentals and applications. These educational institutions provide comprehensive curricula, textbooks, and lecture materials that can serve as reliable resources for individuals interested in learning about gear motors. Additionally, online learning platforms like Coursera, Udemy, or LinkedIn Learning offer courses on topics related to gear motors and motion control.
6. Trade Shows and Exhibitions:
Attending trade shows, exhibitions, and industry conferences related to automation, robotics, or motion control provides opportunities to learn about the latest advancements in gear motor technology. These events often feature product demonstrations, technical presentations, and expert panels where individuals can interact with gear motor manufacturers, industry experts, and other professionals. It’s a great way to stay updated on the latest trends, innovations, and applications of gear motors.
When seeking reliable resources, it’s important to consider the credibility of the source, the expertise of the authors, and the relevance to the specific area of interest. By leveraging these resources, individuals can gain a comprehensive understanding of gear motors and their applications, from basic principles to advanced topics, enabling them to make informed decisions and effectively utilize gear motors in their projects or applications.

What is the significance of gear reduction in gear motors, and how does it affect efficiency?
Gear reduction plays a significant role in gear motors as it enables the motor to deliver higher torque while reducing the output speed. This feature has several important implications for gear motors, including enhanced power transmission, improved control, and potential trade-offs in terms of efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of the significance of gear reduction in gear motors and its effect on efficiency:
Significance of Gear Reduction:
1. Increased Torque: Gear reduction allows gear motors to generate higher torque output compared to a motor without gears. By reducing the rotational speed at the output shaft, gear reduction increases the mechanical advantage of the system. This increased torque is beneficial in applications that require high torque to overcome resistance, such as lifting heavy loads or driving machinery with high inertia.
2. Improved Control: Gear reduction enhances the control and precision of gear motors. By reducing the speed, gear reduction allows for finer control over the motor’s rotational movement. This is particularly important in applications that require precise positioning or accurate speed control. The gear reduction mechanism enables gear motors to achieve smoother and more controlled movements, reducing the risk of overshooting or undershooting the desired position.
3. Load Matching: Gear reduction helps match the motor’s power characteristics to the load requirements. Different applications have varying torque and speed requirements. Gear reduction allows the gear motor to achieve a better match between the motor’s power output and the specific requirements of the load. It enables the motor to operate closer to its peak efficiency by optimizing the torque-speed trade-off.
Effect on Efficiency:
While gear reduction offers several advantages, it can also affect the efficiency of gear motors. Here’s how gear reduction impacts efficiency:
1. Mechanical Efficiency: The gear reduction process introduces mechanical components such as gears, bearings, and lubrication systems. These components introduce additional friction and mechanical losses into the system. As a result, some energy is lost in the form of heat during the gear reduction process. The efficiency of the gear motor is influenced by the quality of the gears, the lubrication used, and the overall design of the gear system. Well-designed and properly maintained gear systems can minimize these losses and optimize mechanical efficiency.
2. System Efficiency: Gear reduction affects the overall system efficiency by impacting the motor’s electrical efficiency. In gear motors, the motor typically operates at higher speeds and lower torques compared to a direct-drive motor. The overall system efficiency takes into account both the electrical efficiency of the motor and the mechanical efficiency of the gear system. While gear reduction can increase the torque output, it also introduces additional losses due to increased mechanical complexity. Therefore, the overall system efficiency may be lower compared to a direct-drive motor for certain applications.
It’s important to note that the efficiency of gear motors is influenced by various factors beyond gear reduction, such as motor design, control systems, and operating conditions. The selection of high-quality gears, proper lubrication, and regular maintenance can help minimize losses and improve efficiency. Additionally, advancements in gear technology, such as the use of precision gears and improved lubricants, can contribute to higher overall efficiency in gear motors.
In summary, gear reduction is significant in gear motors as it provides increased torque, improved control, and better load matching. However, gear reduction can introduce mechanical losses and affect the overall efficiency of the system. Proper design, maintenance, and consideration of application requirements are essential to optimize the balance between torque, speed, and efficiency in gear motors.

What are the different types of gears used in gear motors, and how do they impact performance?
