Product Description
15W/30W/60W 70mm BLDC Electrical Gear Motor with Driver
Introduction
We have both DC gear motor and Brushless dc gear motor, including 5 kinds of 300 products. The watt is from 6W to 400W, voltage is from 12VDC to 310VDC. The advantages of our motors are steady work, big starting, and rated torque, low noise, high efficiency, and long life.
Specification
1. Dimensions: 70mm
2. Rated Power: 15W/30W/60W
3. Voltage: 12/24/310V
5. Motor voltage, power, and speed can be customized according to your request under the allowed circumstance of adoptable dimension.
Motor Data
| Type | Voltage | Rated Power | Rated Torque | No load Speed | No load Current | Rated Speed | Rated Current | Hall | Life | Length | Internal Drive | Weight |
| V | W | N.m | RPM | A | RPM | A | (Y/N) | (Hours) | mm | g | ||
| GSBLD60S15D12 | 12 | 15 | 0.072 | 2800 | < 0.8 | 2000 | 1.56 | Both | > 5000 | 59 | YES | 800 |
| GSBLD60S15D24 | 24 | 15 | 0.072 | 2800 | < 0.5 | 2000 | 0.78 | Both | > 5000 | 59 | YES | 800 |
| GSBLD60S15D310 | 310 | 15 | 0.072 | 2700 | < 0.3 | 2000 | 0.06 | Both | > 5000 | 59 | YES | 800 |
| GSBLD60S30D12 | 12 | 30 | 0.143 | 2800 | < 0.9 | 2000 | 3.13 | Both | > 5000 | 64 | YES | 900 |
| GSBLD60S30D24 | 24 | 30 | 0.143 | 2800 | < 0.5 | 2000 | 1.56 | Both | > 5000 | 64 | YES | 900 |
| GSBLD60S30D310 | 310 | 30 | 0.143 | 2700 | < 0.3 | 2000 | 0.12 | Both | > 5000 | 64 | YES | 900 |
| GSBLD60S30D24 | 24 | 60 | 0.287 | 2800 | < 0.5 | 2000 | 3.13 | Both | > 5000 | 74 | YES | 1200 |
| GSBLD60S30D310 | 310 | 60 | 0.287 | 2700 | < 0.3 | 2000 | 0.24 | Both | > 5000 | 74 | YES | 1200 |
Gearbox Data
| Gear Ratio | 3 | 3.6 | 5 | 6 | 7.5 | 9 | 10 | 12.5 | 15 | 18 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 36 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 75 | 90 | 100 | 120 | 150 | 180 | 200 |
| Output speed RPM |
667 | 556 | 400 | 333 | 267 | 222 | 320 | 160 | 133 | 111 | 100 | 80 | 67 | 56 | 50 | 40 | 33 | 27 | 22 | 20 | 17 | 13 | 11 | 10 |
| Allowance Torque N.m |
0.21 | 0.25 | 0.34 | 0.41 | 0.52 | 0.62 | 0.69 | 0.86 | 1.03 | 1.24 | 1.24 | 1.56 | 1.87 | 2.24 | 2.49 | 3.11 | 3.38 | 4.22 | 4.90 | 4.90 | 4.90 | 4.90 | 4.90 | 4.90 |
Dimensional Drawing
View Of Item
Packing and Delivery
Exhibitions
About CHINAMFG Power
Greensky Power Company Limited is a China-based international company who is specialized in electric motor, gearbox, and controlling system development, manufacturing, quality controlling, and trading.
Mission:
We are dedicated to developing an international electric motor company that can deliver one-stop reliable products with customer-oriented service.
History:
CHINAMFG was established in 2571 by CHINAMFG Cheng in Los Angeles, USA, and moved to HangZhou, China in 2011. In the past years, the team of CHINAMFG continues to create value for our esteemed customers all over the world by building up a wide and reliable supply chain management system, effective quality & delivery time control system, cost efficient manufacturing system, and fast-respond professional service.
Certificates
FAQ
1 Q: What’s your MOQ for the motor?
A: 1unit is ok for sample testing
2 Q: What about your warranty for your motor?
A: One year.
3 Q: Do you provide OEM service with customer-logo?
A: Yes, we could do OEM orders, but we mainly focus on our own brand.
4 Q: How about your payment terms?
A: TT, western union, and PayPal. 100% payment in advance for orders less than $5,000. 30% deposit and balance before delivery for orders over $5,000.
5 Q: How about your packing?
A: Carton, Plywood case. If you need more, we can pack all goods in pallets.
6 Q: What information should be given, if I buy motors from you?
A: Rated power, gearbox ratio, input speed, mounting position. More details, better!
7 Q: How do you deliver the motors?
A: We will compare and choose the most suitable ways of delivery by sea, air or express courier.
We hope you will enjoy cooperating with us.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Household Appliances, Car, Power Tools |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Low Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Excited |
| Function: | Control |
| Casing Protection: | Protection Type |
| Number of Poles: | 4 |
| Samples: |
US$ 100/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What types of feedback mechanisms are commonly integrated into gear motors for control?
Gear motors often incorporate feedback mechanisms to provide control and improve their performance. These feedback mechanisms enable the motor to monitor and adjust its operation based on various parameters. Here are some commonly integrated feedback mechanisms in gear motors:
1. Encoder Feedback:
An encoder is a device that provides position and speed feedback by converting the motor’s mechanical motion into electrical signals. Encoders commonly used in gear motors include:
- Incremental Encoders: These encoders provide information about the motor’s shaft position and speed relative to a reference point. They generate pulses as the motor rotates, allowing precise measurement of position and speed changes.
- Absolute Encoders: Absolute encoders provide the precise position of the motor’s shaft within a full revolution. They do not require a reference point and provide accurate feedback even after power loss or motor restart.
2. Hall Effect Sensors:
Hall effect sensors use the principle of the Hall effect to detect the presence and strength of a magnetic field. They are commonly used in gear motors for speed and position sensing. Hall effect sensors provide feedback by detecting changes in the motor’s magnetic field and converting them into electrical signals.
3. Current Sensors:
Current sensors monitor the electrical current flowing through the motor’s windings. By measuring the current, these sensors provide feedback regarding the motor’s torque, load conditions, and power consumption. Current sensors are essential for motor control strategies such as current limiting, overcurrent protection, and closed-loop control.
4. Temperature Sensors:
Temperature sensors are integrated into gear motors to monitor the motor’s temperature. They provide feedback on the motor’s thermal conditions, allowing the control system to adjust the motor’s operation to prevent overheating. Temperature sensors are crucial for ensuring the motor’s reliability and preventing damage due to excessive heat.
5. Hall Effect Limit Switches:
Hall effect limit switches are used to detect the presence or absence of a magnetic field within a specific range. They are commonly employed as end-of-travel or limit switches in gear motors. Hall effect limit switches provide feedback to the control system, indicating when the motor has reached a specific position or when it has moved beyond the allowed range.
6. Resolver Feedback:
A resolver is an electromagnetic device used to determine the position and speed of a rotating shaft. It provides feedback by generating sine and cosine signals that correspond to the shaft’s angular position. Resolver feedback is commonly used in high-performance gear motors requiring accurate position and speed control.
These feedback mechanisms, when integrated into gear motors, enable precise control, monitoring, and adjustment of various motor parameters. By utilizing feedback signals from encoders, Hall effect sensors, current sensors, temperature sensors, limit switches, or resolvers, the control system can optimize the motor’s performance, ensure accurate positioning, maintain speed control, and protect the motor from excessive loads or overheating.

What is the significance of gear reduction in gear motors, and how does it affect efficiency?
Gear reduction plays a significant role in gear motors as it enables the motor to deliver higher torque while reducing the output speed. This feature has several important implications for gear motors, including enhanced power transmission, improved control, and potential trade-offs in terms of efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of the significance of gear reduction in gear motors and its effect on efficiency:
Significance of Gear Reduction:
1. Increased Torque: Gear reduction allows gear motors to generate higher torque output compared to a motor without gears. By reducing the rotational speed at the output shaft, gear reduction increases the mechanical advantage of the system. This increased torque is beneficial in applications that require high torque to overcome resistance, such as lifting heavy loads or driving machinery with high inertia.
2. Improved Control: Gear reduction enhances the control and precision of gear motors. By reducing the speed, gear reduction allows for finer control over the motor’s rotational movement. This is particularly important in applications that require precise positioning or accurate speed control. The gear reduction mechanism enables gear motors to achieve smoother and more controlled movements, reducing the risk of overshooting or undershooting the desired position.
3. Load Matching: Gear reduction helps match the motor’s power characteristics to the load requirements. Different applications have varying torque and speed requirements. Gear reduction allows the gear motor to achieve a better match between the motor’s power output and the specific requirements of the load. It enables the motor to operate closer to its peak efficiency by optimizing the torque-speed trade-off.
Effect on Efficiency:
While gear reduction offers several advantages, it can also affect the efficiency of gear motors. Here’s how gear reduction impacts efficiency:
1. Mechanical Efficiency: The gear reduction process introduces mechanical components such as gears, bearings, and lubrication systems. These components introduce additional friction and mechanical losses into the system. As a result, some energy is lost in the form of heat during the gear reduction process. The efficiency of the gear motor is influenced by the quality of the gears, the lubrication used, and the overall design of the gear system. Well-designed and properly maintained gear systems can minimize these losses and optimize mechanical efficiency.
2. System Efficiency: Gear reduction affects the overall system efficiency by impacting the motor’s electrical efficiency. In gear motors, the motor typically operates at higher speeds and lower torques compared to a direct-drive motor. The overall system efficiency takes into account both the electrical efficiency of the motor and the mechanical efficiency of the gear system. While gear reduction can increase the torque output, it also introduces additional losses due to increased mechanical complexity. Therefore, the overall system efficiency may be lower compared to a direct-drive motor for certain applications.
It’s important to note that the efficiency of gear motors is influenced by various factors beyond gear reduction, such as motor design, control systems, and operating conditions. The selection of high-quality gears, proper lubrication, and regular maintenance can help minimize losses and improve efficiency. Additionally, advancements in gear technology, such as the use of precision gears and improved lubricants, can contribute to higher overall efficiency in gear motors.
In summary, gear reduction is significant in gear motors as it provides increased torque, improved control, and better load matching. However, gear reduction can introduce mechanical losses and affect the overall efficiency of the system. Proper design, maintenance, and consideration of application requirements are essential to optimize the balance between torque, speed, and efficiency in gear motors.

What is a gear motor, and how does it combine the functions of gears and a motor?
A gear motor is a type of motor that incorporates gears into its design to combine the functions of gears and a motor. It consists of a motor, which provides the mechanical power, and a set of gears, which transmit and modify this power to achieve specific output characteristics. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a gear motor is and how it combines the functions of gears and a motor:
A gear motor typically consists of two main components: the motor and the gear system. The motor is responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy, generating rotational motion. The gear system, on the other hand, consists of multiple gears with different sizes and tooth configurations. These gears are meshed together in a specific arrangement to transmit and modify the output torque and speed of the motor.
The gears in a gear motor serve several functions:
1. Torque Amplification:
One of the primary functions of the gear system in a gear motor is to amplify the torque output of the motor. By using gears with different sizes, the input torque can be effectively multiplied or reduced. This allows the gear motor to provide higher torque at lower speeds or lower torque at higher speeds, depending on the gear arrangement. This torque amplification is beneficial in applications where high torque is required, such as in heavy machinery or vehicles.
2. Speed Reduction or Increase:
The gear system in a gear motor can also be used to reduce or increase the rotational speed of the motor output. By utilizing gears with different numbers of teeth, the gear ratio can be adjusted to achieve the desired speed output. For example, a gear motor with a higher gear ratio will output lower speed but higher torque, whereas a gear motor with a lower gear ratio will output higher speed but lower torque. This speed control capability allows for precise matching of motor output to the requirements of specific applications.
3. Directional Control:
Gears in a gear motor can be used to control the direction of rotation of the motor output shaft. By employing different combinations of gears, such as spur gears, bevel gears, or worm gears, the rotational direction can be changed. This directional control is crucial in applications where bidirectional movement is required, such as in conveyor systems or robotic arms.
4. Load Distribution:
The gear system in a gear motor helps distribute the load evenly across multiple gears, which reduces the stress on individual gears and increases the overall durability and lifespan of the motor. By sharing the load among multiple gears, the gear motor can handle higher torque applications without putting excessive strain on any particular gear. This load distribution capability is especially important in heavy-duty applications that require continuous operation under demanding conditions.
By combining the functions of gears and a motor, gear motors offer several advantages. They provide torque amplification, speed control, directional control, and load distribution capabilities, making them suitable for various applications that require precise and controlled mechanical power. Gear motors are commonly used in industries such as robotics, automotive, manufacturing, and automation, where reliable and efficient power transmission is essential.


editor by CX 2024-05-16
China Standard CHINAMFG L-Shape AC Gear Motor for Biomass Pellet Boiler System vacuum pump diy
Product Description
Greensky L-shape AC Gear Motor for Biomass Pellet Boiler System
Introduction
Generally,Mirco induction motor refers to the motor rotated by the induction.Induction motor relies on capacitor and eletromagnetism when starting and rotating.Though its starting torque is not very high, it has a simple structure,high efficiency and can rotate continue.
Specification
Note:
Motor voltage, power and speed will be customized according to your request under the allowed circumstance of adoptable dimension.
View Of Item
About CHINAMFG Power
Greensky Power Company Limited is a China based international company who is specialized in electric motor, gearbox and controlling system developing, manufacturing, quality controlling and trading.
Mission:
We are dedicated to develop an international electric motor company who can deliver one-stop reliable products with customer-oriented service.
History:
Greensky was established in 2571 by CHINAMFG Cheng in Los Angeles, USA and moved to HangZhou, China in 2011. In the past 8 years, the team of CHINAMFG continues to create the value to our esteemed customers all over the world by building up wide and reliable supply chain management system, effective quality & delivery time control system, cost efficiency manufacturing system and fast-respond professional service.
Location: Xihu (West Lake) Dis. district, HangZhou, China
Xihu (West Lake) Dis. is a high-tech zone which is the center of oversea Chinese talent entrepreneurs. Some famous neighbours include Alibaba, Netease and Geely corporation.
Background:
Greensky is a subsidiary of EagleEye Capital Limited who has 3 manufacturing plants and 1 sales office with more than 500 employees and overall 200 million sales.
Company Facilities
Certificates
Overseas Exhibitions
FAQ:
1 Q: What’s your MOQ ?
A: 1unit is acceptable.
2 Q: What about your warranty?
A: 1-2 years.
3 Q: Do you provide OEM service with customer-logo?
A: Yes, we could do OEM orders.
4 Q: How about your payment terms ?
A: TT, western union and paypal. 100% payment in advanced for orders less $10,000. 30% deposit and balance before delivery for orders over $10,000.
5 Q: How about your packing ?
A: Carton, Plywood case and foam inside. If you need more, we can pack all goods with pallet
6 Q: What information should be given in the inquiry?
A: Rated power, gearbox ratio, input speed, mounting position. More details, better!
7 Q: How do you deliver our order?
A: We will compare and choose the most suitable ways of delivery by sea, air or express courier.
Welcome your inquiry! We’re at your service for 7×24 hours.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industrial |
|---|---|
| Speed: | Constant Speed |
| Number of Stator: | Single-Phase |
| Casing Protection: | Protection Type |
| Number of Poles: | 4 |
| Starting Mode: | Auto-induction Voltage-reduced Starting |
| Samples: |
US$ 200/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How is the efficiency of a gear motor measured, and what factors can affect it?
The efficiency of a gear motor is a measure of how effectively it converts electrical input power into mechanical output power. It indicates the motor’s ability to minimize losses and maximize its energy conversion efficiency. The efficiency of a gear motor is typically measured using specific methods, and several factors can influence it. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Measuring Efficiency:
The efficiency of a gear motor is commonly measured by comparing the mechanical output power (Pout) to the electrical input power (Pin). The formula to calculate efficiency is:
Efficiency = (Pout / Pin) * 100%
The mechanical output power can be determined by measuring the torque (T) produced by the motor and the rotational speed (ω) at which it operates. The formula for mechanical power is:
Pout = T * ω
The electrical input power can be measured by monitoring the current (I) and voltage (V) supplied to the motor. The formula for electrical power is:
Pin = V * I
By substituting these values into the efficiency formula, the efficiency of the gear motor can be calculated as a percentage.
Factors Affecting Efficiency:
Several factors can influence the efficiency of a gear motor. Here are some notable factors:
- Friction and Mechanical Losses: Friction between moving parts, such as gears and bearings, can result in mechanical losses and reduce the overall efficiency of the gear motor. Minimizing friction through proper lubrication, high-quality components, and efficient design can help improve efficiency.
- Gearing Efficiency: The design and quality of the gears used in the gear motor can impact its efficiency. Gear trains can introduce mechanical losses due to gear meshing, misalignment, or backlash. Using well-designed gears with proper tooth profiles and minimizing gear train losses can improve efficiency.
- Motor Type and Construction: Different types of motors (e.g., brushed DC, brushless DC, AC induction) have varying efficiency characteristics. Motor construction, such as the quality of magnetic materials, winding resistance, and rotor design, can also affect efficiency. Choosing motors with higher efficiency ratings can improve overall gear motor efficiency.
- Electrical Losses: Electrical losses, such as resistive losses in motor windings or in the motor drive circuitry, can reduce efficiency. Minimizing resistance, optimizing motor drive electronics, and using efficient control algorithms can help mitigate electrical losses.
- Load Conditions: The operating conditions and load characteristics placed on the gear motor can impact its efficiency. Heavy loads, high speeds, or frequent acceleration and deceleration can increase losses and reduce efficiency. Matching the gear motor’s specifications to the application requirements and optimizing load conditions can improve efficiency.
- Temperature: Elevated temperatures can significantly affect the efficiency of a gear motor. Excessive heat can increase resistive losses, reduce lubrication effectiveness, and affect the magnetic properties of motor components. Proper cooling and thermal management techniques are essential to maintain optimal efficiency.
By considering these factors and implementing measures to minimize losses and optimize performance, the efficiency of a gear motor can be enhanced. Manufacturers often provide efficiency specifications for gear motors, allowing users to select motors that best meet their efficiency requirements for specific applications.

How do gear motors compare to other types of motors in terms of power and efficiency?
Gear motors can be compared to other types of motors in terms of power output and efficiency. The choice of motor type depends on the specific application requirements, including the desired power level, efficiency, speed range, torque characteristics, and control capabilities. Here’s a detailed explanation of how gear motors compare to other types of motors in terms of power and efficiency:
1. Gear Motors:
Gear motors combine a motor with a gear mechanism to deliver increased torque output and improved control. The gear reduction enables gear motors to provide higher torque while reducing the output speed. This makes gear motors suitable for applications that require high torque, precise positioning, and controlled movements. However, the gear reduction process introduces mechanical losses, which can slightly reduce the overall efficiency of the system compared to direct-drive motors. The efficiency of gear motors can vary depending on factors such as gear quality, lubrication, and maintenance.
2. Direct-Drive Motors:
Direct-drive motors, also known as gearless or integrated motors, do not use a gear mechanism. They provide a direct connection between the motor and the load, eliminating the need for gear reduction. Direct-drive motors offer advantages such as high efficiency, low maintenance, and compact design. Since there are no gears involved, direct-drive motors experience fewer mechanical losses and can achieve higher overall efficiency compared to gear motors. However, direct-drive motors may have limitations in terms of torque output and speed range, and they may require more complex control systems to achieve precise positioning.
3. Stepper Motors:
Stepper motors are a type of gear motor that excels in precise positioning applications. They operate by converting electrical pulses into incremental steps of movement. Stepper motors offer excellent positional accuracy and control. They are capable of precise positioning and can hold a position without power. Stepper motors have relatively high torque at low speeds, making them suitable for applications that require precise control and positioning, such as robotics, 3D printers, and CNC machines. However, stepper motors may have lower overall efficiency compared to direct-drive motors due to the additional power required to overcome the detents between steps.
4. Servo Motors:
Servo motors are another type of gear motor known for their high torque, high speed, and excellent positional accuracy. Servo motors combine a motor, a feedback device (such as an encoder), and a closed-loop control system. They offer precise control over position, speed, and torque. Servo motors are widely used in applications that require accurate and responsive positioning, such as industrial automation, robotics, and camera pan-tilt systems. Servo motors can achieve high efficiency when properly optimized and controlled but may have slightly lower efficiency compared to direct-drive motors due to the additional complexity of the control system.
5. Efficiency Considerations:
When comparing power and efficiency among different motor types, it’s important to consider the specific requirements and operating conditions of the application. Factors such as load characteristics, speed range, duty cycle, and control requirements influence the overall efficiency of the motor system. While direct-drive motors generally offer higher efficiency due to the absence of mechanical losses from gears, gear motors can deliver higher torque output and enhanced control capabilities. The efficiency of gear motors can be optimized through proper gear selection, lubrication, and maintenance practices.
In summary, gear motors offer increased torque and improved control compared to direct-drive motors. However, gear reduction introduces mechanical losses that can slightly impact the overall efficiency of the system. Direct-drive motors, on the other hand, provide high efficiency and compact design but may have limitations in terms of torque and speed range. Stepper motors and servo motors, both types of gear motors, excel in precise positioning applications but may have slightly lower efficiency compared to direct-drive motors. The selection of the most suitable motor type depends on the specific requirements of the application, balancing power, efficiency, speed range, and control capabilities.

Can you explain the advantages of using gear motors in various mechanical systems?
Gear motors offer several advantages when utilized in various mechanical systems. Their unique characteristics make them well-suited for applications that require controlled power transmission, precise speed control, and torque amplification. Here’s a detailed explanation of the advantages of using gear motors:
1. Torque Amplification:
One of the key advantages of gear motors is their ability to amplify torque. By using different gear ratios, gear motors can increase or decrease the output torque from the motor. This torque amplification is crucial in applications that require high torque output, such as lifting heavy loads or operating machinery with high resistance. Gear motors allow for efficient power transmission, enabling the system to handle demanding tasks effectively.
2. Speed Control:
Gear motors provide precise speed control, allowing for accurate and controlled movement in mechanical systems. By selecting the appropriate gear ratio, the rotational speed of the output shaft can be adjusted to match the requirements of the application. This speed control capability ensures that the mechanical system operates at the desired speed, whether it needs to be fast or slow. Gear motors are commonly used in applications such as conveyors, robotics, and automated machinery, where precise speed control is essential.
3. Directional Control:
Another advantage of gear motors is their ability to control the rotational direction of the output shaft. By using different types of gears, such as spur gears, bevel gears, or worm gears, the direction of rotation can be easily changed. This directional control is beneficial in applications that require bidirectional movement, such as in actuators, robotic arms, and conveyors. Gear motors offer reliable and efficient directional control, contributing to the versatility and functionality of mechanical systems.
4. Efficiency and Power Transmission:
Gear motors are known for their high efficiency in power transmission. The gear system helps distribute the load across multiple gears, reducing the strain on individual components and minimizing power losses. This efficient power transmission ensures that the mechanical system operates with optimal energy utilization and minimizes wasted power. Gear motors are designed to provide reliable and consistent power transmission, resulting in improved overall system efficiency.
5. Compact and Space-Saving Design:
Gear motors are compact in size and offer a space-saving solution for mechanical systems. By integrating the motor and gear system into a single unit, gear motors eliminate the need for additional components and reduce the overall footprint of the system. This compact design is especially beneficial in applications with limited space constraints, allowing for more efficient use of available space while still delivering the necessary power and functionality.
6. Durability and Reliability:
Gear motors are designed to be robust and durable, capable of withstanding demanding operating conditions. The gear system helps distribute the load, reducing the stress on individual gears and increasing overall durability. Additionally, gear motors are often constructed with high-quality materials and undergo rigorous testing to ensure reliability and longevity. This makes gear motors well-suited for continuous operation in industrial and commercial applications, where reliability is crucial.
By leveraging the advantages of torque amplification, speed control, directional control, efficiency, compact design, durability, and reliability, gear motors provide a reliable and efficient solution for various mechanical systems. They are widely used in industries such as robotics, automation, manufacturing, automotive, and many others, where precise and controlled mechanical power transmission is essential.


editor by CX 2024-05-16
China Standard 8mm Large Rated Torque Micro Reduction Gear Motor with Encoder supplier
Product Description
Large Rated Torque Micro Reduction Gear Motor with Encoder
Product Description
1)Specification
Model: ZWMD008008-47
Rated Voltage: 4.2v
No Load Speed: 306 rpm
No Load Current: 95 mA
Rated Load Speed: 240 rpm
Rated Load Current: 160 mA
Rated Load Torque: 30 gf.cm
Rated Torque of Gear Box: 200 gf.cm
Instant Torque of Gear Box: 600 gf.cm
Overall Length L: 28.5mm
Gear Box Length L1: 14.0 mm
Gearbox Specifications:
| Outer Diameter | 8mm | |
| Material | Metal | |
| Direction of Rotation | cw&ccw | |
| Gear Backlash | ≤3° | |
| Bearing | Porous Bearing | Rolling Bearing |
| Axial Endplay | ≤0.3mm | ≤0.2mm |
| Radial Load on Output Shaft | ≤2N | ≤5N |
| Operating Temperature Range | -20…+85ºC | |
| Gearbox Stages: | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Reduction Ratio | 4/5 | 13/19/28 | 47/69/102/152 | 168/249/369/546/809 |
| Max Rated Torque (gf.cm max) | 250 | 400 | 600 | 750 |
| Max Instant Torque (gf.cm max) | 500 | 800 | 1200 | 1500 |
| Gearbox Efficiency | 85 | 73 | 62 | 55 |
| Length | 11.6 | 14.3 | 17 | 19.7 |
Motor Specifications:
| Motors (Optional) | Brushed DC motor, Stepper motor |
| Voltage (Optional) | 3-12V |
| Input Speed | ≤30000rpm |
| Current | 150mA max |
Performance Data:
| Model | Rated Speed | Max Speed | Max Rated Torque | Max Instant Torque | Reduction Ratio | Length(L1) | Overall Length(L) |
| rpm | rpm | gf.cm | gf.cm | mm | mm | ||
| ZWMD008008-4 | 2083 | 8333 | 250 | 500 | 3.6 | 11.6 | 26.1 |
| ZWMD008008-5 | 1406 | 5625 | 250 | 500 | 5.3 | ||
| ZWMD008008-13 | 579 | 2315 | 400 | 800 | 13.0 | 14.3 | 28.8 |
| ZWMD008008-19 | 391 | 1563 | 400 | 800 | 19.2 | ||
| ZWMD008008-28 | 264 | 1055 | 400 | 800 | 28.4 | ||
| ZWMD008008-47 | 161 | 643 | 600 | 1200 | 46.7 | 17.0 | 31.5 |
| ZWMD008008-69 | 109 | 434 | 600 | 1200 | 69.1 | ||
| ZWMD008008-102 | 73 | 293 | 600 | 1200 | 102.4 | ||
| ZWMD008008-152 | 49 | 198 | 600 | 1200 | 151.7 | ||
| ZWMD008008-168 | 45 | 179 | 750 | 1500 | 168.0 | 19.7 | 34.2 |
| ZWMD008008-249 | 30 | 121 | 750 | 1500 | 248.8 | ||
| ZWMD008008-369 | 20 | 81 | 750 | 1500 | 368.6 | ||
| ZWMD008008-546 | 14 | 55 | 750 | 1500 | 546.1 | ||
| ZWMD008008-809 | 9 | 37 | 750 | 1500 | 809.1 |
*The above specifications are subject to change without prior notice. They are for reference only and can be customized as required.
Can be Integrated Drive Control Module.
Please let us know your requirements and we will provide you with micro transmission solutions.
2)2D Drawing
Detailed Photos
Application
| Smart wearable devices | watch,VR,AR,XR and etc. |
| Household application | kitchen appliances, sewing machines, corn popper, vacuum cleaner, garden tool, sanitary ware, window curtain, intelligent closestool, sweeping robot, power seat, standing desk, electric sofa, TV, computer, treadmill, spyhole, cooker hood, electric drawer, electric mosquito net, intelligent cupboard, intelligent wardrobe, automatic soap dispenser, UV baby bottle sterilizer, lifting hot pot cookware, dishwasher, washing machine, food breaking machine, dryer, air conditioning, dustbin, coffee machine, whisk,smart lock,bread maker,Window cleaning robot and etc. |
| communication equipment | 5G base station,video conference,mobile phone and etc. |
| Office automation equipments | scanners, printers, multifunction machines copy machines, fax (FAX paper cutter), computer peripheral, bank machine, screen, lifting socket, display,notebook PC and etc. |
| Automotive products | conditioning damper actuator, car DVD,door lock actuator, retractable rearview mirror, meters, optic axis control device, head light beam level adjuster, car water pump, car antenna, lumbar support, EPB, car tail gate electric putter, HUD, head-up display, vehicle sunroof, EPS, AGS, car window, head restraint, E-booster, car seat, vehicle charging station and etc. |
| Toys and models | radio control model, automatic cruise control, ride-on toy, educational robot, programming robot, medical robot, automatic feeder, intelligent building blocks, escort robot and etc. |
| Medical equipments | blood pressure meter, breath machine, medical cleaning pump, medical bed, blood pressure monitors, medical ventilator, surgical staplers, infusion pump, dental instrument, self-clotting cutter, wound cleaning pump for orthopedic surgery,electronic cigarette, eyebrow pencil,fascia gun, , surgical robot,laboratory automation and etc. |
| Industrials | flow control valves, seismic testing,automatic reclosing,Agricultural unmanned aerial vehicle,automatic feeder ,intelligent express cabinet and etc. |
| Electric power tools | electric drill, screwdriver,garden tool and etc. |
| Precision instruments | optics instruments,automatic vending machine, wire-stripping machine and etc. |
| Personal care | tooth brush, hair clipper, electric shaver, massager, vibrator, hair dryer, rubdown machine, scissor hair machine, foot grinder,anti-myopia pen, facial beauty equipment, hair curler,Electric threading knife,POWER PERFECT PORE, Puff machine,eyebrow tweezers and etc. |
| Consumer electronics | camera, mobile phone,digital camera, automatic retracting device,camcorder, kinescope DVD,headphone stereo, cassette tape recorder, bluetooth earbud charging case, turntable, tablet,UAV(unmanned aerial vehicle),surveillance camera,PTZ camera, rotating smart speaker and etc. |
| robots | educational robot, programming robot, medical robot, escort robot and etc. |
Company Profile
Company Information:
HangZhou CHINAMFG Machinery & Electronics Co., Ltd was established in 2001,We provide the total drive solution for customers from design, tooling fabrication, components manufacturing and assembly.
1) Competitive Advantages
- 1) Competitive Advantages
19+year experience in manufacturing motor gearbox
We provide technical support from r&d, prototype, testing, assembly and serial production , ODM &OEM
Competitive Price
Product Performance: Low noise, High efficiency, Long lifespan
Prompt Delivery: 15 working days after payment
Small Orders Accepted
2) Main Products
-
Precision reduction gearbox and its diameter:3.4mm-38mm,voltage:1.5-24V,power: 0.01-40W,output speed:5-2000rpm and output torque:1.0 gf.cm -50kgf.cm,
- Customized worm and gear transmission machinery;
- Precise electromechanical motion module;
- Precise component and assembly of plastic and metal powder injection.
Our Services
- ODM & OEM
- Gearbox design and development
- Related technology support
- Micro drive gearbox custom solution
Packaging & Shipping
1) Packing Details
packed in nylon firstly, then carton, and then reinforced with wooden case for outer packing.
Or according to client’s requirement.
2) Shipping Details
samples will be shipped within 10 days;
batch order leading time according to the actual situation.
Certifications
Certifications
We Have passed to hold ISO9001:2015(CN11/3571),ISO14001:2004(U006616E0153R3M), ISO13485:2016(CN18/42018) and IATF16949:2016(CN11/3571.01).
and more…
FAQ
FAQ
1. Can you make the gearbox with custom specifications?
YES. We have design and development team, also a great term of engineers, each of them have
many work years experience.
2.Do you provide the samples?
YES. Our company can provide the samples to you, and the delivery time is about 5-15days according to the specification of gearbox you need.
3.What is your MOQ?
Our MOQ is 2000pcs. But at the beginning of our business, we accept small order.
4. Do you have the item in stock?
I am sorry we donot have the item in stock, All products are made with orders.
5. Do you provide technology support?
YES. Our company have design and development team, we can provide technology support if you
need.
6.How to ship to us?
We will ship the goods to you according to the DHL or UPS or FEDEX etc account you provide.
7.How to pay the money?
We accept T/T in advance. Also we have different bank account for receiving money, like US dollors or RMB etc.
8. How can I know the product is suitable for me?
Frist, you need to provide us the more details information about the product. We will recommend the item to you according to your requirement of specification. After you confirm, we will prepare the samples to you. also we will offer some good advances according to your product use.
9. Can I come to your company to visit?
YES, you can come to our company to visit at anytime, and welcome to visit our company.
10. How do contact us ?
Please send an inquiry
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Household Appliances, Car, Power Tools, Eyebrow Pencil |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Low Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Permanent Magnet |
| Function: | Control |
| Casing Protection: | Drip-Proof |
| Number of Poles: | 4 |
| Samples: |
US$ 80/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can gear motors be used in robotics, and if so, what are some notable applications?
Yes, gear motors are widely used in robotics due to their ability to provide torque, precise control, and compact size. They play a crucial role in various robotic applications, enabling the movement, manipulation, and control of robotic systems. Here are some notable applications of gear motors in robotics:
1. Robotic Arm Manipulation:
Gear motors are commonly used in robotic arms to provide precise and controlled movement. They enable the articulation of the arm’s joints, allowing the robot to reach different positions and orientations. Gear motors with high torque capabilities are essential for lifting, rotating, and manipulating objects with varying weights and sizes.
2. Mobile Robots:
Gear motors are employed in mobile robots, including wheeled robots and legged robots, to drive their locomotion. They provide the necessary torque and control for the robot to move, turn, and navigate in different environments. Gear motors with appropriate gear ratios ensure the robot’s mobility, stability, and maneuverability.
3. Robotic Grippers and End Effectors:
Gear motors are used in robotic grippers and end effectors to control the opening, closing, and gripping force. By integrating gear motors into the gripper mechanism, robots can grasp and manipulate objects of various shapes, sizes, and weights. The gear motors enable precise control over the gripping action, allowing the robot to handle delicate or fragile objects with care.
4. Autonomous Drones and UAVs:
Gear motors are utilized in the propulsion systems of autonomous drones and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). They drive the propellers or rotors, providing the necessary thrust and control for the drone’s flight. Gear motors with high power-to-weight ratios, efficient energy conversion, and precise speed control are crucial for achieving stable and maneuverable flight in drones.
5. Humanoid Robots:
Gear motors are integral to the movement and functionality of humanoid robots. They are used in robotic joints, such as hips, knees, and shoulders, to enable human-like movements. Gear motors with appropriate torque and speed capabilities allow humanoid robots to walk, run, climb stairs, and perform complex motions resembling human actions.
6. Robotic Exoskeletons:
Gear motors play a vital role in robotic exoskeletons, which are wearable robotic devices designed to augment human strength and assist in physical tasks. Gear motors are used in the exoskeleton’s joints and actuators, providing the necessary torque and control to enhance human abilities. They enable users to perform tasks with reduced effort, assist in rehabilitation, or provide support in physically demanding environments.
These are just a few notable applications of gear motors in robotics. Their versatility, torque capabilities, precise control, and compact size make them indispensable components in various robotic systems. Gear motors enable robots to perform complex tasks, move with agility, interact with the environment, and assist humans in a wide range of applications, from industrial automation to healthcare and exploration.

Can you explain the role of backlash in gear motors and how it’s managed in design?
Backlash plays a significant role in gear motors and is an important consideration in their design and operation. Backlash refers to the slight clearance or play between the teeth of gears in a gear system. It affects the precision, accuracy, and responsiveness of the gear motor. Here’s an explanation of the role of backlash in gear motors and how it is managed in design:
1. Role of Backlash:
Backlash in gear motors can have both positive and negative effects:
- Compensation for Misalignment: Backlash can help compensate for minor misalignments between gears, shafts, or the load. It allows a small amount of movement before engaging the next set of teeth, reducing the risk of damage due to misalignment. This can be particularly beneficial in applications where precise alignment is challenging or subject to variations.
- Negative Impact on Accuracy and Responsiveness: Backlash can introduce a delay or “dead zone” in the motion transmission. When changing the direction of rotation or reversing the load, the gear teeth must first overcome the clearance or play before engaging in the opposite direction. This delay can reduce the overall accuracy, responsiveness, and repeatability of the gear motor, especially in applications that require precise positioning or rapid changes in direction or speed.
2. Managing Backlash in Design:
Designers employ various techniques to manage and minimize backlash in gear motors:
- Tight Manufacturing Tolerances: Proper manufacturing techniques and tight tolerances can help minimize backlash. Precision machining and quality control during the production of gears and gear components ensure closer tolerances, reducing the amount of play between gear teeth.
- Preload or Pre-tensioning: Applying a preload or pre-tensioning force to the gear system can help reduce backlash. This technique involves introducing an initial force or tension that eliminates the clearance between gear teeth. It ensures immediate contact and engagement of the gear teeth, minimizing the dead zone and improving the overall responsiveness and accuracy of the gear motor.
- Anti-Backlash Gears: Anti-backlash gears are designed specifically to minimize or eliminate backlash. They typically feature modifications to the gear tooth profile, such as modified tooth shapes or special tooth arrangements, to reduce clearance. Anti-backlash gears can be used in gear motor designs to improve precision and minimize the effects of backlash.
- Backlash Compensation: In some cases, backlash compensation techniques can be employed. These techniques involve monitoring the position or movement of the load and applying control algorithms to compensate for the backlash. By accounting for the clearance and adjusting the control signals accordingly, the effects of backlash can be mitigated, improving accuracy and responsiveness.
3. Application-Specific Considerations:
The management of backlash in gear motors should be tailored to the specific application requirements:
- Positioning Accuracy: Applications that require precise positioning, such as robotics or CNC machines, may require tighter backlash control to ensure accurate and repeatable movements.
- Dynamic Response: Applications that involve rapid changes in direction or speed, such as high-speed automation or servo control systems, may require reduced backlash to maintain responsiveness and minimize overshoot or lag.
- Load Characteristics: The nature of the load and its impact on the gear system should be considered. Heavy loads or applications with significant inertial forces may require additional backlash management techniques to maintain stability and accuracy.
In summary, backlash in gear motors can affect precision, accuracy, and responsiveness. While it can compensate for misalignments, backlash may introduce delays and reduce the overall performance of the gear motor. Designers manage backlash through tight manufacturing tolerances, preload techniques, anti-backlash gears, and backlash compensation methods. The management of backlash depends on the specific application requirements, considering factors such as positioning accuracy, dynamic response, and load characteristics.