Various types of gears are used in gear motors, each with its unique characteristics and impact on performance. The choice of gear type depends on the specific requirements of the application, including torque, speed, efficiency, noise level, and space constraints. Here’s a detailed explanation of the different types of gears used in gear motors and their impact on performance:
1. Spur Gears:
Spur gears are the most common type of gears used in gear motors. They have straight teeth that are parallel to the gear’s axis and mesh with another spur gear to transmit power. Spur gears provide high efficiency, reliable operation, and cost-effectiveness. However, they can generate significant noise due to the meshing of teeth, and they may produce axial thrust forces. Spur gears are suitable for applications that require high torque transmission and moderate to high rotational speeds.
2. Helical Gears:
Helical gears have angled teeth that are cut at an angle to the gear’s axis. This helical tooth configuration enables gradual engagement and smoother tooth contact, resulting in reduced noise and vibration compared to spur gears. Helical gears provide higher load-carrying capacity and are suitable for applications that require high torque transmission and moderate to high rotational speeds. They are commonly used in gear motors where low noise operation is desired, such as in automotive applications and industrial machinery.
3. Bevel Gears:
Bevel gears have teeth that are cut on a conical surface. They are used to transmit power between intersecting shafts, usually at right angles. Bevel gears can have straight teeth (straight bevel gears) or curved teeth (spiral bevel gears). These gears provide efficient power transmission and precise motion control in applications where shafts need to change direction. Bevel gears are commonly used in gear motors for applications such as steering systems, machine tools, and printing presses.
4. Worm Gears:
Worm gears consist of a worm (a type of screw) and a mating gear called a worm wheel or worm gear. The worm has a helical thread that meshes with the worm wheel, resulting in a compact and high gear reduction ratio. Worm gears provide high torque transmission, low noise operation, and self-locking properties, which prevent reverse motion. They are commonly used in gear motors for applications that require high gear reduction and locking capabilities, such as in lifting mechanisms, conveyor systems, and machine tools.
5. Planetary Gears:
Planetary gears, also known as epicyclic gears, consist of a central sun gear, multiple planet gears, and an outer ring gear. The planet gears mesh with both the sun gear and the ring gear, creating a compact and efficient gear system. Planetary gears offer high torque transmission, high gear reduction ratios, and excellent load distribution. They are commonly used in gear motors for applications that require high torque and compact size, such as in robotics, automotive transmissions, and industrial machinery.
6. Rack and Pinion:
Rack and pinion gears consist of a linear rack (a straight toothed bar) and a pinion gear (a spur gear with a small diameter). The pinion gear meshes with the rack to convert rotary motion into linear motion or vice versa. Rack and pinion gears provide precise linear motion control and are commonly used in gear motors for applications such as linear actuators, CNC machines, and steering systems.
The choice of gear type in a gear motor depends on factors such as the desired torque, speed, efficiency, noise level, and space constraints. Each type of gear offers specific advantages and impacts the performance of the gear motor differently. By selecting the appropriate gear type, gear motors can be optimized for their intended applications, ensuring efficient and reliable power transmission.


editor by CX 2024-04-11
China Professional 36mm Micro Speed Reducer Powder Transmission High Precision Planetary Gearboxes & Geared Motors vacuum pump electric
Product Description
We are a factory specialized in metal parts hardware & metal gearbox geared motor through powder metallurgy process .We services with ODM/OEM gearbox design and development , gearmotors manufacture.
Low-Cost, High-Efficiency Planetary Gear Systems
Planetary gearboxes are especially efficient, they are suitable for continuous, intermittent and alternating operation as well as for clockwise and anticlockwise rotation. Their use results in an increased performance of the entire drive train since the choice of the right gearbox allows for a smaller motor and thereby increases the economic efficiency of the entire drive train.
planetary gearbox with optimized helical gearset teeth was developed for highly demanding applications. These gearbox is perfect for applications ranging from basic machinedesign to printing, packaging, and robotics.
Description:
Product Name : 36mm planet gearbox with DC brushed motors high torque geared motor / Speed reducer / steel gearbox
Gearbox Type: Planetary
Material: Steel
Gear Ratio : 5:1 , 10:1 , 20:1 , 25:1 , 30:1 , 40:1 , 50:1 , 60:1 ,70:1…100:1… optional
Gearbox diameter : 6mm , 8mm , 12mm , 16mm , 22mm , 24mm ,28mm, 32mm ,36mm, 38mm , 42mm ……
3V , 6V ,12V ,24V available .