Can you explain the advantages of using gear motors in various mechanical systems?
Gear motors offer several advantages when utilized in various mechanical systems. Their unique characteristics make them well-suited for applications that require controlled power transmission, precise speed control, and torque amplification. Here’s a detailed explanation of the advantages of using gear motors:
1. Torque Amplification:
One of the key advantages of gear motors is their ability to amplify torque. By using different gear ratios, gear motors can increase or decrease the output torque from the motor. This torque amplification is crucial in applications that require high torque output, such as lifting heavy loads or operating machinery with high resistance. Gear motors allow for efficient power transmission, enabling the system to handle demanding tasks effectively.
2. Speed Control:
Gear motors provide precise speed control, allowing for accurate and controlled movement in mechanical systems. By selecting the appropriate gear ratio, the rotational speed of the output shaft can be adjusted to match the requirements of the application. This speed control capability ensures that the mechanical system operates at the desired speed, whether it needs to be fast or slow. Gear motors are commonly used in applications such as conveyors, robotics, and automated machinery, where precise speed control is essential.
3. Directional Control:
Another advantage of gear motors is their ability to control the rotational direction of the output shaft. By using different types of gears, such as spur gears, bevel gears, or worm gears, the direction of rotation can be easily changed. This directional control is beneficial in applications that require bidirectional movement, such as in actuators, robotic arms, and conveyors. Gear motors offer reliable and efficient directional control, contributing to the versatility and functionality of mechanical systems.
4. Efficiency and Power Transmission:
Gear motors are known for their high efficiency in power transmission. The gear system helps distribute the load across multiple gears, reducing the strain on individual components and minimizing power losses. This efficient power transmission ensures that the mechanical system operates with optimal energy utilization and minimizes wasted power. Gear motors are designed to provide reliable and consistent power transmission, resulting in improved overall system efficiency.
5. Compact and Space-Saving Design:
Gear motors are compact in size and offer a space-saving solution for mechanical systems. By integrating the motor and gear system into a single unit, gear motors eliminate the need for additional components and reduce the overall footprint of the system. This compact design is especially beneficial in applications with limited space constraints, allowing for more efficient use of available space while still delivering the necessary power and functionality.
6. Durability and Reliability:
Gear motors are designed to be robust and durable, capable of withstanding demanding operating conditions. The gear system helps distribute the load, reducing the stress on individual gears and increasing overall durability. Additionally, gear motors are often constructed with high-quality materials and undergo rigorous testing to ensure reliability and longevity. This makes gear motors well-suited for continuous operation in industrial and commercial applications, where reliability is crucial.
By leveraging the advantages of torque amplification, speed control, directional control, efficiency, compact design, durability, and reliability, gear motors provide a reliable and efficient solution for various mechanical systems. They are widely used in industries such as robotics, automation, manufacturing, automotive, and many others, where precise and controlled mechanical power transmission is essential.


editor by CX 2024-05-15
China best ZD GB755/IEC-60034 Standard 3~1800K Reduction Ratio Horizonal/Vertical Small AC Gear Motor vacuum pump design
Product Description
Model Selection
ZD Leader has a wide range of micro motor production lines in the industry, including DC Motor, AC Motor, Brushless Motor, Planetary Gear Motor, Drum Motor, Planetary Gearbox, RV Reducer and Harmonic Gearbox etc. Through technical innovation and customization, we help you create outstanding application systems and provide flexible solutions for various industrial automation situations.
• Model Selection
Our professional sales representive and technical team will choose the right model and transmission solutions for your usage depend on your specific parameters.
• Drawing Request
If you need more product parameters, catalogues, CAD or 3D drawings, please contact us.
• On Your Need
We can modify standard products or customize them to meet your specific needs.
Detailed Photos
Product Description
Features:
1.Basic stctrue:ZH(Horizonal),ZV(Vertical)
2.Output:100W,200W,400W,750W,1100W,1500W,2200W,3700W
3.Gear ratio:3,5,10…1800
4.Motor basic data:
S:3-phase motor,220-240/380-415V,50/60Hz
C:1-phase motor,220v,50-50Hz
E:1-phase motor,110v,50/60Hz
DV:Double Voltage motor,110/220V,50Hz/60Hz
Z:Light type duty
5.Brake unit: B: DC90V brake unit YB: With rsisase brake unit
Product Parameters
| Item | 3-phase motor | 1-phase motor |
| Protection | IP54 with alum alloy terminal box,and other is IP20 | |
| Frame material | Alum alloy for 100-2200W Frame,Alum alloy for 1#,2#,3#gear case,4#,5#,6# cast iron for others | |
| Duty | Continuous running | |
| INS.Class | B/F | |
| Environment | Temp:-10—+40centigrade Humidity:<90% |
|
| Voltage | 220V-240V/380-415V,50/60Hz | 110V/50/60Hz,220V/50/60Hz |
| Pole | 4P(6P) | 4P(6P) |
| Height | <1000m | |
| Starting | Direct start | 0.1-.02kw capacitor 0.4-1.5kw double capacitors |
| Standard | GB755/IEC-60034 | |
Main parts notes:
| Parts name | Notes |
| Gearbox | The output shaft diameter of gearbox 1#,2#,3# are 18,22,28mm separately.the material of gearbox is alum alloy.4#,5#,6# are 32,40,50 respectively.Gearbox is made of cast iron. |
| Gear piece | The material 40Cr mixes to HB280,then dealed with high frequency quencher HRC50.Gear should be processed by milling with high precision.The class is 6. |
| Gear shaft | The material 20CrMnTi will be changed into HRC60 through processing of cementite quencher.Gear shaft will be processed with gear hobbing.Precision class is 6. |
| Motor shaft | The material 40Cr mixes to HB280,then dealed with high frequency quencher HRC54.Finally,gear is cut for the second.motor shaft will be processed with gear hobbing.Precision class is 5-6. |
| Ball bearing | We adopt tight bearing with high precision,to make sure longterm running lift. |
| Oil seal | Gear shaft gives priorith to enduring high temp,avoiding oil infiltration. |
| Terminal box | Two type.one is al alloy,which equips good capability of waterproof and dustproof.Protection grade is IP54.The other is steel case with deft structure.Protection grade is IP20. |
Gear of small series:
1.The material of rotor is 40Cr,quench to HRC50-55 after rough rolling,two times hard cutting,the gear precision can arrive ISO class6-7.
2.The material of shafe gear is 20CrMnTi,quench to HRC58-61 after rough rolling,two times hard cutting,the gear precision can arrive ISO class6-7.
2.The material of plate gear is 40Cr,quench to HRC48-51 after rough rolling,grind,the precision can arrive ISO class6-7.
Brake series:
1.Economical and compact.
2.High pressure-resistance,good insulation,insulation class F,can work in different kinds of ambient.
3.Long life,adopting abrasion-resistance lead-free,non asbestos friction plate,making sure the long life.
4.It”s selective of assembling hole diameter and easy assembling.
5.Multiple assembling way meets different customers.
Other Related Products
Click here to find what you are looking for:
Company Profile
FAQ
Q: What’re your main products?
A: We currently produce Brushed Dc Motors, Brushed Dc Gear Motors, Planetary Dc Gear Motors, Brushless Dc Motors, Stepper motors, Ac Motors and High Precision Planetary Gear Box etc. You can check the specifications for above motors on our website and you can email us to recommend needed motors per your specification too.
Q: How to select a suitable motor?
A:If you have motor pictures or drawings to show us, or you have detailed specs like voltage, speed, torque, motor size, working mode of the motor, needed lifetime and noise level etc, please do not hesitate to let us know, then we can recommend suitable motor per your request accordingly.
Q: Do you have a customized service for your standard motors?
A: Yes, we can customize per your request for the voltage, speed, torque and shaft size/shape. If you need additional wires/cables soldered on the terminal or need to add connectors, or capacitors or EMC we can make it too.
Q: Do you have an individual design service for motors?
A: Yes, we would like to design motors individually for our customers, but it may need some mold developing cost and design charge.
Q: What’s your lead time?
A: Generally speaking, our regular standard product will need 15-30days, a bit longer for customized products. But we are very flexible on the lead time, it will depend on the specific orders.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Moving Machinery |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Constant Speed |
| Power Source: | AC Motor |
| Casing Protection: | Closed Type |
| Number of Poles: | 4 |
| Certification: | ISO9001, CCC |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What are the maintenance requirements for gear motors, and how can longevity be maximized?
Gear motors, like any mechanical system, require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Proper maintenance practices help prevent failures, minimize downtime, and extend the lifespan of gear motors. Here are some maintenance requirements for gear motors and ways to maximize their longevity:
1. Lubrication:
Regular lubrication is essential for gear motors to reduce friction, wear, and heat generation. The gears, bearings, and other moving parts should be properly lubricated according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Lubricants should be selected based on the motor’s specifications and operating conditions. Regular inspection and replenishment of lubricants, as well as periodic oil or grease changes, should be performed to maintain optimal lubrication levels and ensure long-lasting performance.
2. Inspection and Cleaning:
Regular inspection and cleaning of gear motors are crucial for identifying any signs of wear, damage, or contamination. Inspecting the gears, bearings, shafts, and connections can help detect any abnormalities or misalignments. Cleaning the motor’s exterior and ventilation channels to remove dust, debris, or moisture buildup is also important in preventing malfunctions and maintaining proper cooling. Any loose or damaged components should be repaired or replaced promptly.
3. Temperature and Environmental Considerations:
Monitoring and controlling the temperature and environmental conditions surrounding gear motors can significantly impact their longevity. Excessive heat can degrade lubricants, damage insulation, and lead to premature component failure. Ensuring proper ventilation, heat dissipation, and avoiding overloading the motor can help manage temperature effectively. Similarly, protecting gear motors from moisture, dust, chemicals, and other environmental contaminants is vital to prevent corrosion and damage.
4. Load Monitoring and Optimization:
Monitoring and optimizing the load placed on gear motors can contribute to their longevity. Operating gear motors within their specified load and speed ranges helps prevent excessive stress, overheating, and premature wear. Avoiding sudden and frequent acceleration or deceleration, as well as preventing overloading or continuous operation near the motor’s maximum capacity, can extend its lifespan.
5. Alignment and Vibration Analysis:
Proper alignment of gear motor components, such as gears, couplings, and shafts, is crucial for smooth and efficient operation. Misalignment can lead to increased friction, noise, and premature wear. Regularly checking and adjusting alignment, as well as performing vibration analysis, can help identify any misalignment or excessive vibration that may indicate underlying issues. Addressing alignment and vibration problems promptly can prevent further damage and maximize the motor’s longevity.
6. Preventive Maintenance and Regular Inspections:
Implementing a preventive maintenance program is essential for gear motors. This includes establishing a schedule for routine inspections, lubrication, and cleaning, as well as conducting periodic performance tests and measurements. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance tasks, such as belt tension checks, bearing replacements, or gear inspections, can help identify and address potential issues before they escalate into major failures.
By adhering to these maintenance requirements and best practices, the longevity of gear motors can be maximized. Regular maintenance, proper lubrication, load optimization, temperature control, and timely repairs or replacements of worn components contribute to the reliable operation and extended lifespan of gear motors.

What are some common challenges or issues associated with gear motors, and how can they be addressed?
Gear motors, like any mechanical system, can face certain challenges or issues that may affect their performance, reliability, or longevity. However, many of these challenges can be addressed through proper design, maintenance, and operational practices. Here are some common challenges associated with gear motors and potential solutions:
1. Gear Wear and Failure:
Over time, gears in a gear motor can experience wear, resulting in decreased performance or even failure. The following measures can address this challenge:
- Proper Lubrication: Regular lubrication with the appropriate lubricant can minimize friction and wear between gear teeth. It is essential to follow manufacturer recommendations for lubrication intervals and use high-quality lubricants suitable for the specific gear motor.
- Maintenance and Inspection: Routine maintenance and periodic inspections can help identify early signs of gear wear or damage. Timely replacement of worn gears or components can prevent further damage and ensure the gear motor’s optimal performance.
- Material Selection: Choosing gears made from durable and wear-resistant materials, such as hardened steel or specialized alloys, can increase their lifespan and resistance to wear.
2. Backlash and Inaccuracy:
Backlash, as discussed earlier, can introduce inaccuracies in gear motor systems. The following approaches can help address this issue:
- Anti-Backlash Gears: Using anti-backlash gears, which are designed to minimize or eliminate backlash, can significantly reduce inaccuracies caused by gear play.
- Tight Manufacturing Tolerances: Ensuring precise manufacturing tolerances during gear production helps minimize backlash and improve overall accuracy.
- Backlash Compensation: Implementing control algorithms or mechanisms to compensate for backlash can help mitigate its effects and improve the accuracy of the gear motor.
3. Noise and Vibrations:
Gear motors can generate noise and vibrations during operation, which may be undesirable in certain applications. The following strategies can help mitigate this challenge:
- Noise Dampening: Incorporating noise-dampening features, such as vibration-absorbing materials or isolation mounts, can reduce noise and vibrations transmitted from the gear motor to the surrounding environment.
- Quality Gears and Bearings: Using high-quality gears and bearings can minimize vibrations and noise generation. Precision-machined gears and well-maintained bearings help ensure smooth operation and reduce unwanted noise.
- Proper Alignment: Ensuring accurate alignment of gears, shafts, and other components reduces the likelihood of noise and vibrations caused by misalignment. Regular inspections and adjustments can help maintain optimal alignment.
4. Overheating and Thermal Management:
Heat buildup can be a challenge in gear motors, especially during prolonged or heavy-duty operation. Effective thermal management techniques can address this issue:
- Adequate Ventilation: Providing proper ventilation and airflow around the gear motor helps dissipate heat. This can involve designing cooling fins, incorporating fans or blowers, or ensuring sufficient clearance for air circulation.
- Heat Dissipation Materials: Using heat-dissipating materials, such as aluminum or copper, in motor housings or heat sinks can improve heat dissipation and prevent overheating.
- Monitoring and Control: Implementing temperature sensors and thermal protection mechanisms allows for real-time monitoring of the gear motor’s temperature. If the temperature exceeds safe limits, the motor can be automatically shut down or adjusted to prevent damage.
5. Load Variations and Shock Loads:
Unexpected load variations or shock loads can impact the performance and durability of gear motors. The following measures can help address this challenge:
- Proper Sizing and Selection: Choosing gear motors with appropriate torque and load capacity ratings for the intended application helps ensure they can handle expected load variations and occasional shock loads without exceeding their limits.
- Shock Absorption: Incorporating shock-absorbing mechanisms, such as dampers or resilient couplings, can help mitigate the effects of sudden load changes or impacts on the gear motor.
- Load Monitoring: Implementing load monitoring systems or sensors allows for real-time monitoring of load variations. This information can be used to adjust operation or trigger protective measures when necessary.
By addressing these common challenges associated with gear motors through appropriate design considerations, regular maintenance, and operational practices, it is possible to enhance their performance, reliability, and longevity.

How does the gearing mechanism in a gear motor contribute to torque and speed control?
The gearing mechanism in a gear motor plays a crucial role in controlling torque and speed. By utilizing different gear ratios and configurations, the gearing mechanism allows for precise manipulation of these parameters. Here’s a detailed explanation of how the gearing mechanism contributes to torque and speed control in a gear motor:
The gearing mechanism consists of multiple gears with varying sizes, tooth configurations, and arrangements. Each gear in the system engages with another gear, creating a mechanical connection. When the motor rotates, it drives the rotation of the first gear, which then transfers the motion to subsequent gears, ultimately resulting in the output shaft’s rotation.
Torque Control:
The gearing mechanism in a gear motor enables torque control through the principle of mechanical advantage. The gear system utilizes gears with different numbers of teeth, known as gear ratio, to adjust the torque output. When a smaller gear (pinion) engages with a larger gear (gear), the pinion rotates faster than the gear but exerts more force or torque. This results in torque amplification, allowing the gear motor to deliver higher torque at the output shaft while reducing the rotational speed. Conversely, if a larger gear engages with a smaller gear, torque reduction occurs, resulting in higher rotational speed at the output shaft.
By selecting the appropriate gear ratio, the gearing mechanism effectively adjusts the torque output of the gear motor to match the requirements of the application. This torque control capability is essential in applications that demand high torque for heavy lifting or overcoming resistance, as well as applications that require lower torque but higher rotational speed.
Speed Control:
The gearing mechanism also contributes to speed control in a gear motor. The gear ratio determines the relationship between the rotational speed of the input shaft (driven by the motor) and the output shaft. When a gear motor has a higher gear ratio (more teeth on the driven gear compared to the driving gear), it reduces the output speed while increasing the torque. Conversely, a lower gear ratio increases the output speed while reducing the torque.
By choosing the appropriate gear ratio, the gearing mechanism allows for precise speed control in a gear motor. This is particularly useful in applications that require specific speed ranges or variations, such as conveyor systems, robotic movements, or machinery that needs to operate at different speeds for different tasks. The speed control capability of the gearing mechanism enables the gear motor to match the desired speed requirements of the application accurately.
In summary, the gearing mechanism in a gear motor contributes to torque and speed control by utilizing different gear ratios and configurations. It enables torque amplification or reduction, depending on the gear arrangement, allowing the gear motor to deliver the required torque output. Additionally, the gear ratio also determines the relationship between the rotational speed of the input and output shafts, providing precise speed control. These torque and speed control capabilities make gear motors versatile and suitable for a wide range of applications in various industries.


editor by CX 2024-04-16
China Standard CHINAMFG 12mm N20 Small Size for Intelligent Lock RC Car Toys Robots 12V DC Gear Motor vacuum pump diy
Product Description
10mm 3V High Precision CCTV Camera Geared Motor With Gearbox
Product Parameters
Model: ZWBMD571571-168
- Rated Voltage: 3.0V
- No Load Speed: 98 rpm
- No Load Current: 80mA
- Rated Load Speed: 86 rpm
- Rated Load Current: 220mA
- Rated Load Torque: 106 gf.cm
- Rated Torque of Gear Box: 2,000 gf.cm
- Instant Torque of Gear Box: 6,000 gf.cm
- Overall Length L: 34 mm
- Gear Box Length L1: 19 mm
| Model | Application Parameters | Rated Torque of Gear Box | Instant Torque of Gear Box | Gear Ratio | Gear Box Length L1 |
|||||||
| Rated | At No Load | At Rated Load | Overall Length L |
|||||||||
| Voltage | Speed | Current | Speed | Current | Torque | |||||||
| VDC | rpm | mA | rpm | mA | gf.cm | mN.m | mm | gf.cm | gf.cm | mm | ||
| ZWBMD571571-46 | 3.0 | 375 | 80 | 315 | 215 | 39 | 3.8 | 30.9 | 2000 | 6000 | 46 | 15.9 |
| ZWBMD571571-69 | 3.0 | 250 | 80 | 210 | 215 | 58 | 5.7 | 2000 | 6000 | 69 | ||
| ZWBMD571571-102 | 3.0 | 169 | 80 | 142 | 215 | 86 | 8.4 | 2000 | 6000 | 102 | ||
| ZWBMD571571-151 | 3.0 | 114 | 80 | 96 | 215 | 127 | 12.5 | 2000 | 6000 | 151 | ||
| ZWBMD571571-168 | 3.0 | 98 | 80 | 86 | 220 | 106 | 10.4 | 34 | 2000 | 6000 | 168 | 19 |
| ZWBMD571571-249 | 3.0 | 66 | 80 | 58 | 220 | 158 | 15 | 2000 | 6000 | 249 | ||
| ZWBMD571571-368 | 3.0 | 45 | 80 | 39 | 220 | 233 | 23 | 2000 | 6000 | 368 | ||
| ZWBMD571571-546 | 3.0 | 30 | 80 | 27 | 220 | 346 | 34 | 2000 | 6000 | 546 | ||
| ZWBMD571571-809 | 3.0 | 20 | 80 | 18 | 220 | 512 | 50 | 2000 | 6000 | 809 | ||
above specifications just for reference and customizable according to requirements.
Please let us know your requirements and we will provide you with micro transmission solutions.
Detailed Photos
Application
| Smart wearable devices | watch,VR,AR,XR and etc. |
| Household application | kitchen appliances, sewing machines, corn popper, vacuum cleaner, garden tool, sanitary ware, window curtain, intelligent closestool, sweeping robot, power seat, standing desk, electric sofa, TV, computer, treadmill, spyhole, cooker hood, electric drawer, electric mosquito net, intelligent cupboard, intelligent wardrobe, automatic soap dispenser, UV baby bottle sterilizer, lifting hot pot cookware, dishwasher, washing machine, food breaking machine, dryer, air conditioning, dustbin, coffee machine, whisk,smart lock,bread maker,Window cleaning robot and etc. |
| communication equipment | 5G base station,video conference,mobile phone and etc. |
| Office automation equipments | scanners, printers, multifunction machines copy machines, fax (FAX paper cutter), computer peripheral, bank machine, screen, lifting socket, display,notebook PC and etc. |
| Automotive products | conditioning damper actuator, car DVD,door lock actuator, retractable rearview mirror, meters, optic axis control device, head light beam level adjuster, car water pump, car antenna, lumbar support, EPB, car tail gate electric putter, HUD, head-up display, vehicle sunroof, EPS, AGS, car window, head restraint, E-booster, car seat, vehicle charging station and etc. |
| Toys and models | radio control model, automatic cruise control, ride-on toy, educational robot, programming robot, medical robot, automatic feeder, intelligent building blocks, escort robot and etc. |
| Medical equipments | blood pressure meter, breath machine, medical cleaning pump, medical bed, blood pressure monitors, medical ventilator, surgical staplers, infusion pump, dental instrument, self-clotting cutter, wound cleaning pump for orthopedic surgery,electronic cigarette, eyebrow pencil,fascia gun, , surgical robot,laboratory automation and etc. |
| Industrials | flow control valves, seismic testing,automatic reclosing,Agricultural unmanned aerial vehicle,automatic feeder ,intelligent express cabinet and etc. |
| Electric power tools | electric drill, screwdriver,garden tool and etc. |
| Precision instruments | optics instruments,automatic vending machine, wire-stripping machine and etc. |
| Personal care | tooth brush, hair clipper, electric shaver, massager, vibrator, hair dryer, rubdown machine, scissor hair machine, foot grinder,anti-myopia pen, facial beauty equipment, hair curler,Electric threading knife,POWER PERFECT PORE, Puff machine,eyebrow tweezers and etc. |
| Consumer electronics | camera, mobile phone,digital camera, automatic retracting device,camcorder, kinescope DVD,headphone stereo, cassette tape recorder, bluetooth earbud charging case, turntable, tablet,UAV(unmanned aerial vehicle),surveillance camera,PTZ camera, rotating smart speaker and etc. |
| robots | educational robot, programming robot, medical robot, escort robot and etc. |
Company Profile
HangZhou CHINAMFG Machinery & Electronics Co., Ltd was established in 2001,We provide the total drive solution for customers from design, tooling fabrication, components manufacturing and assembly.
Workshop
Testing Equipment
1) Competitive Advantages
- 1) Competitive Advantages
19+year experience in manufacturing motor gearbox
We provide technical support from r&d, prototype, testing, assembly and serial production , ODM &OEM
Competitive Price
Product Performance: Low noise, High efficiency, Long lifespan
Prompt Delivery: 15 working days after payment
Small Orders Accepted
2) Main Products
-
Precision reduction gearbox and its diameter:3.4mm-38mm,voltage:1.5-24V,power: 0.01-40W,output speed:5-2000rpm and output torque:1.0 gf.cm -50kgf.cm,
- Customized worm and gear transmission machinery;
- Precise electromechanical motion module;
- Precise component and assembly of plastic and metal powder injection.
Our Services
- ODM & OEM
- Gearbox design and development
- Related technology support
- Micro drive gearbox custom solution
Packaging & Shipping
1) Packing Details
packed in nylon firstly, then carton, and then reinforced with wooden case for outer packing.
Or according to client’s requirement.
2) Shipping Details
samples will be shipped within 10 days;
batch order leading time according to the actual situation.
Certifications
Certifications
We Have passed to hold ISO9001:2015(CN11/3571),ISO14001:2004(U006616E0153R3M), ISO13485:2016(CN18/42018) and IATF16949:2016(CN11/3571.01).
and more…
FAQ
FAQ
1. Can you make the gearbox with custom specifications?
YES. We have design and development team, also a great term of engineers, each of them have
many work years experience.
2.Do you provide the samples?
YES. Our company can provide the samples to you, and the delivery time is about 5-15days according to the specification of gearbox you need.
3.What is your MOQ?
Our MOQ is 2000pcs. But at the beginning of our business, we accept small order.
4. Do you have the item in stock?
I am sorry we donot have the item in stock, All products are made with orders.
5. Do you provide technology support?
YES. Our company have design and development team, we can provide technology support if you
need.
6.How to ship to us?
We will ship the goods to you according to the DHL or UPS or FEDEX etc account you provide.
7.How to pay the money?
We accept T/T in advance. Also we have different bank account for receiving money, like US dollors or RMB etc.
8. How can I know the product is suitable for me?
Frist, you need to provide us the more details information about the product. We will recommend the item to you according to your requirement of specification. After you confirm, we will prepare the samples to you. also we will offer some good advances according to your product use.
9. Can I come to your company to visit?
YES, you can come to our company to visit at anytime, and welcome to visit our company.
10. How do contact us ?
Please send an inquiry
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Household Appliances, Car, Power Tools, CCTV Camera |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Low Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Permanent Magnet |
| Function: | Control |
| Casing Protection: | Drip-Proof |
| Number of Poles: | 4 |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Where can individuals find reliable resources for learning more about gear motors and their applications?
Individuals seeking to learn more about gear motors and their applications have access to various reliable resources that provide valuable information and insights. Here are some sources where individuals can find reliable information about gear motors:
1. Manufacturer Websites:
Manufacturer websites are a primary source of information about gear motors. Gear motor manufacturers often provide detailed product specifications, application guides, technical documentation, and educational materials on their websites. These resources offer insights into different gear motor types, features, performance characteristics, and application considerations. Manufacturer websites are a reliable and convenient starting point for learning about gear motors.
2. Industry Associations and Organizations:
Industry associations and organizations related to mechanical engineering, automation, and motion control often have resources and publications dedicated to gear motors. These organizations provide technical articles, whitepapers, industry standards, and guidelines related to gear motor design, selection, and application. Examples of such associations include the American Gear Manufacturers Association (AGMA), International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), and Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
3. Technical Publications and Journals:
Technical publications and journals focused on engineering, robotics, and motion control are valuable sources of in-depth knowledge about gear motors. Publications like IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, Mechanical Engineering magazine, or Motion System Design magazine often feature articles, case studies, and research papers on gear motor technology, advancements, and applications. These publications provide authoritative and up-to-date information from industry experts and researchers.
4. Online Forums and Communities:
Online forums and communities dedicated to engineering, robotics, and automation can be excellent resources for discussions, insights, and practical experiences related to gear motors. Websites like Stack Exchange, engineering-focused subreddits, or specialized forums provide platforms for individuals to ask questions, share knowledge, and engage in discussions with professionals and enthusiasts in the field. Participating in these communities allows individuals to learn from real-world experiences and gain practical insights.
5. Educational Institutions and Courses:
Technical colleges, universities, and vocational training centers often offer courses or programs in mechanical engineering, mechatronics, or automation that cover gear motor fundamentals and applications. These educational institutions provide comprehensive curricula, textbooks, and lecture materials that can serve as reliable resources for individuals interested in learning about gear motors. Additionally, online learning platforms like Coursera, Udemy, or LinkedIn Learning offer courses on topics related to gear motors and motion control.
6. Trade Shows and Exhibitions:
Attending trade shows, exhibitions, and industry conferences related to automation, robotics, or motion control provides opportunities to learn about the latest advancements in gear motor technology. These events often feature product demonstrations, technical presentations, and expert panels where individuals can interact with gear motor manufacturers, industry experts, and other professionals. It’s a great way to stay updated on the latest trends, innovations, and applications of gear motors.
When seeking reliable resources, it’s important to consider the credibility of the source, the expertise of the authors, and the relevance to the specific area of interest. By leveraging these resources, individuals can gain a comprehensive understanding of gear motors and their applications, from basic principles to advanced topics, enabling them to make informed decisions and effectively utilize gear motors in their projects or applications.

What is the significance of gear reduction in gear motors, and how does it affect efficiency?
Gear reduction plays a significant role in gear motors as it enables the motor to deliver higher torque while reducing the output speed. This feature has several important implications for gear motors, including enhanced power transmission, improved control, and potential trade-offs in terms of efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of the significance of gear reduction in gear motors and its effect on efficiency:
Significance of Gear Reduction:
1. Increased Torque: Gear reduction allows gear motors to generate higher torque output compared to a motor without gears. By reducing the rotational speed at the output shaft, gear reduction increases the mechanical advantage of the system. This increased torque is beneficial in applications that require high torque to overcome resistance, such as lifting heavy loads or driving machinery with high inertia.
2. Improved Control: Gear reduction enhances the control and precision of gear motors. By reducing the speed, gear reduction allows for finer control over the motor’s rotational movement. This is particularly important in applications that require precise positioning or accurate speed control. The gear reduction mechanism enables gear motors to achieve smoother and more controlled movements, reducing the risk of overshooting or undershooting the desired position.
3. Load Matching: Gear reduction helps match the motor’s power characteristics to the load requirements. Different applications have varying torque and speed requirements. Gear reduction allows the gear motor to achieve a better match between the motor’s power output and the specific requirements of the load. It enables the motor to operate closer to its peak efficiency by optimizing the torque-speed trade-off.
Effect on Efficiency:
While gear reduction offers several advantages, it can also affect the efficiency of gear motors. Here’s how gear reduction impacts efficiency:
1. Mechanical Efficiency: The gear reduction process introduces mechanical components such as gears, bearings, and lubrication systems. These components introduce additional friction and mechanical losses into the system. As a result, some energy is lost in the form of heat during the gear reduction process. The efficiency of the gear motor is influenced by the quality of the gears, the lubrication used, and the overall design of the gear system. Well-designed and properly maintained gear systems can minimize these losses and optimize mechanical efficiency.
2. System Efficiency: Gear reduction affects the overall system efficiency by impacting the motor’s electrical efficiency. In gear motors, the motor typically operates at higher speeds and lower torques compared to a direct-drive motor. The overall system efficiency takes into account both the electrical efficiency of the motor and the mechanical efficiency of the gear system. While gear reduction can increase the torque output, it also introduces additional losses due to increased mechanical complexity. Therefore, the overall system efficiency may be lower compared to a direct-drive motor for certain applications.
It’s important to note that the efficiency of gear motors is influenced by various factors beyond gear reduction, such as motor design, control systems, and operating conditions. The selection of high-quality gears, proper lubrication, and regular maintenance can help minimize losses and improve efficiency. Additionally, advancements in gear technology, such as the use of precision gears and improved lubricants, can contribute to higher overall efficiency in gear motors.
In summary, gear reduction is significant in gear motors as it provides increased torque, improved control, and better load matching. However, gear reduction can introduce mechanical losses and affect the overall efficiency of the system. Proper design, maintenance, and consideration of application requirements are essential to optimize the balance between torque, speed, and efficiency in gear motors.

Can you explain the advantages of using gear motors in various mechanical systems?
Gear motors offer several advantages when utilized in various mechanical systems. Their unique characteristics make them well-suited for applications that require controlled power transmission, precise speed control, and torque amplification. Here’s a detailed explanation of the advantages of using gear motors:
1. Torque Amplification:
One of the key advantages of gear motors is their ability to amplify torque. By using different gear ratios, gear motors can increase or decrease the output torque from the motor. This torque amplification is crucial in applications that require high torque output, such as lifting heavy loads or operating machinery with high resistance. Gear motors allow for efficient power transmission, enabling the system to handle demanding tasks effectively.
2. Speed Control:
Gear motors provide precise speed control, allowing for accurate and controlled movement in mechanical systems. By selecting the appropriate gear ratio, the rotational speed of the output shaft can be adjusted to match the requirements of the application. This speed control capability ensures that the mechanical system operates at the desired speed, whether it needs to be fast or slow. Gear motors are commonly used in applications such as conveyors, robotics, and automated machinery, where precise speed control is essential.
3. Directional Control:
Another advantage of gear motors is their ability to control the rotational direction of the output shaft. By using different types of gears, such as spur gears, bevel gears, or worm gears, the direction of rotation can be easily changed. This directional control is beneficial in applications that require bidirectional movement, such as in actuators, robotic arms, and conveyors. Gear motors offer reliable and efficient directional control, contributing to the versatility and functionality of mechanical systems.
4. Efficiency and Power Transmission:
Gear motors are known for their high efficiency in power transmission. The gear system helps distribute the load across multiple gears, reducing the strain on individual components and minimizing power losses. This efficient power transmission ensures that the mechanical system operates with optimal energy utilization and minimizes wasted power. Gear motors are designed to provide reliable and consistent power transmission, resulting in improved overall system efficiency.
5. Compact and Space-Saving Design:
Gear motors are compact in size and offer a space-saving solution for mechanical systems. By integrating the motor and gear system into a single unit, gear motors eliminate the need for additional components and reduce the overall footprint of the system. This compact design is especially beneficial in applications with limited space constraints, allowing for more efficient use of available space while still delivering the necessary power and functionality.
6. Durability and Reliability:
Gear motors are designed to be robust and durable, capable of withstanding demanding operating conditions. The gear system helps distribute the load, reducing the stress on individual gears and increasing overall durability. Additionally, gear motors are often constructed with high-quality materials and undergo rigorous testing to ensure reliability and longevity. This makes gear motors well-suited for continuous operation in industrial and commercial applications, where reliability is crucial.
By leveraging the advantages of torque amplification, speed control, directional control, efficiency, compact design, durability, and reliability, gear motors provide a reliable and efficient solution for various mechanical systems. They are widely used in industries such as robotics, automation, manufacturing, automotive, and many others, where precise and controlled mechanical power transmission is essential.


editor by CX 2024-04-09
China Standard 12V Low Rpm DC Motor with Gear Reduction (TT555122500) with high quality
Product Description
A. Specification of 12V Low Rpm DC Motor with Gear Reduction (TT555122500):
1. Voltage: 3V, 6V, 12V, 24V
2. Speed: 1-60rpm
3. Rated torque: 3-60kg. Cm
4. Ratio: 1: 37 to 1: 1166
5. Direction of rotation: CW/CCW
6. Packing: 55X35X18CM 24PCS/ CTN 14KGS Net weight
7. Application: Household appliancesslot machinesmoney detector automatic actuator. Coffee machine towel disposalcoin refund devicesperistaltic pump Lighting stage lamp
8. The data sheet and price range are only for referece, Motor’s price are decide by toque and ratio reduciton, Please contact with me if want more informations.
| Motor name | Rated volt. v | No load | Load torque | Stall torque | |||||
| Current | Speed | Current | Speed | Torque | Output power | Torque | Gear trains | ||
| mA | r/min | mA | r/min | kg · cm | W | kg. cm | mm | ||
| TT545122500-36K | 12 | ≤ 100 | 60 | ≤ 330 | 46 | 2.7 | 1.2 | 6 | 3 |
| TT545122500-676 | 12 | ≤ 100 | 33 | ≤ 330 | 26 | 4.6 | 1.2 | 15 | 3 |
| TT545122500-90K | 12 | ≤ 100 | 23 | ≤ 330 | 18 | 6.9 | 1.2 | 21 | 3 |
| TT545122500-150K | 12 | ≤ 100 | 14.9 | ≤ 330 | 11 | 10 | 1.2 | 30 | 4 |
| TT545122500-196K | 12 | ≤ 100 | 11.5 | ≤ 330 | 8.5 | 12.9 | 1.1 | 39 | 4 |
| TT545122500-277K | 12 | ≤ 100 | 8 | ≤ 330 | 6 | 18.3 | 1.1 | 54 | 4 |
| Motor name | Rated volt. v | No load | Load torque | Stall torque | |||||
| Current | Speed | Current | Speed | Torque | Output power | Torque | Gear trains | ||
| mA | r/min | mA | r/min | kg · cm | W | kg. cm | mm | ||
| TT545122500-394K | 12 | ≤ 100 | 5.6 | ≤ 330 | 4.2 | 26.4 | 1.1 | 78 | 4 |
| TT545122500-624K | 12 | ≤ 100 | 3.6 | ≤ 330 | 2.7 | 37 | 1 | 111 | 5 |
| TT545122500-1166K | 12 | ≤ 100 | 1.9 | ≤ 230 | 1.6 | 60 | 1 | 180 | 5 |
B. Company Capacity
1. Production line
2. Test equipment:
3. Certificates:
4 Exhibitions And Customer Visit:
5. FAQ(Q=Question, A=Answer)
Q: What’s your main products?
A:We currently produce Brushed Dc Motors, Brushed Dc gear Motors, Planetary Dc Gear Motors, Brushless Dc Motors, Stepper motors and Ac Motors etc. You can check the specifications for above motors on our website and you can email us to recommend needed motors per your specification too.
Q:How to select a suitable motor?
A:If you have motor pictures or drawings to show us, or you have detailed specs like voltage, speed, torque, motor size, working mode of the motor, needed life time and noise level etc, please do not hesitate to let us know, then we can recommend suitable motor per your request accordingly.
Q: Do you have customized service for your standard motors?
A:Yes, we can customize per your request for the voltage, speed, torque and shaft size/shape. If you need additional wires/cables soldered on the terminal or need to add connectors, or capacitors or EMC we can make it too.
Q:Do you have individual design service for motors?
A:Yes, we would like to design motors individually for our customers, but it may need some mould charge and design charge.
Q:Can I have samples for testing first?
A:Yes, definitely you can. After confirmed the needed motor specs, we will quote and provide a proforma invoice for samples, once we get the payment, we will get a PASS from our account department to proceed samples accordingly.
Q:How do you make sure motor quality?
A:We have our own inspection procedures: for incoming materials, we have signed sample and drawing to make sure qualified incoming materials; for production process, we have tour inspection in the process and final inspection to make sure qualified products before shipping.
Q:What’s your lead time?
A:Generally speaking, our regular standard product will need 25-30days, a bit longer for customized products. But we are very flexible on the lead time, it will depends on the specific orders
Q:What’s your payment term?
A:For all our new customers, we will need 40% deposite, 60% paid before shipment.
Q:When will you reply after got my inquiries?
A:We will response within 24 hours once get your inquires.
Q:How can I trust you to make sure my money is safe?
A:We are certified by the third party SGS and we have exported to over 85 countries up to June.2017. You can check our reputation with our current customers in your country (if our customers do not mind), or you can order via alibaba to get trade assurance from alibaba to make sure your money is safe.
Q:What’s the minimum order quantity?
A:Our minimum order quantity depends on different motor models, please email us to check. Also, we usually do not accept personal use motor orders.
Q:What’s your shipping method for motors?
A:For samples and packages less than 100kg, we usually suggest express shipping; For heavy packages, we usually suggest air shipping or sea shipping. But it all depends on our customers’ needs.
Q:What certifications do you have?
A:We currently have CE and ROSH certifications.
Q:Can you send me your price list?
A:Since we have hundreds of different products, and price varies per different specifications, we are not able to offer a price list. But we can quote within 24 hours once got your inquirues to make sure you can get the price in time.
Q:Can I visit your company?
A:Yes, welcome to visit our company, but please let us know at least 2 weeks in advance to help us make sure no other meetings during the day you visit us. Thanks!
Weclome contact with us if have any questions about this motor or other products! /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Vending Machine, Coffee Machine |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Low Speed |
| Function: | Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Protection Type |
| Structure and Working Principle: | Brush |
| Certification: | ISO9001, Ce, RoHS |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What types of feedback mechanisms are commonly integrated into gear motors for control?
Gear motors often incorporate feedback mechanisms to provide control and improve their performance. These feedback mechanisms enable the motor to monitor and adjust its operation based on various parameters. Here are some commonly integrated feedback mechanisms in gear motors:
1. Encoder Feedback:
An encoder is a device that provides position and speed feedback by converting the motor’s mechanical motion into electrical signals. Encoders commonly used in gear motors include:
- Incremental Encoders: These encoders provide information about the motor’s shaft position and speed relative to a reference point. They generate pulses as the motor rotates, allowing precise measurement of position and speed changes.
- Absolute Encoders: Absolute encoders provide the precise position of the motor’s shaft within a full revolution. They do not require a reference point and provide accurate feedback even after power loss or motor restart.
2. Hall Effect Sensors:
Hall effect sensors use the principle of the Hall effect to detect the presence and strength of a magnetic field. They are commonly used in gear motors for speed and position sensing. Hall effect sensors provide feedback by detecting changes in the motor’s magnetic field and converting them into electrical signals.
3. Current Sensors:
Current sensors monitor the electrical current flowing through the motor’s windings. By measuring the current, these sensors provide feedback regarding the motor’s torque, load conditions, and power consumption. Current sensors are essential for motor control strategies such as current limiting, overcurrent protection, and closed-loop control.
4. Temperature Sensors:
Temperature sensors are integrated into gear motors to monitor the motor’s temperature. They provide feedback on the motor’s thermal conditions, allowing the control system to adjust the motor’s operation to prevent overheating. Temperature sensors are crucial for ensuring the motor’s reliability and preventing damage due to excessive heat.
5. Hall Effect Limit Switches:
Hall effect limit switches are used to detect the presence or absence of a magnetic field within a specific range. They are commonly employed as end-of-travel or limit switches in gear motors. Hall effect limit switches provide feedback to the control system, indicating when the motor has reached a specific position or when it has moved beyond the allowed range.
6. Resolver Feedback:
A resolver is an electromagnetic device used to determine the position and speed of a rotating shaft. It provides feedback by generating sine and cosine signals that correspond to the shaft’s angular position. Resolver feedback is commonly used in high-performance gear motors requiring accurate position and speed control.
These feedback mechanisms, when integrated into gear motors, enable precise control, monitoring, and adjustment of various motor parameters. By utilizing feedback signals from encoders, Hall effect sensors, current sensors, temperature sensors, limit switches, or resolvers, the control system can optimize the motor’s performance, ensure accurate positioning, maintain speed control, and protect the motor from excessive loads or overheating.