Planetary Gearbox advantages:
- Easy and functional flange, foot, or shaft-mounting design
- High torque transmitted
- Extended range of transmission ratios and output speeds available
Features:
The highest dynamics in multiple axis systems
Unrivaled price-performance ratio
Low heat generation at highest speeds
For any mounting position
Lifetime lubrication for maintenance-free operation
Precise gearing
Application:
monitor,automatic vending machine,automatic cruise control,door lock actuator, retractable rearview mirror, meters, optic axis control device, head light beam level adjuster,printers,conditioning damper actuator,Car tail gate electric putter,tooth brush,vibrator, sanitary ware,coffee machine,Sweeping robot,etc.
A planetary gear set is made up of 3 types of gears , a sun gear , planet gears and a ring gear . The sun gear at high speed is located at the center of the gears , and transmits torque to the planet gears which are typically mounted on the moveable carrier .The planet gears around the central axis rotation ,mesh with the sun gear and an outer ring gear . As all the planet carriers turns , it delivers low-speed, high-torque output .
Workshop
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Vertical Type |
| Layout: | Coaxial |
| Gear Shape: | Cylindrical Gear |
| Step: | Double-Step |
| Samples: |
US$ 2/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Are gear motors suitable for both heavy-duty industrial applications and smaller-scale uses?
Yes, gear motors are suitable for both heavy-duty industrial applications and smaller-scale uses. Their versatility and ability to provide torque multiplication make them valuable in a wide range of applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of why gear motors are suitable for both types of applications:
1. Heavy-Duty Industrial Applications:
Gear motors are commonly used in heavy-duty industrial applications due to their robustness and ability to handle high loads. Here are the reasons why they are suitable for such applications:
- Torque Multiplication: Gear motors are designed to provide high torque output, making them ideal for applications that require substantial force to move or operate heavy machinery, conveyors, or equipment.
- Load Handling: Industrial settings often involve heavy loads and demanding operating conditions. Gear motors, with their ability to handle high loads, are well-suited for tasks such as lifting, pulling, pushing, or driving heavy materials or equipment.
- Durability: Heavy-duty industrial applications require components that can withstand harsh environments, frequent use, and demanding operating conditions. Gear motors are typically constructed with durable materials and designed to withstand heavy vibrations, shock loads, and temperature variations.
- Speed Reduction: Many industrial processes require the reduction of motor speed to achieve the desired output speed. Gear motors offer precise speed reduction capabilities through gear ratios, allowing for optimal control and operation of machinery and equipment.
2. Smaller-Scale Uses:
While gear motors excel in heavy-duty industrial applications, they are also suitable for smaller-scale uses across various industries and applications. Here’s why gear motors are well-suited for smaller-scale uses:
- Compact Size: Gear motors are available in compact sizes, making them suitable for applications with limited space or small-scale machinery, devices, or appliances.
- Torque and Power Control: Even in smaller-scale applications, there may be a need for torque multiplication or precise power control. Gear motors can provide the necessary torque and power output for tasks such as precise positioning, controlling speed, or driving small loads.
- Versatility: Gear motors come in various configurations, such as parallel shaft, planetary, or worm gear designs, offering flexibility to match specific requirements. They can be adapted to different applications, including robotics, medical devices, automotive systems, home automation, and more.
- Efficiency: Gear motors are designed to be efficient, converting the electrical input power into mechanical output power with minimal losses. This efficiency is advantageous for smaller-scale applications where energy conservation and battery life are critical.
Overall, gear motors are highly versatile and suitable for both heavy-duty industrial applications and smaller-scale uses. Their ability to provide torque multiplication, handle high loads, offer precise speed control, and accommodate various sizes and configurations makes them a reliable choice in a wide range of applications. Whether it’s powering large industrial machinery or driving small-scale automation systems, gear motors provide the necessary torque, control, and durability required for efficient operation.

How does the voltage and power rating of a gear motor impact its suitability for different tasks?
The voltage and power rating of a gear motor are important factors that influence its suitability for different tasks. These specifications determine the motor’s electrical characteristics and its ability to perform specific tasks effectively. Here’s a detailed explanation of how voltage and power rating impact the suitability of a gear motor for different tasks:
1. Voltage Rating:
The voltage rating of a gear motor refers to the electrical voltage it requires to operate optimally. Here’s how the voltage rating affects suitability:
- Compatibility with Power Supply: The gear motor’s voltage rating must match the available power supply. Using a motor with a voltage rating that is too high or too low for the power supply can lead to improper operation or damage to the motor.
- Electrical Safety: Adhering to the specified voltage rating ensures electrical safety. Using a motor with a higher voltage rating than recommended can pose safety hazards, while using a motor with a lower voltage rating may result in inadequate performance.
- Application Flexibility: Different tasks or applications may have specific voltage requirements. For example, low-voltage gear motors are commonly used in battery-powered devices or applications with low-power requirements, while high-voltage gear motors are suitable for industrial applications or tasks that require higher power output.
2. Power Rating:
The power rating of a gear motor indicates its ability to deliver mechanical power. It is typically specified in units of watts (W) or horsepower (HP). The power rating impacts the suitability of a gear motor in the following ways:
- Load Capacity: The power rating determines the maximum load that a gear motor can handle. Motors with higher power ratings are capable of driving heavier loads or handling tasks that require more torque.
- Speed and Torque: The power rating affects the motor’s speed and torque characteristics. Motors with higher power ratings generally offer higher speeds and greater torque output, making them suitable for applications that require faster operation or the ability to overcome higher resistance or loads.
- Efficiency and Energy Consumption: The power rating is related to the motor’s efficiency and energy consumption. Higher power-rated motors may be more efficient, resulting in lower energy losses and reduced operating costs over time.
- Thermal Considerations: Motors with higher power ratings may generate more heat during operation. It is crucial to consider the motor’s power rating in relation to its thermal management capabilities to prevent overheating and ensure long-term reliability.
Considerations for Task Suitability:
When selecting a gear motor for a specific task, it is important to consider the following factors in relation to the voltage and power rating:
- Required Torque and Load: Assess the torque and load requirements of the task to ensure that the gear motor’s power rating is sufficient to handle the expected load without being overloaded.
- Speed and Precision: Consider the desired speed and precision of the task. Motors with higher power ratings generally offer better speed control and accuracy.
- Power Supply Availability: Evaluate the availability and compatibility of the power supply with the gear motor’s voltage rating. Ensure that the power supply can provide the required voltage for the motor’s optimal operation.
- Environmental Factors: Consider any specific environmental factors, such as temperature or humidity, that may impact the gear motor’s performance. Ensure that the motor’s voltage and power ratings are suitable for the intended operating conditions.
In summary, the voltage and power rating of a gear motor have significant implications for its suitability in different tasks. The voltage rating determines compatibility with the power supply and ensures electrical safety, while the power rating influences load capacity, speed, torque, efficiency, and thermal considerations. When choosing a gear motor, it is crucial to carefully evaluate the task requirements and consider the voltage and power rating in relation to factors such as torque, speed, power supply availability, and environmental conditions.

Are there specific considerations for selecting the right gear motor for a particular application?
When selecting a gear motor for a specific application, several considerations need to be taken into account. The choice of the right gear motor is crucial to ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and reliability. Here’s a detailed explanation of the specific considerations for selecting the right gear motor for a particular application:
1. Torque Requirement:
The torque requirement of the application is a critical factor in gear motor selection. Determine the maximum torque that the gear motor needs to deliver to perform the required tasks. Consider both the starting torque (the torque required to initiate motion) and the operating torque (the torque required to sustain motion). Select a gear motor that can provide adequate torque to handle the load requirements of the application. It’s important to account for any potential torque spikes or variations during operation.
2. Speed Requirement:
Consider the desired speed range or specific speed requirements of the application. Determine the rotational speed (in RPM) that the gear motor needs to achieve to meet the application’s performance criteria. Select a gear motor with a suitable gear ratio that can achieve the desired speed at the output shaft. Ensure that the gear motor can maintain the required speed consistently and accurately throughout the operation.
3. Duty Cycle:
Evaluate the duty cycle of the application, which refers to the ratio of operating time to rest or idle time. Consider whether the application requires continuous operation or intermittent operation. Determine the duty cycle’s impact on the gear motor, including factors such as heat generation, cooling requirements, and potential wear and tear. Select a gear motor that is designed to handle the expected duty cycle and ensure long-term reliability and durability.
4. Environmental Factors:
Take into account the environmental conditions in which the gear motor will operate. Consider factors such as temperature extremes, humidity, dust, vibrations, and exposure to chemicals or corrosive substances. Choose a gear motor that is specifically designed to withstand and perform optimally under the anticipated environmental conditions. This may involve selecting gear motors with appropriate sealing, protective coatings, or materials that can resist corrosion and withstand harsh environments.