How do gear motors compare to other types of motors in terms of power and efficiency?
Gear motors can be compared to other types of motors in terms of power output and efficiency. The choice of motor type depends on the specific application requirements, including the desired power level, efficiency, speed range, torque characteristics, and control capabilities. Here’s a detailed explanation of how gear motors compare to other types of motors in terms of power and efficiency:
1. Gear Motors:
Gear motors combine a motor with a gear mechanism to deliver increased torque output and improved control. The gear reduction enables gear motors to provide higher torque while reducing the output speed. This makes gear motors suitable for applications that require high torque, precise positioning, and controlled movements. However, the gear reduction process introduces mechanical losses, which can slightly reduce the overall efficiency of the system compared to direct-drive motors. The efficiency of gear motors can vary depending on factors such as gear quality, lubrication, and maintenance.
2. Direct-Drive Motors:
Direct-drive motors, also known as gearless or integrated motors, do not use a gear mechanism. They provide a direct connection between the motor and the load, eliminating the need for gear reduction. Direct-drive motors offer advantages such as high efficiency, low maintenance, and compact design. Since there are no gears involved, direct-drive motors experience fewer mechanical losses and can achieve higher overall efficiency compared to gear motors. However, direct-drive motors may have limitations in terms of torque output and speed range, and they may require more complex control systems to achieve precise positioning.
3. Stepper Motors:
Stepper motors are a type of gear motor that excels in precise positioning applications. They operate by converting electrical pulses into incremental steps of movement. Stepper motors offer excellent positional accuracy and control. They are capable of precise positioning and can hold a position without power. Stepper motors have relatively high torque at low speeds, making them suitable for applications that require precise control and positioning, such as robotics, 3D printers, and CNC machines. However, stepper motors may have lower overall efficiency compared to direct-drive motors due to the additional power required to overcome the detents between steps.
4. Servo Motors:
Servo motors are another type of gear motor known for their high torque, high speed, and excellent positional accuracy. Servo motors combine a motor, a feedback device (such as an encoder), and a closed-loop control system. They offer precise control over position, speed, and torque. Servo motors are widely used in applications that require accurate and responsive positioning, such as industrial automation, robotics, and camera pan-tilt systems. Servo motors can achieve high efficiency when properly optimized and controlled but may have slightly lower efficiency compared to direct-drive motors due to the additional complexity of the control system.
5. Efficiency Considerations:
When comparing power and efficiency among different motor types, it’s important to consider the specific requirements and operating conditions of the application. Factors such as load characteristics, speed range, duty cycle, and control requirements influence the overall efficiency of the motor system. While direct-drive motors generally offer higher efficiency due to the absence of mechanical losses from gears, gear motors can deliver higher torque output and enhanced control capabilities. The efficiency of gear motors can be optimized through proper gear selection, lubrication, and maintenance practices.
In summary, gear motors offer increased torque and improved control compared to direct-drive motors. However, gear reduction introduces mechanical losses that can slightly impact the overall efficiency of the system. Direct-drive motors, on the other hand, provide high efficiency and compact design but may have limitations in terms of torque and speed range. Stepper motors and servo motors, both types of gear motors, excel in precise positioning applications but may have slightly lower efficiency compared to direct-drive motors. The selection of the most suitable motor type depends on the specific requirements of the application, balancing power, efficiency, speed range, and control capabilities.

What are the different types of gears used in gear motors, and how do they impact performance?
Various types of gears are used in gear motors, each with its unique characteristics and impact on performance. The choice of gear type depends on the specific requirements of the application, including torque, speed, efficiency, noise level, and space constraints. Here’s a detailed explanation of the different types of gears used in gear motors and their impact on performance:
1. Spur Gears:
Spur gears are the most common type of gears used in gear motors. They have straight teeth that are parallel to the gear’s axis and mesh with another spur gear to transmit power. Spur gears provide high efficiency, reliable operation, and cost-effectiveness. However, they can generate significant noise due to the meshing of teeth, and they may produce axial thrust forces. Spur gears are suitable for applications that require high torque transmission and moderate to high rotational speeds.
2. Helical Gears:
Helical gears have angled teeth that are cut at an angle to the gear’s axis. This helical tooth configuration enables gradual engagement and smoother tooth contact, resulting in reduced noise and vibration compared to spur gears. Helical gears provide higher load-carrying capacity and are suitable for applications that require high torque transmission and moderate to high rotational speeds. They are commonly used in gear motors where low noise operation is desired, such as in automotive applications and industrial machinery.
3. Bevel Gears:
Bevel gears have teeth that are cut on a conical surface. They are used to transmit power between intersecting shafts, usually at right angles. Bevel gears can have straight teeth (straight bevel gears) or curved teeth (spiral bevel gears). These gears provide efficient power transmission and precise motion control in applications where shafts need to change direction. Bevel gears are commonly used in gear motors for applications such as steering systems, machine tools, and printing presses.
4. Worm Gears:
Worm gears consist of a worm (a type of screw) and a mating gear called a worm wheel or worm gear. The worm has a helical thread that meshes with the worm wheel, resulting in a compact and high gear reduction ratio. Worm gears provide high torque transmission, low noise operation, and self-locking properties, which prevent reverse motion. They are commonly used in gear motors for applications that require high gear reduction and locking capabilities, such as in lifting mechanisms, conveyor systems, and machine tools.
5. Planetary Gears:
Planetary gears, also known as epicyclic gears, consist of a central sun gear, multiple planet gears, and an outer ring gear. The planet gears mesh with both the sun gear and the ring gear, creating a compact and efficient gear system. Planetary gears offer high torque transmission, high gear reduction ratios, and excellent load distribution. They are commonly used in gear motors for applications that require high torque and compact size, such as in robotics, automotive transmissions, and industrial machinery.
6. Rack and Pinion:
Rack and pinion gears consist of a linear rack (a straight toothed bar) and a pinion gear (a spur gear with a small diameter). The pinion gear meshes with the rack to convert rotary motion into linear motion or vice versa. Rack and pinion gears provide precise linear motion control and are commonly used in gear motors for applications such as linear actuators, CNC machines, and steering systems.
The choice of gear type in a gear motor depends on factors such as the desired torque, speed, efficiency, noise level, and space constraints. Each type of gear offers specific advantages and impacts the performance of the gear motor differently. By selecting the appropriate gear type, gear motors can be optimized for their intended applications, ensuring efficient and reliable power transmission.


editor by CX 2024-04-09
China Standard 7ik750gn-Af 750W 110V 50Hz/60Hz Single Phase AC Induction Gear Motor manufacturer
Product Description
| PRODUCT DETAILS |
7IK750A-AF 750W 110V 50HZ/60HZ Single Phase AC Induction Motor
Our company focuses on the production of Micro, Compact and Large AC Geared Motors, Permanent Magnet Brushed DC Motors, Stepper Motors, Servo Motors, High-precision Planetary Reducers, Hypoids, Speed Controllers, Inverters, etc.; Products can be independently combined, matched, and diversified solutions according to your demands.
Our products are widely used in various industrial assembly lines, intelligent equipment, animal husbandry machinery, printing machinery, textile machinery, instrumentation, food machinery, power transmission and transformation equipment, gate machines, medical equipment, logistics equipment, security inspection facilities, financial equipment, New energy, industrial robots and other industries.
If you can not find suitable models on our shop, please feel free to send your detailed demands, we will suggest the most suitable models for you.
Motor Specifications
| Motor Type | Motor Model | Power | Voltage | Frequency | Current | Starting Torque |
Rated Torque | Rated Speed | Rated Time | Capacitor | |
| Motor with Round Shaft | Motor with Gear Shaft | W | V | Hz | A | N.m | N.m | RPM | min | μF/VAC | |
| Induction Motor | 7IK750A-AF | 7IK750GN-AF | 750 | 1PH110 | 50 | 9.7 | 8.57 | 5.04 | 1400 | Continuous | 80/250 |
| 60 | 9.7 | 7.16 | 4.21 | 1680 | Continuous | 80/250 | |||||
| 7IK750A-CF | 7IK750GN-CF | 750 | 1PH220 | 50 | 4.85 | 8.57 | 5.04 | 1400 | Continuous | 24/450 | |
| 60 | 4.85 | 7.16 | 4.21 | 1680 | Continuous | 24/450 | |||||
| 7IK750A-SF | 7IK750GN-SF | 750 | 3PH220 | 50 | 3.64 | 11.78 | 5.12 | 1400 | Continuous | / | |
| 60 | 3.64 | 9.8 | 4.26 | 1680 | Continuous | / | |||||
| 7IK750A-UF | 7IK750GN-UF | 750 | 3PH380 | 50 | 2.10 | 11.78 | 5.12 | 1400 | Continuous | / | |
| 60 | 2.10 | 9.8 | 4.26 | 1680 | Continuous | / | |||||
| Reversibal Motor | 7RK750A-AF | 7RK750GN-AF | 750 | 1PH110 | 50 | 9.7 | 8.57 | 5.04 | 1400 | 30 | 80/250 |
| 60 | 9.7 | 7.16 | 4.21 | 1680 | 30 | 80/250 | |||||
| 7RK750A-CF | 7RK750GN-CF | 750 | 1PH220 | 50 | 4.85 | 8.57 | 5.04 | 1400 | 30 | 24/450 | |
| 60 | 4.85 | 7.16 | 4.21 | 1680 | 30 | 24/450 | |||||
| Brake Motor | 7IK750A-AFM | 7IK750GN-AMF | 750 | 1PH110 | 50 | 9.7 | 8.57 | 5.04 | 1400 | 30 | 80/250 |
| 60 | 9.7 | 7.16 | 4.21 | 1680 | 30 | 80/250 | |||||
| 7IK750A-CFM | 7IK750GN-CMF | 750 | 1PH220 | 50 | 4.85 | 8.57 | 5.04 | 1400 | 30 | 24/450 | |
| 60 | 4.85 | 7.16 | 4.21 | 1680 | 30 | 24/450 | |||||
| 7IK750A-SFM | 7IK750GN-SFM | 750 | 3PH220 | 50 | 3.64 | 11.78 | 5.12 | 1400 | Continuous | / | |
| 60 | 3.64 | 9.8 | 4.26 | 1680 | Continuous | / | |||||
| 7IK750A-UFM | 7IK750GN-UFM | 750 | 3PH380 | 50 | 2.10 | 11.78 | 5.12 | 1400 | Continuous | / | |
| 60 | 2.10 | 9.8 | 4.26 | 1680 | Continuous | / | |||||
| Motor Type | Motor Model | Power | Voltage | Frequency | Speed Control Range | Starting Torque |
Rated Torque N.m |
Rated Time | Capacitor | ||
| Motor with Round Shaft | Motor with Gear Shaft | W | V | Hz | RPM | N.m | 90RPM | 1400RPM | min | μF/VAC | |
| Speed Control Motor | 7IK750RA-AF | 7IK750RGU-AF | 750 | 1PH110 | 50 | 90-1400 | 8.57 | 2.05 | 5.04 | Continuous | 80/250 |
| 60 | 90-1680 | 7.16 | 2.05 | 4.21 | Continuous | 80/250 | |||||
| 7IK750RA-CF | 7IK750RGU-CF | 750 | 1PH220 | 50 | 90-1400 | 7.57 | 2.05 | 5.04 | Continuous | 25/450 | |
| 60 | 90-1680 | 7.16 | 2.05 | 4.21 | Continuous |
25/450 |
|||||
Gearbox Ratio, Speed and Torque
Drawings
| OUR ADVANTAGES |
| ACCESSORIES |
| APPLICATION |
| OUR FACTORY |
Lunyee Industries Development Co., Ltd. is a leading manufacturer for factory automation (FA) products, we focus on power transmission and motion control solutions!
Our main production are power transmission products like AC and DC(brush/brushless) gear motor, stepper motor, high precision planetary gearbox (spur/helical gear) for stepping motor etc.
-WE FOCUS ON CUSTOMER SATISFACTION!
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industrial |
|---|---|
| Speed: | Constant Speed |
| Number of Stator: | Single-Phase |
| Function: | Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Open Type |
| Number of Poles: | 4 |
| Samples: |
US$ 116/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What are the maintenance requirements for gear motors, and how can longevity be maximized?
Gear motors, like any mechanical system, require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Proper maintenance practices help prevent failures, minimize downtime, and extend the lifespan of gear motors. Here are some maintenance requirements for gear motors and ways to maximize their longevity:
1. Lubrication:
Regular lubrication is essential for gear motors to reduce friction, wear, and heat generation. The gears, bearings, and other moving parts should be properly lubricated according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Lubricants should be selected based on the motor’s specifications and operating conditions. Regular inspection and replenishment of lubricants, as well as periodic oil or grease changes, should be performed to maintain optimal lubrication levels and ensure long-lasting performance.
2. Inspection and Cleaning:
Regular inspection and cleaning of gear motors are crucial for identifying any signs of wear, damage, or contamination. Inspecting the gears, bearings, shafts, and connections can help detect any abnormalities or misalignments. Cleaning the motor’s exterior and ventilation channels to remove dust, debris, or moisture buildup is also important in preventing malfunctions and maintaining proper cooling. Any loose or damaged components should be repaired or replaced promptly.
3. Temperature and Environmental Considerations:
Monitoring and controlling the temperature and environmental conditions surrounding gear motors can significantly impact their longevity. Excessive heat can degrade lubricants, damage insulation, and lead to premature component failure. Ensuring proper ventilation, heat dissipation, and avoiding overloading the motor can help manage temperature effectively. Similarly, protecting gear motors from moisture, dust, chemicals, and other environmental contaminants is vital to prevent corrosion and damage.
4. Load Monitoring and Optimization:
Monitoring and optimizing the load placed on gear motors can contribute to their longevity. Operating gear motors within their specified load and speed ranges helps prevent excessive stress, overheating, and premature wear. Avoiding sudden and frequent acceleration or deceleration, as well as preventing overloading or continuous operation near the motor’s maximum capacity, can extend its lifespan.
5. Alignment and Vibration Analysis:
Proper alignment of gear motor components, such as gears, couplings, and shafts, is crucial for smooth and efficient operation. Misalignment can lead to increased friction, noise, and premature wear. Regularly checking and adjusting alignment, as well as performing vibration analysis, can help identify any misalignment or excessive vibration that may indicate underlying issues. Addressing alignment and vibration problems promptly can prevent further damage and maximize the motor’s longevity.
6. Preventive Maintenance and Regular Inspections:
Implementing a preventive maintenance program is essential for gear motors. This includes establishing a schedule for routine inspections, lubrication, and cleaning, as well as conducting periodic performance tests and measurements. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance tasks, such as belt tension checks, bearing replacements, or gear inspections, can help identify and address potential issues before they escalate into major failures.
By adhering to these maintenance requirements and best practices, the longevity of gear motors can be maximized. Regular maintenance, proper lubrication, load optimization, temperature control, and timely repairs or replacements of worn components contribute to the reliable operation and extended lifespan of gear motors.

Can you explain the role of backlash in gear motors and how it’s managed in design?
Backlash plays a significant role in gear motors and is an important consideration in their design and operation. Backlash refers to the slight clearance or play between the teeth of gears in a gear system. It affects the precision, accuracy, and responsiveness of the gear motor. Here’s an explanation of the role of backlash in gear motors and how it is managed in design:
1. Role of Backlash:
Backlash in gear motors can have both positive and negative effects:
- Compensation for Misalignment: Backlash can help compensate for minor misalignments between gears, shafts, or the load. It allows a small amount of movement before engaging the next set of teeth, reducing the risk of damage due to misalignment. This can be particularly beneficial in applications where precise alignment is challenging or subject to variations.
- Negative Impact on Accuracy and Responsiveness: Backlash can introduce a delay or “dead zone” in the motion transmission. When changing the direction of rotation or reversing the load, the gear teeth must first overcome the clearance or play before engaging in the opposite direction. This delay can reduce the overall accuracy, responsiveness, and repeatability of the gear motor, especially in applications that require precise positioning or rapid changes in direction or speed.
2. Managing Backlash in Design:
Designers employ various techniques to manage and minimize backlash in gear motors:
- Tight Manufacturing Tolerances: Proper manufacturing techniques and tight tolerances can help minimize backlash. Precision machining and quality control during the production of gears and gear components ensure closer tolerances, reducing the amount of play between gear teeth.
- Preload or Pre-tensioning: Applying a preload or pre-tensioning force to the gear system can help reduce backlash. This technique involves introducing an initial force or tension that eliminates the clearance between gear teeth. It ensures immediate contact and engagement of the gear teeth, minimizing the dead zone and improving the overall responsiveness and accuracy of the gear motor.
- Anti-Backlash Gears: Anti-backlash gears are designed specifically to minimize or eliminate backlash. They typically feature modifications to the gear tooth profile, such as modified tooth shapes or special tooth arrangements, to reduce clearance. Anti-backlash gears can be used in gear motor designs to improve precision and minimize the effects of backlash.
- Backlash Compensation: In some cases, backlash compensation techniques can be employed. These techniques involve monitoring the position or movement of the load and applying control algorithms to compensate for the backlash. By accounting for the clearance and adjusting the control signals accordingly, the effects of backlash can be mitigated, improving accuracy and responsiveness.
3. Application-Specific Considerations:
The management of backlash in gear motors should be tailored to the specific application requirements:
- Positioning Accuracy: Applications that require precise positioning, such as robotics or CNC machines, may require tighter backlash control to ensure accurate and repeatable movements.
- Dynamic Response: Applications that involve rapid changes in direction or speed, such as high-speed automation or servo control systems, may require reduced backlash to maintain responsiveness and minimize overshoot or lag.
- Load Characteristics: The nature of the load and its impact on the gear system should be considered. Heavy loads or applications with significant inertial forces may require additional backlash management techniques to maintain stability and accuracy.
In summary, backlash in gear motors can affect precision, accuracy, and responsiveness. While it can compensate for misalignments, backlash may introduce delays and reduce the overall performance of the gear motor. Designers manage backlash through tight manufacturing tolerances, preload techniques, anti-backlash gears, and backlash compensation methods. The management of backlash depends on the specific application requirements, considering factors such as positioning accuracy, dynamic response, and load characteristics.

Can you explain the advantages of using gear motors in various mechanical systems?
Gear motors offer several advantages when utilized in various mechanical systems. Their unique characteristics make them well-suited for applications that require controlled power transmission, precise speed control, and torque amplification. Here’s a detailed explanation of the advantages of using gear motors:
1. Torque Amplification:
One of the key advantages of gear motors is their ability to amplify torque. By using different gear ratios, gear motors can increase or decrease the output torque from the motor. This torque amplification is crucial in applications that require high torque output, such as lifting heavy loads or operating machinery with high resistance. Gear motors allow for efficient power transmission, enabling the system to handle demanding tasks effectively.
2. Speed Control:
Gear motors provide precise speed control, allowing for accurate and controlled movement in mechanical systems. By selecting the appropriate gear ratio, the rotational speed of the output shaft can be adjusted to match the requirements of the application. This speed control capability ensures that the mechanical system operates at the desired speed, whether it needs to be fast or slow. Gear motors are commonly used in applications such as conveyors, robotics, and automated machinery, where precise speed control is essential.
3. Directional Control:
Another advantage of gear motors is their ability to control the rotational direction of the output shaft. By using different types of gears, such as spur gears, bevel gears, or worm gears, the direction of rotation can be easily changed. This directional control is beneficial in applications that require bidirectional movement, such as in actuators, robotic arms, and conveyors. Gear motors offer reliable and efficient directional control, contributing to the versatility and functionality of mechanical systems.
4. Efficiency and Power Transmission:
Gear motors are known for their high efficiency in power transmission. The gear system helps distribute the load across multiple gears, reducing the strain on individual components and minimizing power losses. This efficient power transmission ensures that the mechanical system operates with optimal energy utilization and minimizes wasted power. Gear motors are designed to provide reliable and consistent power transmission, resulting in improved overall system efficiency.
5. Compact and Space-Saving Design:
Gear motors are compact in size and offer a space-saving solution for mechanical systems. By integrating the motor and gear system into a single unit, gear motors eliminate the need for additional components and reduce the overall footprint of the system. This compact design is especially beneficial in applications with limited space constraints, allowing for more efficient use of available space while still delivering the necessary power and functionality.
6. Durability and Reliability:
Gear motors are designed to be robust and durable, capable of withstanding demanding operating conditions. The gear system helps distribute the load, reducing the stress on individual gears and increasing overall durability. Additionally, gear motors are often constructed with high-quality materials and undergo rigorous testing to ensure reliability and longevity. This makes gear motors well-suited for continuous operation in industrial and commercial applications, where reliability is crucial.
By leveraging the advantages of torque amplification, speed control, directional control, efficiency, compact design, durability, and reliability, gear motors provide a reliable and efficient solution for various mechanical systems. They are widely used in industries such as robotics, automation, manufacturing, automotive, and many others, where precise and controlled mechanical power transmission is essential.


editor by CX 2024-04-02
China Standard Long Life CE Tyj49 AC Gear Synchronous Motor for Microwave Oven/Fan with high quality
Product Description
Long life Ce Tyj49 AC Gear Synchronous Motor for Microwave Oven/Fan
Specifications:
-Output Speed: 1.04-75RPM
-Voltage: 24-220VAC
-Current: 0.571-0.2A
-Frequency: 50/60Hz
-Input Power: 2.5-7W
-Noise: <45dB
-Rotation: CW/CCW Bi-directional
Drawing:
Specification:
| Model | Output speed (rpm) | Output Torque (kg.cm / lb.in) | Voltage (V.AC) | Current (A) | Frequency (Hz) | Input Power (W) | Noise (dB) | Rotation | ||
| S1 continuous | S2 15 minutes | S2 5 minutes | ||||||||
| S493-45-1.0 | 1.04 | 45 / 39 | 60 / 52.2 | 70 / 60.9 | 24 ********* 110 ********* 220 | <0.2 ********** <0.05 ********* <0.571 |
50/60Hz | 2.5~7 | <45 | CW / CCW / Bi-directional |
| S493-30-1.5 | 1.50 | 30 / 26 | 40 / 34.8 | 46 / 40 | ||||||
| S493-22-2.0 | 2 | 22 / 19 | 30 / 26 | 35 / 30.5 | ||||||
| S493-18-2.5 | 2.5 | 18 / 15.7 | 24 / 20.9 | 28 / 24.4 | ||||||
| S493-11-4.0 | 4 | 11 / 9.6 | 15 / 13 | 17.5 / 15.2 | ||||||
| S493-09-4.8 | 4.8 | 9.4 / 8.2 | 12.5 / 10.9 | 14.5 / 12.6 | ||||||
| S493-09-5.0 | 5 | 9 / 7.8 | 12 / 10.4 | 14 / 12.2 | ||||||
| S493-08-5.8 | 5.8 | 7.6 / 6.6 | 10 / 8.7 | 12 / 10.4 | ||||||
| S493-05-9.0 | 9 | 5 / 4.35 | 6.5 / 5.7 | 7.8 / 6.8 | ||||||
| S493-03-15 | 15 | 3 / 2.6 | 4 / 3.5 | 4.6 / 4 | ||||||
| S493-02-25 | 25 | 1.8 / 1.57 | 2.4 / 2.1 | 2.8 / 2.43 | ||||||
| S493-02-30 | 30 | 1.5 / 1.3 | 2 / 1.74 | 2.3 / 2 | ||||||
| S493-01-45 | 45 | 1 / 0.87 | 1.3 / 1.13 | 1.5 / 1.3 | ||||||
| S493-01-60 | 60 | 0.75 | 1 / 0.87 | 1.2 / 1.04 | ||||||
| S493-01-75 | 75 | 0.6 | 0.8 / 0.7 | 1.0 / 0.87 | ||||||
| Note: Above datas are from motors under 50Hz. If under 60Hz, Speed*1.2 , Torque/1.2 Other speed and torque needed, please contact our sale department | ||||||||||
About Us:
I.CH concentrates on designing the latest technology motors and meet our customer’s requirements, we have the very capable R&D team to ensure products quality and provide all the customers with the best solution, the products like AC Synchronous Motor, Geared Motor, Reversible Synchronous Motor, which uses in household appliance, Auto Control Machine, etc.
Certificate:
Package:
-Rigidly wrap the goods;
-Shipping way: Sea, air or train;
-Lead time: 15 – 40 working days.
Related Products:
FAQ:
Q: What lowest speed can you make?
A: 1 rpm to 2rpm…
Q: What application of your AC reversible synchronous motor?
A: household appliances, Auto Control Machine, etc.
Q: If I place an order, how long will you ship out the goods?
A: For the sample order, it takes approximately 2 weeks; for the batch order, the lead time will be around 40 days.
Q: Do you provide OEM services?
A: Yes, we can provide OEM services for volume production. Feel free to talk to us about your branding needs. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Size: | 49mm |
|---|---|
| Voltage: | 24-220VAC |
| Current: | 0.023-0.2A |
| Frequency: | 50/60Hz |
| Input Power: | 2.5-7W |
| Noise: | 45dB |
| Samples: |
US$ 15/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Are there innovations or emerging technologies in the field of gear motor design?
Yes, there are several innovations and emerging technologies in the field of gear motor design. These advancements aim to improve the performance, efficiency, compactness, and reliability of gear motors. Here are some notable innovations and emerging technologies in gear motor design:
1. Miniaturization and Compact Design:
Advancements in manufacturing techniques and materials have enabled the miniaturization of gear motors without compromising their performance. Gear motors with compact designs are highly sought after in applications where space is limited, such as robotics, medical devices, and consumer electronics. Innovative approaches like micro-gear motors and integrated motor-gear units are being developed to achieve smaller form factors while maintaining high torque and efficiency.
2. High-Efficiency Gearing:
New gear designs focus on improving efficiency by reducing friction and mechanical losses. Advanced gear manufacturing techniques, such as precision machining and 3D printing, allow for the creation of intricate gear tooth profiles that optimize power transmission and minimize losses. Additionally, the use of high-performance materials, coatings, and lubricants helps reduce friction and wear, improving overall gear motor efficiency.
3. Magnetic Gearing:
Magnetic gearing is an emerging technology that replaces traditional mechanical gears with magnetic fields to transmit torque. It utilizes the interaction of permanent magnets to transfer power, eliminating the need for physical gear meshing. Magnetic gearing offers advantages such as high efficiency, low noise, compactness, and maintenance-free operation. While still being developed and refined, magnetic gearing holds promise for various applications, including gear motors.
4. Integrated Electronics and Controls:
Gear motor designs are incorporating integrated electronics and controls to enhance performance and functionality. Integrated motor drives and controllers simplify system integration, reduce wiring complexity, and allow for advanced control features. These integrated solutions offer precise speed and torque control, intelligent feedback mechanisms, and connectivity options for seamless integration into automation systems and IoT (Internet of Things) platforms.
5. Smart and Condition Monitoring Capabilities:
New gear motor designs incorporate smart features and condition monitoring capabilities to enable predictive maintenance and optimize performance. Integrated sensors and monitoring systems can detect abnormal operating conditions, track performance parameters, and provide real-time feedback for proactive maintenance and troubleshooting. This helps prevent unexpected failures, extend the lifespan of gear motors, and improve overall system reliability.
6. Energy-Efficient Motor Technologies:
Gear motor design is influenced by advancements in energy-efficient motor technologies. Brushless DC (BLDC) motors and synchronous reluctance motors (SynRM) are gaining popularity due to their higher efficiency, better power density, and improved controllability compared to traditional brushed DC and induction motors. These motor technologies, when combined with optimized gear designs, contribute to overall system energy savings and performance improvements.
These are just a few examples of the innovations and emerging technologies in gear motor design. The field is continuously evolving, driven by the need for more efficient, compact, and reliable motion control solutions in various industries. Gear motor manufacturers and researchers are actively exploring new materials, manufacturing techniques, control strategies, and system integration approaches to meet the evolving demands of modern applications.

Are there environmental benefits to using gear motors in certain applications?
Yes, there are several environmental benefits associated with the use of gear motors in certain applications. Gear motors offer advantages that can contribute to increased energy efficiency, reduced resource consumption, and lower environmental impact. Here’s a detailed explanation of the environmental benefits of using gear motors:
1. Energy Efficiency:
Gear motors can improve energy efficiency in various ways:
- Torque Conversion: Gear reduction allows gear motors to deliver higher torque output while operating at lower speeds. This enables the motor to perform tasks that require high torque, such as lifting heavy loads or driving machinery with high inertia, more efficiently. By matching the motor’s power characteristics to the load requirements, gear motors can operate closer to their peak efficiency, minimizing energy waste.
- Controlled Speed: Gear reduction provides finer control over the motor’s rotational speed. This allows for more precise speed regulation, reducing the likelihood of energy overconsumption and optimizing energy usage.
2. Reduced Resource Consumption:
The use of gear motors can lead to reduced resource consumption and environmental impact:
- Smaller Motor Size: Gear reduction allows gear motors to deliver higher torque with smaller, more compact motors. This reduction in motor size translates to reduced material and resource requirements during manufacturing. It also enables the use of smaller and lighter equipment, which can contribute to energy savings during operation and transportation.
- Extended Motor Lifespan: The gear mechanism in gear motors helps reduce the load and stress on the motor itself. By distributing the load more evenly, gear motors can help extend the lifespan of the motor, reducing the need for frequent replacements and the associated resource consumption.
3. Noise Reduction:
Gear motors can contribute to a quieter and more environmentally friendly working environment:
- Noise Dampening: Gear reduction can help reduce the noise generated by the motor. The gear mechanism acts as a noise dampener, absorbing and dispersing vibrations and reducing overall noise emission. This is particularly beneficial in applications where noise reduction is important, such as residential areas, offices, or noise-sensitive environments.
4. Precision and Control:
Gear motors offer enhanced precision and control, which can lead to environmental benefits:
- Precise Positioning: Gear motors, especially stepper motors and servo motors, provide precise positioning capabilities. This accuracy allows for more efficient use of resources, minimizing waste and optimizing the performance of machinery or systems.
- Optimized Control: Gear motors enable precise control over speed, torque, and movement. This control allows for better optimization of processes, reducing energy consumption and minimizing unnecessary wear and tear on equipment.
In summary, using gear motors in certain applications can have significant environmental benefits. Gear motors offer improved energy efficiency, reduced resource consumption, noise reduction, and enhanced precision and control. These advantages contribute to lower energy consumption, reduced environmental impact, and a more sustainable approach to power transmission and control. When selecting motor systems for specific applications, considering the environmental benefits of gear motors can help promote energy efficiency and sustainability.

Are there specific considerations for selecting the right gear motor for a particular application?
When selecting a gear motor for a specific application, several considerations need to be taken into account. The choice of the right gear motor is crucial to ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and reliability. Here’s a detailed explanation of the specific considerations for selecting the right gear motor for a particular application:
1. Torque Requirement:
The torque requirement of the application is a critical factor in gear motor selection. Determine the maximum torque that the gear motor needs to deliver to perform the required tasks. Consider both the starting torque (the torque required to initiate motion) and the operating torque (the torque required to sustain motion). Select a gear motor that can provide adequate torque to handle the load requirements of the application. It’s important to account for any potential torque spikes or variations during operation.
2. Speed Requirement:
Consider the desired speed range or specific speed requirements of the application. Determine the rotational speed (in RPM) that the gear motor needs to achieve to meet the application’s performance criteria. Select a gear motor with a suitable gear ratio that can achieve the desired speed at the output shaft. Ensure that the gear motor can maintain the required speed consistently and accurately throughout the operation.
3. Duty Cycle:
Evaluate the duty cycle of the application, which refers to the ratio of operating time to rest or idle time. Consider whether the application requires continuous operation or intermittent operation. Determine the duty cycle’s impact on the gear motor, including factors such as heat generation, cooling requirements, and potential wear and tear. Select a gear motor that is designed to handle the expected duty cycle and ensure long-term reliability and durability.
4. Environmental Factors:
Take into account the environmental conditions in which the gear motor will operate. Consider factors such as temperature extremes, humidity, dust, vibrations, and exposure to chemicals or corrosive substances. Choose a gear motor that is specifically designed to withstand and perform optimally under the anticipated environmental conditions. This may involve selecting gear motors with appropriate sealing, protective coatings, or materials that can resist corrosion and withstand harsh environments.
5. Efficiency and Power Requirements:
Consider the desired efficiency and power consumption of the gear motor. Evaluate the power supply available for the application and select a gear motor that operates within the specified voltage and current ranges. Assess the gear motor’s efficiency to ensure that it maximizes power transmission and minimizes wasted energy. Choosing an efficient gear motor can contribute to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
6. Physical Constraints:
Assess the physical constraints of the application, including space limitations, mounting options, and integration requirements. Consider the size, dimensions, and weight of the gear motor to ensure it can be accommodated within the available space. Evaluate the mounting options and compatibility with the application’s mechanical structure. Additionally, consider any specific integration requirements, such as shaft dimensions, connectors, or interfaces that need to align with the application’s design.
7. Noise and Vibration:
Depending on the application, noise and vibration levels may be critical factors. Evaluate the acceptable noise and vibration levels for the application’s environment and operation. Choose a gear motor that is designed to minimize noise and vibration, such as those with helical gears or precision engineering. This is particularly important in applications that require quiet operation or where excessive noise and vibration may cause issues or discomfort.
By considering these specific factors when selecting a gear motor for a particular application, you can ensure that the chosen gear motor meets the performance requirements, operates efficiently, and provides reliable and consistent power transmission. It’s important to consult with gear motor manufacturers or experts to determine the most suitable gear motor based on the specific application’s needs.