5. Efficiency and Power Requirements:
Consider the desired efficiency and power consumption of the gear motor. Evaluate the power supply available for the application and select a gear motor that operates within the specified voltage and current ranges. Assess the gear motor’s efficiency to ensure that it maximizes power transmission and minimizes wasted energy. Choosing an efficient gear motor can contribute to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
6. Physical Constraints:
Assess the physical constraints of the application, including space limitations, mounting options, and integration requirements. Consider the size, dimensions, and weight of the gear motor to ensure it can be accommodated within the available space. Evaluate the mounting options and compatibility with the application’s mechanical structure. Additionally, consider any specific integration requirements, such as shaft dimensions, connectors, or interfaces that need to align with the application’s design.
7. Noise and Vibration:
Depending on the application, noise and vibration levels may be critical factors. Evaluate the acceptable noise and vibration levels for the application’s environment and operation. Choose a gear motor that is designed to minimize noise and vibration, such as those with helical gears or precision engineering. This is particularly important in applications that require quiet operation or where excessive noise and vibration may cause issues or discomfort.
By considering these specific factors when selecting a gear motor for a particular application, you can ensure that the chosen gear motor meets the performance requirements, operates efficiently, and provides reliable and consistent power transmission. It’s important to consult with gear motor manufacturers or experts to determine the most suitable gear motor based on the specific application’s needs.


editor by CX 2024-04-03
China 24V 2HP Brushless Planetary Magnet Electric DC Gear Geared Motors with Hot selling
Product Description
| Environmental conditions | -20ºC~50ºC |
| Magnet material | Bonder NdfeB |
| Number of poles/phase | 8/3 |
| Insulation class | Class B |
| Insulation resistance | 100MΩmin 500VDC |
Electrical Specifications
| Model | 42BL40-240-2 | 42BL60-240-2 | 42BL80-240-2 | |
| Number of Phases | 8 | |||
| voltage | VDC | 24 | ||
| Rated speed | rpm | 4000 | ||
| Rated torque | N.m | 0.063 | 0.125 | 0.185 |
| Rated current | Amps. | 1.8 | 3.5 | 5.2 |
| Rated power | Watt. | 27 | 52 | 78 |
| Max torque | N.m | 0.185 | 0.38 | 0.55 |
| Torque constant | N.m/Amps. | 0.035 | 0.041 | 0.042 |
| Back EMF | V/Krpm | 3.17 | 3.13 | 3.28 |
| Rotor inertia | kg.mm2 | 5.2 | 9.3 | 13.4 |
| Lenght | mm | 40 | 60 | 80 |
| Net Weight | Kg | 0.3 | 0.47 | 0.65 |
Dimensions
We hold 2 mainly production lines, 1 of which is the brushless motor. The delivery time will be about 10-20 days if the quantity is less than 300 pcs.
|
US $14.99 / Piece | |
10 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Power Tools |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Constant Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Excited |
| Function: | Control, Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Protection Type |
| Number of Poles: | 8 |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 17/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Environmental conditions | -20ºC~50ºC |
| Magnet material | Bonder NdfeB |
| Number of poles/phase | 8/3 |
| Insulation class | Class B |
| Insulation resistance | 100MΩmin 500VDC |
###
| Model | 42BL40-240-2 | 42BL60-240-2 | 42BL80-240-2 | |
| Number of Phases | 8 | |||
| voltage | VDC | 24 | ||
| Rated speed | rpm | 4000 | ||
| Rated torque | N.m | 0.063 | 0.125 | 0.185 |
| Rated current | Amps. | 1.8 | 3.5 | 5.2 |
| Rated power | Watt. | 27 | 52 | 78 |
| Max torque | N.m | 0.185 | 0.38 | 0.55 |
| Torque constant | N.m/Amps. | 0.035 | 0.041 | 0.042 |
| Back EMF | V/Krpm | 3.17 | 3.13 | 3.28 |
| Rotor inertia | kg.mm2 | 5.2 | 9.3 | 13.4 |
| Lenght | mm | 40 | 60 | 80 |
| Net Weight | Kg | 0.3 | 0.47 | 0.65 |
|
US $14.99 / Piece | |
10 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Power Tools |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Constant Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Excited |
| Function: | Control, Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Protection Type |
| Number of Poles: | 8 |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 17/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Environmental conditions | -20ºC~50ºC |
| Magnet material | Bonder NdfeB |
| Number of poles/phase | 8/3 |
| Insulation class | Class B |
| Insulation resistance | 100MΩmin 500VDC |
###
| Model | 42BL40-240-2 | 42BL60-240-2 | 42BL80-240-2 | |
| Number of Phases | 8 | |||
| voltage | VDC | 24 | ||
| Rated speed | rpm | 4000 | ||
| Rated torque | N.m | 0.063 | 0.125 | 0.185 |
| Rated current | Amps. | 1.8 | 3.5 | 5.2 |
| Rated power | Watt. | 27 | 52 | 78 |
| Max torque | N.m | 0.185 | 0.38 | 0.55 |
| Torque constant | N.m/Amps. | 0.035 | 0.041 | 0.042 |
| Back EMF | V/Krpm | 3.17 | 3.13 | 3.28 |
| Rotor inertia | kg.mm2 | 5.2 | 9.3 | 13.4 |
| Lenght | mm | 40 | 60 | 80 |
| Net Weight | Kg | 0.3 | 0.47 | 0.65 |
Benefits of a Planetary Motor
Besides being one of the most efficient forms of a drive, a Planetary Motor also offers a great number of other benefits. These features enable it to create a vast range of gear reductions, as well as generate higher torques and torque density. Let’s take a closer look at the benefits this mechanism has to offer. To understand what makes it so appealing, we’ll explore the different types of planetary systems.
Solar gear
The solar gear on a planetary motor has two distinct advantages. It produces less noise and heat than a helical gear. Its compact footprint also minimizes noise. It can operate at high speeds without sacrificing efficiency. However, it must be maintained with constant care to operate efficiently. Solar gears can be easily damaged by water and other debris. Solar gears on planetary motors may need to be replaced over time.
A planetary gearbox is composed of a sun gear and two or more planetary ring and spur gears. The sun gear is the primary gear and is driven by the input shaft. The other two gears mesh with the sun gear and engage the stationary ring gear. The three gears are held together by a carrier, which sets the spacing. The output shaft then turns the planetary gears. This creates an output shaft that rotates.
Another advantage of planetary gears is that they can transfer higher torques while being compact. These advantages have led to the creation of solar gears. They can reduce the amount of energy consumed and produce more power. They also provide a longer service life. They are an excellent choice for solar-powered vehicles. But they must be installed by a certified solar energy company. And there are other advantages as well. When you install a solar gear on a planetary motor, the energy produced by the sun will be converted to useful energy.
A solar gear on a planetary motor uses a solar gear to transmit torque from the sun to the planet. This system works on the principle that the sun gear rotates at the same rate as the planet gears. The sun gear has a common design modulus of -Ns/Np. Hence, a 24-tooth sun gear equals a 3-1/2 planet gear ratio. When you consider the efficiency of solar gears on planetary motors, you will be able to determine whether the solar gears are more efficient.
Sun gear
The mechanical arrangement of a planetary motor comprises of two components: a ring gear and a sun gear. The ring gear is fixed to the motor’s output shaft, while the sun gear rolls around and orbits around it. The ring gear and sun gear are linked by a planetary carrier, and the torque they produce is distributed across their teeth. The planetary structure arrangement also reduces backlash, and is critical to achieve a quick start and stop cycle.
When the two planetary gears rotate independently, the sun gear will rotate counterclockwise and the ring-gear will turn in the same direction. The ring-gear assembly is mounted in a carrier. The carrier gear and sun gear are connected to each other by a shaft. The planetary gears and sun gear rotate around each other on the ring-gear carrier to reduce the speed of the output shaft. The planetary gear system can be multiplied or staged to obtain a higher reduction ratio.
A planetary gear motor mimics the planetary rotation system. The input shaft turns a central gear, known as the sun gear, while the planetary gears rotate around a stationary sun gear. The motor’s compact design allows it to be easily mounted to a vehicle, and its low weight makes it ideal for small vehicles. In addition to being highly efficient, a planetary gear motor also offers many other benefits.