editor by CX 2024-03-28
China Standard Three Phase 220V 380V 0.1-0.2-0.4-0.75-1.5-2.2kw AC Helical Gear Motor vacuum pump for ac
Product Description
Product Description
MAIN FEATURES:
1) Made of high quality material, non-rusting;Both flange and foot mounting available and suitable for all-round installation
2) Large output torque and high radiating efficiency
3)Precise grinding helical gear with Smooth running and low noise, no deformation,can work long time in dreadful condition
4)Nice appearance, durable service life and small volume, compact structure
5)Both 2 and 3 stage available with wide ratio range from 5 to 200
6)Different output shaft diameter available -40-50mm
7)Modular construction enlarge ratio from 5 to 1400
MAIN MATERIALS:
1)housing with aluminium alloyand cast iron material;
2)Output Shaft Material:20CrMnTi
3)Good quality no noise bearings to keep long service life
4)High performance oil seal to prevent from oil leakage
APPLICATIONS:
G3 Series helical gear motor are wide used for all kinds of automatic equipment, such as chip removal machine, conveyor, packaging equipment, woodworking machinery, farming equipment, slurry scraper ,dryer, mixer and so on.
Detailed Photos
Product Parameters
| (n1=1400r/min 50hz) | |||||||||||||||||
| norminal ratio | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 100 | 120 | 160 | 200 | ||
| 0.1kw | output shaft | Ø18 | Ø22 | ||||||||||||||
| n2* (r/min) | 282 | 138 | 92 | 70 | 56 | 46 | 35 | 28 | 23 | 18 | 14 | – | 11 | 9 | 7 | ||
| M2(Nm) | 50hz | 3.2 | 6.5 | 9.8 | 12.9 | 16.1 | 19.6 | 25.7 | 31.1 | 37.5 | 49.5 | 62.9 | – | 76.1 | 100.7 | 125.4 | |
| 60hz | 3 | 5 | 8 | 11 | 13 | 17 | 21 | 26 | 31 | 41 | 52 | – | 63 | 84 | 105 | ||
| Fr1(N) | 588 | 882 | 980 | 1180 | 1270 | 1370 | 1470 | 1570 | 2160 | 2450 | 2450 | 2450 | 2450 | 2450 | 2450 | ||
| Fr2(N) | 176 | ||||||||||||||||
| norminal ratio | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 100 | 120 | 160 | 200 | ||
| 0.2kw | output shaft | Ø18 | Ø22 | Ø28 | |||||||||||||
| n2* (r/min) | 282 | 138 | 92 | 70 | 56 | 45 | 35 | 29 | 23 | 18 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 8 | 7 | ||
| M2(Nm) | 50hz | 6.5 | 12.6 | 19.1 | 26.3 | 32.6 | 38.9 | 50.4 | 63 | 75.6 | 100.8 | 103.9 | 125.4 | 150 | 200.4 | 250.7 | |
| 60hz | 5.4 | 10.5 | 16.6 | 21.9 | 27.1 | 32.4 | 42 | 52.5 | 63 | 84 | 86.6 | 104.5 | 125 | 167 | 208.9 | ||
| Fr1(N) | 588 | 882 | 980 | 1180 | 1270 | 1760 | 1860 | 1960 | 2160 | 2450 | 2450 | 2840 | 3330 | 3430 | 3430 | ||
| Fr2(N) | 196 | ||||||||||||||||
| norminal ratio | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 100 | 120 | 160 | 200 | ||
| 0.4kw | output shaft | Ø22 | Ø28 | Ø32 | |||||||||||||
| n2* (r/min) | 288 | 144 | 92 | 72 | 58 | 47 | 36 | 29 | 24 | 18 | 14 | 14 | 12 | 9 | 7 | ||
| M2(Nm) | 50hz | 12.9 | 25 | 38.6 | 51.4 | 65.4 | 78.2 | 100.7 | 125.4 | 150 | 200.4 | 206.8 | 250.7 | 301.1 | 400.7 | 461.8 | |
| 60hz | 10.7 | 20.8 | 32.1 | 42.9 | 54.5 | 65.2 | 83.9 | 104.5 | 125 | 167 | 172.3 | 208.9 | 250.9 | 333.9 | 384.8 | ||
| Fr1(N) | 882 | 1180 | 1370 | 1470 | 1670 | 2550 | 2840 | 3140 | 3430 | 3430 | 3430 | 4900 | 5880 | 5880 | 5880 | ||
| Fr2(N) | 245 | ||||||||||||||||
| norminal ratio | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 100 | 120 | 160 | 200 | ||
| 0.75kw | output shaft | Ø28 | Ø32 | Ø40 | |||||||||||||
| n2* (r/min) | 278 | 140 | 94 | 69 | 58 | 46 | 35 | 29 | 24 | 18 | 14 | 14 | 11 | 9 | 7 | ||
| M2(Nm) | 50hz | 24.6 | 48.2 | 72.9 | 97.5 | 122.1 | 145.7 | 187.5 | 235.7 | 282.9 | 376.1 | 387.9 | 439 | 527 | 703 | 764 | |
| 60hz | 20.5 | 40.2 | 60.7 | 81.3 | 201.8 | 121.4 | 156.3 | 196.4 | 235.7 | 313.4 | 323.2 | 366 | 439 | 585 | 732 | ||
| Fr1(N) | 1270 | 1760 | 2160 | 2350 | 2450 | 4571 | 4210 | 4610 | 5490 | 5880 | 5880 | 7060 | 7060 | 7060 | 7060 | ||
| Fr2(N) | 294 | ||||||||||||||||
| norminal ratio | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 100 | 120 | 160 | 200 | ||
| 1.5kw | output shaft | Ø32 | Ø40 | Ø50 | |||||||||||||
| n2* (r/min) | 280 | 140 | 93 | 70 | 55 | 47 | 34 | 27 | 24 | 17 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 8 | 7 | ||
| M2(Nm) | 50hz | 48.2 | 97.5 | 145.7 | 193.9 | 242.1 | 272 | 351 | 439 | 527 | 703 | 724 | 878 | 1060 | 1230 | 1230 | |
| 60hz | 40.2 | 81.3 | 121.4 | 161.6 | 201.8 | 226 | 293 | 366 | 439 | 585 | 603 | 732 | 878 | 1170 | 1230 | ||
| Fr1(N) | 1760 | 2450 | 2840 | 3230 | 3820 | 5100 | 5880 | 7060 | 7060 | 7060 | 7060 | 9800 | 9800 | 9800 | 9800 | ||
| Fr2(N) | 343 | ||||||||||||||||
| norminal ratio | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 80 | 100 | ||||||
| 2.2kw | output shaft | Ø40 | Ø50 | ||||||||||||||
| n2* (r/min) | 272 | 136 | 95 | 68 | 54 | 45 | 36 | 28 | 24 | 18 | 14 | ||||||
| M2(Nm) | 50hz | 67 | 133 | 200 | 266 | 332 | 399 | 515 | 644 | 773 | 1571 | 1230 | |||||
| 60hz | 56 | 111 | 167 | 221 | 277 | 332 | 429 | 537 | 644 | 858 | 1080 | ||||||
| Fr1(N) | 2160 | 3140 | 3530 | 4571 | 4700 | 6960 | 7250 | 8620 | 9800 | 9800 | 9800 | ||||||
| Fr2(N) | 392 | ||||||||||||||||
Outline and mounting dimension:
| G3FM: THREE PHASE GEAR MOTOR WITH FLANGE (n1=1400r/min) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Power kw | output shaft | ratio | A | F | I | J | M | O | O1 | P | Q | R | S | T | U | W | X | Y | Y1 | |
| standard | brake | |||||||||||||||||||
| 0.1kw | Ø18 | 5–30-40-50 | 236 | 270 | 192.5 | 11 | 16.5 | 170 | 4 | 10 | 30 | 145 | 35 | 18 | 20.5 | 129 | 6 | 157 | 80 | 81 |
| Ø22 | -160-200 | 262 | 296 | 197.5 | 11 | 19 | 185 | 4 | 12 | 40 | 148 | 47 | 22 | 24.5 | 129 | 6 | 171.5 | 89.5 | 83.5 | |
| 0.2kw | Ø18 | 5- | 267 | 270 | 192.5 | 11 | 16.5 | 170 | 4 | 10 | 30 | 145 | 35 | 18 | 20.5 | 129 | 6 | 161 | 80 | 81 |
| Ø22 | -80-100 | 293 | 296 | 197.5 | 11 | 19 | 185 | 4 | 12 | 40 | 148 | 47 | 22 | 24.5 | 129 | 6 | 171.5 | 89.5 | 83.5 | |
| Ø28 | 306 | 309.5 | 208.5 | 11 | 23.5 | 215 | 4 | 15 | 45 | 170 | 50 | 28 | 31 | 129 | 8 | 198.5 | 105.5 | 88 | ||
| 0.4kw | Ø22 | 5- | 314 | 324.5 | 204 | 11 | 19 | 185 | 4 | 12 | 40 | 148 | 47 | 22 | 24.5 | 139 | 6 | 171.5 | 89.5 | 88.5 |
| Ø28 | -80-100 | 330 | 337.5 | 215 | 11 | 23.5 | 215 | 4 | 15 | 45 | 170 | 50 | 28 | 31 | 139 | 8 | 198.5 | 105.5 | 93 | |
| Ø32 | 349 | 357 | 229.5 | 13 | 28.5 | 250 | 4 | 15 | 55 | 180 | 60 | 32 | 35 | 139 | 10 | 234 | 126 | 98 | ||
| 0.75kw | Ø28 | 5- | 350.5 | 343.5 | 227.5 | 11 | 23.5 | 215 | 4 | 15 | 45 | 170 | 50 | 28 | 31 | 159 | 8 | 198.5 | 105.5 | 103 |
| Ø32 | -80-100 | 379.5 | 387 | 242 | 13 | 28.5 | 250 | 4 | 15 | 55 | 180 | 60 | 32 | 35 | 159 | 10 | 234 | 126 | 108 | |
| Ø40 | 401.5 | 408.5 | 270 | 18 | 34 | 310 | 5 | 18 | 65 | 230 | 71 | 40 | 43 | 185 | 12 | 284 | 149 | 126.5 | ||
| 1.5kw | Ø32 | 5- | 420.5 | 441 | 254 | 13 | 28.5 | 250 | 5 | 15 | 55 | 180 | 60 | 32 | 35 | 185 | 10 | 234 | 126 | 121 |
| Ø40 | -80-100 | 457.5 | 478 | 270 | 18 | 34 | 310 | 5 | 18 | 65 | 230 | 71 | 40 | 43 | 185 | 12 | 284 | 149 | 126.5 | |
| Ø50 | 485.5 | 506 | 300 | 22 | 40 | 360 | 5 | 25 | 75 | 270 | 83 | 50 | 53.5 | 185 | 14 | 325 | 173.5 | 132.5 | ||
| 2.2kw | Ø40 | 5- | 466.5 | 487 | 270 | 18 | 34 | 310 | 5 | 18 | 65 | 230 | 71 | 40 | 43 | 185 | 12 | 284 | 149 | 126.5 |
| Ø50 | -80-100 | 510.5 | 531 | 300 | 22 | 40 | 360 | 5 | 25 | 75 | 270 | 83 | 50 | 53.5 | 185 | 14 | 325 | 173.5 | 132.5 | |
| G3LM: THREE PHASE GEAR MOTOR WITH FOOT (n1=1400r/min) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Power kw | output shaft | ratio | A | D | E | F | J | G | H | K | P | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Y1 | |
| standard | brake | |||||||||||||||||||
| 0.1kw | Ø18 | 5–30-40-50 | 236 | 270 | 40 | 110 | 135 | 16.5 | 65 | 9 | 45 | 30 | 18 | 20.5 | 129 | 183 | 6 | 133 | 85 | 10 |
| Ø22 | -160-200 | 262 | 296 | 65 | 130 | 155 | 19 | 90 | 11 | 55 | 40 | 22 | 24.5 | 129 | 193 | 6 | 139.5 | 90 | 12 | |
| 0.2kw | Ø18 | 5- | 267 | 270 | 40 | 110 | 135 | 16.5 | 65 | 9 | 45 | 30 | 18 | 20.5 | 129 | 183 | 6 | 133 | 85 | 10 |
| Ø22 | -80-100 | 293 | 296 | 65 | 130 | 155 | 19 | 90 | 11 | 55 | 40 | 22 | 24.5 | 129 | 193 | 6 | 139.5 | 90 | 12 | |
| Ø28 | 306 | 309.5 | 90 | 140 | 175 | 23.5 | 125 | 11 | 65 | 45 | 28 | 31 | 129 | 203 | 8 | 170 | 110 | 15 | ||
| 0.4kw | Ø22 | 5- | 314 | 324.5 | 65 | 130 | 155 | 19 | 90 | 11 | 55 | 40 | 22 | 24.5 | 139 | 199.5 | 6 | 141.5 | 90 | 12 |
| Ø28 | -80-100 | 330 | 337.5 | 90 | 140 | 175 | 23.5 | 125 | 11 | 65 | 45 | 28 | 31 | 139 | 210 | 8 | 170 | 110 | 15 | |
| Ø32 | 349 | 357 | 130 | 170 | 208 | 28.5 | 170 | 13 | 70 | 55 | 32 | 35 | 139 | 226 | 10 | 198 | 130 | 18 | ||
| 0.75kw | Ø28 | 5- | 350.5 | 343.5 | 90 | 140 | 175 | 23.5 | 125 | 11 | 65 | 45 | 28 | 31 | 159 | 222 | 8 | 170 | 110 | 15 |
| Ø32 | -80-100 | 379.5 | 387 | 130 | 170 | 208 | 28.5 | 170 | 13 | 70 | 55 | 32 | 35 | 159 | 238.5 | 10 | 198 | 130 | 18 | |
| Ø40 | 401.5 | 408.5 | 150 | 210 | 254 | 34 | 196 | 15 | 90 | 65 | 40 | 43 | 185 | 249 | 12 | 230 | 150 | 20 | ||
| 1.5kw | Ø32 | 5- | 420.5 | 441 | 130 | 170 | 208 | 28.5 | 170 | 13 | 70 | 55 | 32 | 35 | 185 | 250.5 | 10 | 198 | 130 | 18 |
| Ø40 | -80-100 | 457.5 | 478 | 150 | 210 | 254 | 34 | 196 | 15 | 90 | 65 | 40 | 43 | 185 | 260 | 12 | 230 | 150 | 20 | |
| Ø50 | 485.5 | 506 | 160 | 230 | 290 | 40 | 210 | 18 | 100 | 75 | 50 | 53.5 | 185 | 288 | 14 | 265 | 170 | 25 | ||
| 2.2kw | Ø40 | 5- | 466.5 | 487 | 150 | 210 | 254 | 34 | 196 | 15 | 90 | 65 | 40 | 43 | 185 | 260 | 12 | 230 | 150 | 20 |
| Ø50 | -80-100 | 510.5 | 531 | 160 | 230 | 290 | 40 | 210 | 18 | 100 | 75 | 50 | 53.5 | 185 | 288 | 14 | 265 | 170 | 25 | |
| G3FS: IEC GEAR REDUCER WITH FOOT (n1=1400r/min) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Power kw | output shaft | ratio | A | B | C | F | I | J | L | M | N | O | O1 | P | Q | R | S | S1 | T | T1 | W | W1 | X | Y | Y1 |
| 0.12kw | Ø18 | 5–30-40-50 | 147 | 95 | 115 | 154 | 11 | 16.5 | 4.5 | 170 | 140 | 4 | 10 | 30 | 145 | 35 | 18 | 11 | 20.5 | 12.8 | 6 | 4 | 163 | 80 | 86.5 |
| Ø22 | -160-200 | 173 | 95 | 115 | 164 | 11 | 19 | 4.5 | 185 | 140 | 4 | 12 | 40 | 148 | 47 | 22 | 11 | 24.5 | 12.8 | 6 | 4 | 171.5 | 89.5 | 89 | |
| 0.18kw | Ø18 | 5- | 147 | 95 | 115 | 154 | 11 | 16.5 | 4.5 | 170 | 140 | 4 | 10 | 30 | 145 | 35 | 18 | 11 | 20.5 | 12.8 | 6 | 4 | 163 | 80 | 86.5 |
| Ø22 | -80-100 | 173 | 95 | 115 | 164 | 11 | 19 | 4.5 | 185 | 140 | 4 | 12 | 40 | 148 | 47 | 22 | 11 | 24.5 | 12.8 | 6 | 4 | 171.5 | 89.5 | 89 | |
| Ø28 | 186.5 | 95 | 115 | 186 | 11 | 23.5 | 4.5 | 215 | 140 | 4 | 15 | 45 | 170 | 50 | 28 | 11 | 31 | 12.8 | 8 | 4 | 198.5 | 105.5 | 93.5 | ||
| 0.37kw | Ø22 | 5- | 181.5 | 110 | 130 | 164 | 11 | 19 | 4.5 | 185 | 160 | 4 | 12 | 40 | 148 | 47 | 22 | 14 | 24.5 | 16.3 | 6 | 5 | 201 | 89.5 | 99 |
| Ø28 | -80-100 | 198 | 110 | 130 | 186 | 11 | 23.5 | 4.5 | 215 | 160 | 4 | 15 | 45 | 170 | 50 | 28 | 14 | 31 | 16.3 | 8 | 5 | 198.5 | 105.5 | 103.5 | |
| Ø32 | 216.5 | 110 | 130 | 215 | 13 | 28.5 | 4.5 | 250 | 160 | 4 | 15 | 55 | 180 | 60 | 32 | 14 | 35 | 16.3 | 10 | 5 | 234 | 126 | 108.5 | ||
| 0.75kw | Ø28 | 5- | 206.5 | 130 | 165 | 185 | 11 | 23.5 | 4.5 | 215 | 200 | 4 | 15 | 45 | 170 | 50 | 28 | 19 | 31 | 21.8 | 8 | 6 | 216.5 | 105.5 | 123.5 |
| Ø32 | -80-100 | 235 | 130 | 165 | 215 | 13 | 28.5 | 4.5 | 250 | 200 | 4 | 15 | 55 | 180 | 60 | 32 | 19 | 35 | 21.8 | 10 | 6 | 236.5 | 126 | 128.5 | |
| Ø40 | 260.5 | 130 | 165 | 270 | 18 | 34 | 4.5 | 310 | 200 | 5 | 18 | 65 | 230 | 71 | 40 | 19 | 43 | 21.8 | 12 | 8 | 284 | 149 | 134 | ||
| 1.5kw | Ø32 | 5- | 252 | 130 | 165 | 215 | 13 | 28.5 | 4.5 | 250 | 200 | 5 | 15 | 55 | 180 | 60 | 32 | 24 | 35 | 27.3 | 10 | 8 | 236.5 | 126 | 128.5 |
| Ø40 | -80-100 | 293.5 | 130 | 165 | 270 | 18 | 34 | 4.5 | 310 | 200 | 5 | 18 | 65 | 230 | 71 | 40 | 24 | 43 | 27.3 | 12 | 8 | 284 | 149 | 134 | |
| Ø50 | 321.5 | 130 | 165 | 300 | 22 | 40 | 4.5 | 360 | 200 | 5 | 25 | 75 | 270 | 83 | 50 | 24 | 53.5 | 27.3 | 14 | 8 | 323.5 | 173.5 | 140 | ||
| 2.2kw | Ø40 | 5- | 290 | 180 | 215 | 270 | 18 | 34 | 5.5 | 310 | 250 | 5 | 18 | 65 | 230 | 71 | 40 | 28 | 43 | 31.3 | 12 | 8 | 284 | 149 | 134 |
| Ø50 | -80-100 | 334 | 180 | 215 | 300 | 22 | 40 | 5.5 | 360 | 250 | 5 | 25 | 75 | 270 | 83 | 50 | 28 | 53.5 | 31.3 | 14 | 8 | 323.5 | 173.5 | 140 | |
| G3LS: IEC GEAR REDUCER WITH FOOT (n1=1400r/min) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Power kw | output shaft | ratio | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | J | K | L | N | P | S | S1 | T | T1 | W | W1 | X | Y | Y1 | Z |
| 0.12kw | Ø18 | 5–30-40-50 | 147 | 95 | 115 | 40 | 110 | 135 | 65 | 9 | 16.5 | 45 | 4.5 | 140 | 30 | 18 | 11 | 20.5 | 12.8 | 6 | 4 | 138.5 | 85 | 10 | M8 |
| Ø22 | -160-200 | 173 | 95 | 115 | 65 | 130 | 154 | 90 | 11 | 19 | 55 | 4.5 | 140 | 40 | 22 | 11 | 24.5 | 12.8 | 6 | 4 | 141 | 90 | 12 | M8 | |
| 0.18kw | Ø18 | 5- | 147 | 95 | 115 | 40 | 110 | 135 | 65 | 9 | 16.5 | 45 | 4.5 | 140 | 30 | 18 | 11 | 20.5 | 12.8 | 6 | 4 | 138.5 | 85 | 10 | M8 |
| Ø22 | -80-100 | 173 | 95 | 115 | 65 | 130 | 154 | 90 | 11 | 19 | 55 | 4.5 | 140 | 40 | 22 | 11 | 24.5 | 12.8 | 6 | 4 | 141 | 90 | 12 | M8 | |
| Ø28 | 186.5 | 95 | 115 | 90 | 140 | 175 | 125 | 11 | 23.5 | 65 | 4.5 | 140 | 45 | 28 | 11 | 31 | 12.8 | 8 | 4 | 170 | 110 | 15 | M8 | ||
| 0.37kw | Ø22 | 5- | 181.5 | 110 | 130 | 65 | 130 | 154 | 90 | 11 | 19 | 55 | 4.5 | 160 | 40 | 22 | 14 | 24.5 | 16.3 | 6 | 5 | 151 | 90 | 12 | M8 |
| Ø28 | -80-100 | 198 | 110 | 130 | 90 | 140 | 175 | 125 | 11 | 23.5 | 65 | 4.5 | 160 | 45 | 28 | 14 | 31 | 16.3 | 8 | 5 | 170 | 110 | 15 | M8 | |
| Ø32 | 216.5 | 110 | 130 | 130 | 170 | 208 | 170 | 13 | 28.5 | 70 | 4.5 | 160 | 55 | 32 | 14 | 35 | 16.3 | 10 | 5 | 198 | 130 | 18 | M8 | ||
| 0.75kw | Ø28 | 5- | 206.5 | 130 | 165 | 90 | 140 | 175 | 125 | 11 | 23.5 | 65 | 4.5 | 200 | 45 | 28 | 19 | 31 | 21.8 | 8 | 6 | 186.5 | 110 | 15 | M10 |
| Ø32 | -80-100 | 235 | 130 | 165 | 130 | 170 | 208 | 170 | 13 | 28.5 | 70 | 4.5 | 200 | 55 | 32 | 19 | 35 | 21.8 | 10 | 6 | 201.5 | 130 | 18 | M10 | |
| Ø40 | 260.5 | 130 | 165 | 150 | 210 | 254 | 196 | 15 | 34 | 90 | 4.5 | 200 | 65 | 40 | 19 | 43 | 21.8 | 12 | 8 | 230 | 150 | 20 | M10 | ||
| 1.5kw | Ø32 | 5- | 252 | 130 | 165 | 130 | 170 | 208 | 170 | 13 | 28.5 | 70 | 4.5 | 200 | 55 | 32 | 24 | 35 | 27.3 | 10 | 8 | 201.5 | 130 | 18 | M10 |
| Ø40 | -80-100 | 293.5 | 130 | 165 | 150 | 210 | 254 | 196 | 15 | 34 | 90 | 4.5 | 200 | 65 | 40 | 24 | 43 | 27.3 | 12 | 8 | 230 | 150 | 20 | M10 | |
| Ø50 | 321.5 | 130 | 165 | 160 | 230 | 290 | 210 | 18 | 40 | 100 | 4.5 | 200 | 75 | 50 | 24 | 53.5 | 27.3 | 14 | 8 | 265 | 170 | 25 | M10 | ||
| 2.2kw | Ø40 | 5- | 290 | 180 | 215 | 150 | 210 | 254 | 196 | 15 | 34 | 90 | 5.5 | 250 | 65 | 40 | 28 | 43 | 31.3 | 12 | 8 | 230 | 150 | 20 | M12 |
| Ø50 | -80-100 | 334 | 180 | 215 | 160 | 230 | 290 | 210 | 18 | 40 | 100 | 5.5 | 250 | 75 | 50 | 28 | 53.5 | 31.3 | 14 | 8 | 265 | 170 | 25 | M12 | |
Company Profile
We are a professional reducer manufacturer located in HangZhou, ZHangZhoug province.Our leading products is full range of RV571-150 worm reducers , also supplied GKM hypoid helical gearbox, GRC inline helical gearbox, PC units, UDL Variators and AC Motors, G3 helical gear motor.Products are widely used for applications such as: foodstuffs, ceramics, packing, chemicals, pharmacy, plastics, paper-making, construction machinery, metallurgic mine, environmental protection engineering, and all kinds of automatic lines, and assembly lines.With fast delivery, superior after-sales service, advanced producing facility, our products sell well both at home and abroad. We have exported our reducers to Southeast Asia, Eastern Europe and the Middle East and so on.Our aim is to develop and innovate on the basis of high quality, and create a good reputation for reducers.
Workshop:
Exhibition
ZheJiang PTC Fair:
Packaging & Shipping
After Sales Service
1.Maintenance Time and Warranty:Within 1 year after receiving goods.
2.Other Service: Including modeling selection guide, installation guide, and problem resolution guide, etc
FAQ
1.Q:Can you make as per customer drawing?
A: Yes, we offer customized service for customers accordingly. We can use customer’s nameplate for gearboxes.
2.Q:What is your terms of payment ?
A: 30% deposit before production,balance T/T before delivery.
3.Q:Are you a trading company or manufacturer?
A:We are a manufacurer with advanced equipment and experienced workers.
4.Q:What’s your production capacity?
A:4000-5000 PCS/MONTH
5.Q:Free sample is available or not?
A:Yes, we can supply free sample if customer agree to pay for the courier cost
6.Q:Do you have any certificate?
A:Yes, we have CE certificate and SGS certificate report.
Contact information:
Ms Lingel Pan
For any questions just feel free ton contact me. Many thanks for your kind attention to our company!
| Application: | Motor, Machinery, Marine, Agricultural Machinery, Power Transmission Applications |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Clutch, Change Drive Torque, Change Drive Direction, Speed Changing, Speed Reduction |
| Layout: | Coaxial |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Vertical or Horizontal Type |
| Step: | Two Stage- Three Stage |
| Samples: |
US$ 35/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
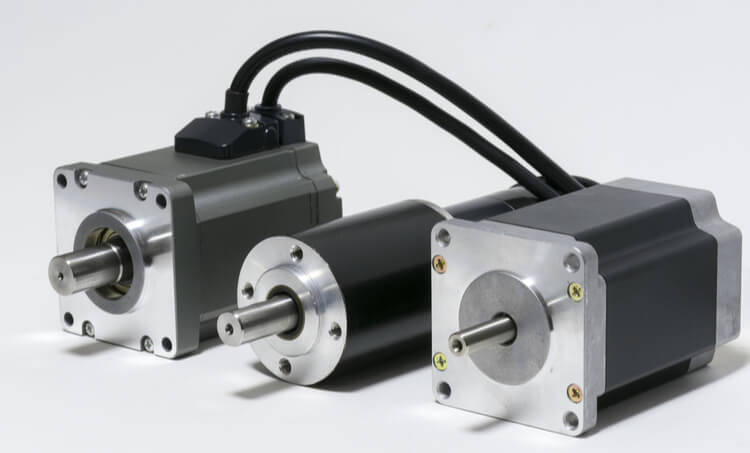