A planetary gearbox uses a sun gear to provide torque to the other gears. The planet pinions mesh with an internal tooth ring gear to generate rotation. The carrier also acts as a hub between the input gear and output shaft. The output shaft combines these two components, giving a higher torque. There are three types of planetary gearboxes: the sun gear and a wheel drive planetary gearbox.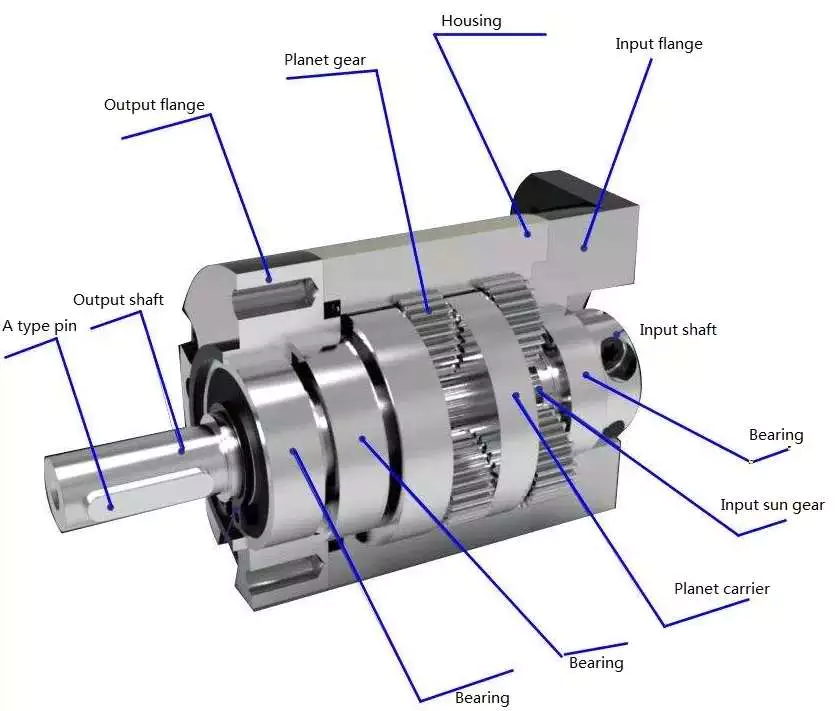
Planetary gear
A planetary motor gear works by distributing rotational force along a separating plate and a cylindrical shaft. A shock-absorbing device is included between the separating plate and cylindrical shaft. This depressed portion prevents abrasion wear and foreign particles from entering the device. The separating plate and shaft are positioned coaxially. In this arrangement, the input shaft and output shaft are rotated relative to one another. The rotatable disc absorbs the impact.
Another benefit of a planetary motor gear is its efficiency. Planetary motor gears are highly efficient at transferring power, with 97% of the input energy being transferred to the output. They can also have high gear ratios, and offer low noise and backlash. This design also allows the planetary gearbox to work with electric motors. In addition, planetary gears also have a long service life. The efficiency of planetary gears is due in part to the large number of teeth.
Other benefits of a planetary motor gear include the ease of changing ratios, as well as the reduced safety stock. Unlike other gears, planetary gears don’t require special tools for changing ratios. They are used in numerous industries, and share parts across multiple sizes. This means that they are cost-effective to produce and require less safety stock. They can withstand high shock and wear, and are also compact. If you’re looking for a planetary motor gear, you’ve come to the right place.
The axial end surface of a planetary gear can be worn down by abrasion with a separating plate. In addition, foreign particles may enter the planetary gear device. These particles can damage the gears or even cause noise. As a result, you should check planetary gears for damage and wear. If you’re looking for a gear, make sure it has been thoroughly tested and installed by a professional.
Planetary gearbox
A planetary motor and gearbox are a common combination of electric and mechanical power sources. They share the load of rotation between multiple gear teeth to increase the torque capacity. This design is also more rigid, with low backlash that can be as low as one or two arc minutes. The advantages of a planetary gearmotor over a conventional electric motor include compact size, high efficiency, and less risk of gear failure. Planetary gear motors are also more reliable and durable than conventional electric motors.
A planetary gearbox is designed for a single stage of reduction, or a multiple-stage unit can be built with several individual cartridges. Gear ratios may also be selected according to user preference, either to face mount the output stage or to use a 5mm hex shaft. For multi-stage planetary gearboxes, there are a variety of different options available. These include high-efficiency planetary gearboxes that achieve a 98% efficiency at single reduction. In addition, they are noiseless, and reduce heat loss.
A planetary gearbox may be used to increase torque in a robot or other automated system. There are different types of planetary gear sets available, including gearboxes with sliding or rolling sections. When choosing a planetary gearset, consider the environment and other factors such as backlash, torque, and ratio. There are many advantages to a planetary gearbox and the benefits and drawbacks associated with it.
Planetary gearboxes are similar to those in a solar system. They feature a central sun gear in the middle, two or more outer gears, and a ring gear at the output. The planetary gears rotate in a ring-like structure around a stationary sun gear. When the gears are engaged, they are connected by a carrier that is fixed to the machine’s shaft.
Planetary gear motor
Planetary gear motors reduce the rotational speed of an armature by one or more times. The reduction ratio depends on the structure of the planetary gear device. The planetary gear device has an output shaft and an armature shaft. A separating plate separates the two. The output shaft moves in a circular pattern to turn the pinion 3. When the pinion rotates to the engagement position, it is engaged with the ring gear 4. The ring gear then transmits the rotational torque to the armature shaft. The result is that the engine cranks up.
Planetary gear motors are cylindrical in shape and are available in various power levels. They are typically made of steel or brass and contain multiple gears that share the load. These motors can handle massive power transfers. The planetary gear drive, on the other hand, requires more components, such as a sun’s gear and multiple planetary gears. Consequently, it may not be suitable for all types of applications. Therefore, the planetary gear drive is generally used for more complex machines.
Brush dusts from the electric motor may enter the planetary gear device and cause it to malfunction. In addition, abrasion wear on the separating plate can affect the gear engagement of the planetary gear device. If this occurs, the gears will not engage properly and may make noise. In order to prevent such a situation from occurring, it is important to regularly inspect planetary gear motors and their abrasion-resistant separating plates.
Planetary gear motors come in many different power levels and sizes. These motors are usually cylindrical in shape and are made of steel, brass, plastic, or a combination of both materials. A planetary gear motor can be used in applications where space is an issue. This motor also allows for low gearings in small spaces. The planetary gearing allows for large amounts of power transfer. The output shaft size is dependent on the gear ratio and the motor speed.


editor by czh 2022-11-24
in Vienna Austria sales price shop near me near me shop factory supplier 6W 25W 40W 90W 370W High Power Single Phase 3pH Geared Electric Motors AC Induction Gear Motor manufacturer best Cost Custom Cheap wholesaler

“We are always serving our buyers with our greatest items.” Getting amassed valuable expertise in cooperating with foreign customers, Our AdvantagesProducts Big volume in Inventory, No MOQ required We comply with all the global expectations, this sort of as ISO9001 and TS16949 specifications.
6w 15w 25w 40w 60w 90w High EPT Single Phase 3ph Geared Electric powered Motors AC Induction Equipment Motor
one. LigEPT bodyweight, small dimension and basic set up
2. Wide pace ranges and high torque
three. Low sound and large efficien
four. Steady and protected,EPT life span
5. Multi-framework, different assembling approaches
6. A single-cease remedy with pace controller, driver, encoder, brake and transformor offered.
Specifications
If this product is not what you want, please freely tell us about your need. We will supply you with a ideal motor solution and value quickly.
Related Merchandise Photos
EPT amp Supply
Certifications
Business Overview
Greensky EPT Firm Constrained is a EPT based mostly global company who is EPTized in electric powered motor, EPT and controlling technique deveXiHu (West Lake) Dis.Hu (West Lake) Dis.ing, manufacturing, top quality controlling and trading.
Mission:We are focused to deveXiHu (West Lake) Dis.Hu (West Lake) Dis. an worldwide electric powered motor firm who can supply one particular-cease reputable products with customer-oriEPTd services.
Historical past:Greensky was estabEPTd in 2571 by York Cheng in Los Angeles, United states and moved to HangZhou, EPT in 2011. In the past years, the group of Greensky continues to produce the worth to our esteemed clients all more than the entire world by developing up vast and dependable source chain administration system, efficient high quality amp shipping time control system, value efficiency producing system and quickly-react professional service.
EPTs
FAQ
one Q: What is your MOQ for AC Motor?
A: 1unit is ok for sample testing
2 Q: What about your warranty for your AC Motor?
A: A single year.
three Q: Do you offer OEM services with buyer-logo?
A: Of course, we could do OEM orders, but we mostly emphasis on our own brand.
4 Q: How about your payment terms ?
A: TT, western union and paypal. 100% payment EPTd for orders less $five,000. 30% deposit and equilibrium just before supply for
orders more than $five,000.
five Q: How about your EPT ?
A: Carton, Plywood scenario. If you want more, we can pack all items with pallet
6 Q: What details ought to be presented, if I acquire from you?
A: Rated EPT, EPT ratio, input pace, mounting situation. Much more information, better!
seven Q: How do you provide the AC Motor?
A: We will evaluate and choose the most suited waEPTof shipping by sea, air or categorical courier.
We hope you will enEPT cooperating with us.