Are there specific maintenance requirements for AC motors to ensure optimal performance?
Yes, AC motors have specific maintenance requirements to ensure their optimal performance and longevity. Regular maintenance helps prevent unexpected failures, maximizes efficiency, and extends the lifespan of the motor. Here are some key maintenance practices for AC motors:
- Cleaning and Inspection: Regularly clean the motor to remove dust, dirt, and debris that can accumulate on the motor surfaces and hinder heat dissipation. Inspect the motor for any signs of damage, loose connections, or abnormal noise/vibration. Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage.
- Lubrication: Check the motor’s lubrication requirements and ensure proper lubrication of bearings, gears, and other moving parts. Insufficient or excessive lubrication can lead to increased friction, overheating, and premature wear. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for lubrication intervals and use the recommended lubricants.
- Belt and Pulley Maintenance: If the motor is coupled with a belt and pulley system, regularly inspect and adjust the tension of the belts. Improper belt tension can affect motor performance and efficiency. Replace worn-out belts and damaged pulleys as needed.
- Cooling System Maintenance: AC motors often have cooling systems such as fans or heat sinks to dissipate heat generated during operation. Ensure that these cooling systems are clean and functioning properly. Remove any obstructions that may impede airflow and compromise cooling efficiency.
- Electrical Connections: Regularly inspect the motor’s electrical connections for signs of loose or corroded terminals. Loose connections can lead to voltage drops, increased resistance, and overheating. Tighten or replace any damaged connections and ensure proper grounding.
- Vibration Analysis: Periodically perform vibration analysis on the motor to detect any abnormal vibrations. Excessive vibration can indicate misalignment, unbalanced rotors, or worn-out bearings. Address the underlying causes of vibration to prevent further damage and ensure smooth operation.
- Motor Testing: Conduct regular motor testing, such as insulation resistance testing and winding resistance measurement, to assess the motor’s electrical condition. These tests can identify insulation breakdown, winding faults, or other electrical issues that may affect motor performance and reliability.
- Professional Maintenance: For more complex maintenance tasks or when dealing with large industrial motors, it is advisable to involve professional technicians or motor specialists. They have the expertise and tools to perform in-depth inspections, repairs, and preventive maintenance procedures.
It’s important to note that specific maintenance requirements may vary depending on the motor type, size, and application. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for the particular AC motor in use. By following proper maintenance practices, AC motors can operate optimally, minimize downtime, and have an extended service life.

Can you explain the difference between single-phase and three-phase AC motors?
In the realm of AC motors, there are two primary types: single-phase and three-phase motors. These motors differ in their construction, operation, and applications. Let’s explore the differences between single-phase and three-phase AC motors:
- Number of Power Phases: The fundamental distinction between single-phase and three-phase motors lies in the number of power phases they require. Single-phase motors operate using a single alternating current (AC) power phase, while three-phase motors require three distinct AC power phases, typically referred to as phase A, phase B, and phase C.
- Power Supply: Single-phase motors are commonly connected to standard residential or commercial single-phase power supplies. These power supplies deliver a voltage with a sinusoidal waveform, oscillating between positive and negative cycles. In contrast, three-phase motors require a dedicated three-phase power supply, typically found in industrial or commercial settings. Three-phase power supplies deliver three separate sinusoidal waveforms with a specific phase shift between them, resulting in a more balanced and efficient power delivery system.
- Starting Mechanism: Single-phase motors often rely on auxiliary components, such as capacitors or starting windings, to initiate rotation. These components help create a rotating magnetic field necessary for motor startup. Once the motor reaches a certain speed, these auxiliary components may be disconnected or deactivated. Three-phase motors, on the other hand, typically do not require additional starting mechanisms. The three-phase power supply inherently generates a rotating magnetic field, enabling self-starting capability.
- Power and Torque Output: Three-phase motors generally offer higher power and torque output compared to single-phase motors. The balanced nature of three-phase power supply allows for a more efficient distribution of power across the motor windings, resulting in increased performance capabilities. Three-phase motors are commonly used in applications requiring high power demands, such as industrial machinery, pumps, compressors, and heavy-duty equipment. Single-phase motors, with their lower power output, are often used in residential appliances, small commercial applications, and light-duty machinery.
- Efficiency and Smoothness of Operation: Three-phase motors typically exhibit higher efficiency and smoother operation than single-phase motors. The balanced three-phase power supply helps reduce electrical losses and provides a more constant and uniform torque output. This results in improved motor efficiency, reduced vibration, and smoother rotation. Single-phase motors, due to their unbalanced power supply, may experience more pronounced torque variations and slightly lower efficiency.
- Application Suitability: The choice between single-phase and three-phase motors depends on the specific application requirements. Single-phase motors are suitable for powering smaller appliances, such as fans, pumps, household appliances, and small tools. They are commonly used in residential settings where single-phase power is readily available. Three-phase motors are well-suited for industrial and commercial applications that demand higher power levels and continuous operation, including large machinery, conveyors, elevators, air conditioning systems, and industrial pumps.
It’s important to note that while single-phase and three-phase motors have distinct characteristics, there are also hybrid motor designs, such as dual-voltage motors or capacitor-start induction-run (CSIR) motors, which aim to bridge the gap between the two types and offer flexibility in certain applications.
When selecting an AC motor, it is crucial to consider the specific power requirements, available power supply, and intended application to determine whether a single-phase or three-phase motor is most suitable for the task at hand.

What are the key advantages of using AC motors in industrial applications?
AC motors offer several key advantages that make them highly suitable for industrial applications. Here are some of the main advantages:
- Simple and Robust Design: AC motors, particularly induction motors, have a simple and robust design, making them reliable and easy to maintain. They consist of fewer moving parts compared to other types of motors, which reduces the likelihood of mechanical failure and the need for frequent maintenance.
- Wide Range of Power Ratings: AC motors are available in a wide range of power ratings, from small fractional horsepower motors to large industrial motors with several megawatts of power. This versatility allows for their application in various industrial processes and machinery, catering to different power requirements.
- High Efficiency: AC motors, especially modern designs, offer high levels of efficiency. They convert electrical energy into mechanical energy with minimal energy loss, resulting in cost savings and reduced environmental impact. High efficiency also means less heat generation, contributing to the longevity and reliability of the motor.
- Cost-Effectiveness: AC motors are generally cost-effective compared to other types of motors. Their simple construction and widespread use contribute to economies of scale, making them more affordable for industrial applications. Additionally, AC motors often have lower installation and maintenance costs due to their robust design and ease of operation.
- Flexible Speed Control: AC motors, particularly induction motors, offer various methods for speed control, allowing for precise adjustment of motor speed to meet specific industrial requirements. Speed control mechanisms such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) enable enhanced process control, energy savings, and improved productivity.
- Compatibility with AC Power Grid: AC motors are compatible with the standard AC power grid, which is widely available in industrial settings. This compatibility simplifies the motor installation process and eliminates the need for additional power conversion equipment, reducing complexity and cost.
- Adaptability to Various Environments: AC motors are designed to operate reliably in a wide range of environments. They can withstand variations in temperature, humidity, and dust levels commonly encountered in industrial settings. Additionally, AC motors can be equipped with protective enclosures to provide additional resistance to harsh conditions.
These advantages make AC motors a popular choice for industrial applications across various industries. Their simplicity, reliability, cost-effectiveness, energy efficiency, and speed control capabilities contribute to improved productivity, reduced operational costs, and enhanced process control in industrial settings.


editor by CX 2023-11-30
China Standard ZD 72mm 3000RPM Rated Speed Brush/Brushless Precision Planetary Transmission Gear Motor with high quality
Product Description
ZD 72mm 3000RPM Rated Speed Brush/Brushless Precision Planetary Transmission Gear Motor
Detailed Photos
Product Parameters
MODEL:Z72BLDPN24120-30S(72PN3.65)
Other Related Products
Click Here For More Details
Company Profile
FAQ
Q: What’re your main products?
A: We currently produce Brushed Dc Motors, Brushed Dc Gear Motors, Planetary Dc Gear Motors, Brushless Dc Motors, Stepper motors, Ac Motors and High Precision Planetary Gear Box etc. You can check the specifications for above motors on our website and you can email us to recommend needed motors per your specification too.
Q: How to select a suitable motor?
A:If you have motor pictures or drawings to show us, or you have detailed specs like voltage, speed, torque, motor size, working mode of the motor, needed lifetime and noise level etc, please do not hesitate to let us know, then we can recommend suitable motor per your request accordingly.
Q: Do you have a customized service for your standard motors?
A: Yes, we can customize per your request for the voltage, speed, torque and shaft size/shape. If you need additional wires/cables soldered on the terminal or need to add connectors, or capacitors or EMC we can make it too.
Q: Do you have an individual design service for motors?
A: Yes, we would like to design motors individually for our customers, but it may need some mold developing cost and design charge.
Q: What’s your lead time?
A: Generally speaking, our regular standard product will need 15-30days, a bit longer for customized products. But we are very flexible on the lead time, it will depend on the specific orders.
Please contact us if you have detailed requests, thank you !
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars |
|---|---|
| Function: | Change Drive Torque, Speed Changing |
| Layout: | Transmission |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Horizontal Type |
| Step: | Three-Step |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What Is a Gear Motor?
A gear motor is an electric motor coupled with a gear train. It uses either DC or AC power to achieve its purpose. The primary benefit of a gear reducer is its ability to multiply torque while maintaining a compact size. The trade-off of this additional torque comes in the form of a reduced output shaft speed and overall efficiency. However, proper gear technology and ratios provide optimum output and speed profiles. This type of motor unlocks the full potential of OEM equipment.
Inertial load
Inertial load on a gear motor is the amount of force a rotating device produces due to its inverse square relationship with its inertia. The greater the inertia, the less torque can be produced by the gear motor. However, if the inertia is too high, it can cause problems with positioning, settling time, and controlling torque and velocity. Gear ratios should be selected for optimal power transfer.
The duration of acceleration and braking time of a gear motor depends on the type of driven load. An inertia load requires longer acceleration time whereas a friction load requires breakaway torque to start the load and maintain it at its desired speed. Too short a time period can cause excessive gear loading and may result in damaged gears. A safe approach is to disconnect the load when power is disconnected to prevent inertia from driving back through the output shaft.
Inertia is a fundamental concept in the design of motors and drive systems. The ratio of mass and inertia of a load to a motor determines how well the motor can control its speed during acceleration or deceleration. The mass moment of inertia, also called rotational inertia, is dependent on the mass, geometry, and center of mass of an object.
Applications
There are many applications of gear motors. They provide a powerful yet efficient means of speed and torque control. They can be either AC or DC, and the two most common motor types are the three-phase asynchronous and the permanent magnet synchronous servomotor. The type of motor used for a given application will determine its cost, reliability, and complexity. Gear motors are typically used in applications where high torque is required and space or power constraints are significant.
There are two types of gear motors. Depending on the ratio, each gear has an output shaft and an input shaft. Gear motors use hydraulic pressure to produce torque. The pressure builds on one side of the motor until it generates enough torque to power a rotating load. This type of motors is not recommended for applications where load reversals occur, as the holding torque will diminish with age and shaft vibration. However, it can be used for precision applications.
The market landscape shows the competitive environment of the gear motor industry. This report also highlights key items, income and value creation by region and country. The report also examines the competitive landscape by region, including the United States, China, India, the GCC, South Africa, Brazil, and the rest of the world. It is important to note that the report contains segment-specific information, so that readers can easily understand the market potential of the geared motors market.
Size
The safety factor, or SF, of a gear motor is an important consideration when selecting one for a particular application. It compensates for the stresses placed on the gearing and enables it to run at maximum efficiency. Manufacturers provide tables detailing typical applications, with multiplication factors for duty. A gear motor with a SF of three or more is suitable for difficult applications, while a gearmotor with a SF of one or two is suitable for relatively easy applications.
The global gear motor market is highly fragmented, with numerous small players catering to various end-use industries. The report identifies various industry trends and provides comprehensive information on the market. It outlines historical data and offers valuable insights on the industry. The report also employs several methodologies and approaches to analyze the market. In addition to providing historical data, it includes detailed information by market segment. In-depth analysis of market segments is provided to help identify which technologies will be most suitable for which applications.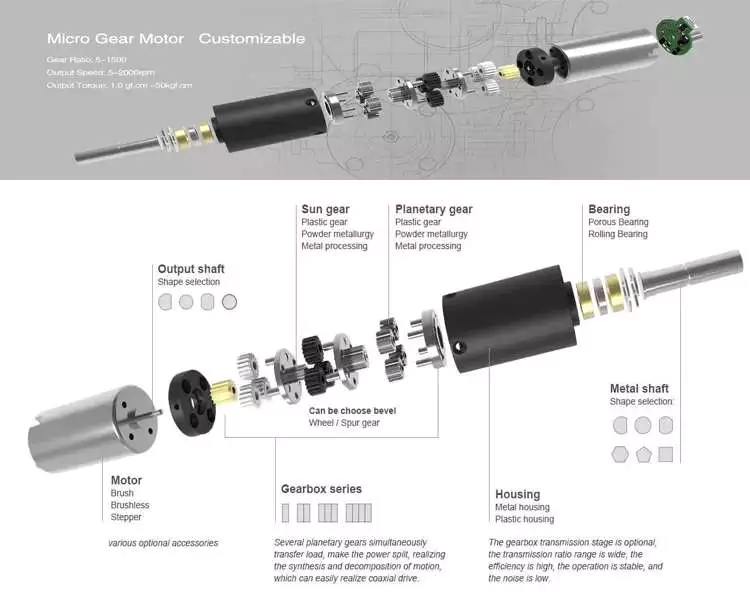
Cost
A gear motor is an electric motor that is paired with a gear train. They are available in AC or DC power systems. Compared to conventional motors, gear reducers can maximize torque while maintaining compact dimensions. But the trade-off is the reduced output shaft speed and overall efficiency. However, when used correctly, a gear motor can produce optimal output and mechanical fit. To understand how a gear motor works, let’s look at two types: right-angle geared motors and inline geared motors. The first two types are usually used in automation equipment and in agricultural and medical applications. The latter type is designed for rugged applications.
In addition to its efficiency, DC gear motors are space-saving and have low energy consumption. They can be used in a number of applications including money counters and printers. Automatic window machines and curtains, glass curtain walls, and banknote vending machines are some of the other major applications of these motors. They can cost up to 10 horsepower, which is a lot for an industrial machine. However, these are not all-out expensive.
Electric gear motors are versatile and widely used. However, they do not work well in applications requiring high shaft speed and torque. Examples of these include conveyor drives, frozen beverage machines, and medical tools. These applications require high shaft speed, so gear motors are not ideal for these applications. However, if noise and other problems are not a concern, a motor-only solution may be the better choice. This way, you can use a single motor for multiple applications.
Maintenance
Geared motors are among the most common equipment used for drive trains. Proper maintenance can prevent damage and maximize their efficiency. A guide to gear motor maintenance is available from WEG. To prevent further damage, follow these maintenance steps:
Regularly check electrical connections. Check for loose connections and torque them to the recommended values. Also, check the contacts and relays to make sure they are not tangled or damaged. Check the environment around the gear motor to prevent dust from clogging the passageway of electric current. A proper maintenance plan will help you identify problems and extend their life. The manual will also tell you about any problems with the gearmotor. However, this is not enough – it is important to check the condition of the gearbox and its parts.
Conduct visual inspection. The purpose of visual inspection is to note any irregularities that may indicate possible problems with the gear motor. A dirty motor may be an indication of a rough environment and a lot of problems. You can also perform a smell test. If you can smell a burned odor coming from the windings, there may be an overheating problem. Overheating can cause the windings to burn and damage.
Reactive maintenance is the most common method of motor maintenance. In this type of maintenance, you only perform repairs if the motor stops working due to a malfunction. Regular inspection is necessary to avoid unexpected motor failures. By using a logbook to document motor operations, you can determine when it is time to replace the gear motor. In contrast to preventive maintenance, reactive maintenance requires no regular tests or services. However, it is recommended to perform inspections every six months.


editor by CX 2023-05-06