Product Description
nema17 Planetary Gearbox Stepping Motor price on hot sale
General Specificati
| Housing Material | Metal |
| Bearing at Output | Ball Bearings |
| Max.Radial Load(12mm from flange) | ≤80N |
| Max.Shaft Axial Load | ≤30N |
| Radial Play of Shaft (near to Flange) | ≤0.06mm |
| Axial Play of Shaft | ≤0.3mm |
| Backlash at No-load | 1.5° |
Electrical Specification:
| Model No. | Step Angle | Motor Length | Current /Phase |
Resistance /Phase |
Inductance /Phase |
Holding Torque | # of Leads | Detent Torque | Rotor Inertia | Mass |
| ( °) | (L)mm | A | Ω | mH | kg.cm | No. | g.cm | g.cm | Kg | |
| JK42HS34-1334 | 1.8 | 34 | 1.33 | 2.1 | 2.5 | 2.2 | 4 | 120 | 34 | 0.22 |
| JK42HS34-0406 | 1.8 | 34 | 0.4 | 24 | 15 | 1.6 | 6 | 120 | 34 | 0.22 |
| JK42HS40-1684 | 1.8 | 40 | 1.68 | 1.65 | 3.2 | 3.6 | 4 | 150 | 54 | 0.28 |
| JK42HS40-1206 | 1.8 | 40 | 1.2 | 3 | 2.7 | 2.9 | 6 | 150 | 54 | 0.28 |
| JK42HS48-1684 | 1.8 | 48 | 1.68 | 1.65 | 2.8 | 4.4 | 4 | 260 | 68 | 0.35 |
| JK42HS48-1206 | 1.8 | 48 | 1.2 | 3.3 | 2.8 | 3.17 | 6 | 260 | 68 | 0.35 |
| JK42HS60-1704 | 1.8 | 60 | 1.7 | 3 | 6.2 | 7.3 | 4 | 280 | 102 | 0.5 |
| JK42HS60-1206 | 1.8 | 60 | 1.2 | 6 | 7 | 5.6 | 6 | 280 | 102 | 0.5 |
42HS Planetary Gearbox Specifications
| Reduction ratio | 3.71 | 5.18 | 13.76 | 19.2 | 26.8 | 51 | 71 | 99.5 | 139 |
| Number of gear trains | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||||
| Length(L2) mm | 27.3 | 35 | 42.7 | ||||||
| Max.rated torque kg.cm | 20 | 30 | 40 | ||||||
| Short time permissible torque kg.cm | 40 | 60 | 80 | ||||||
| Weight g | 350 | 450 | 550 | ||||||
Products of special request can be made according to the customer request !
company information:
our certification:
Our Company offers 3 major series of products:Hybrid Stepper motors, Brushless Dc motor and Dc Brush motor.
We are always continues develop new type models.If you need other kinds of parts, please don’t hesitate to contact us.
Amy Gao
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Household Appliances, Car, Power Tools |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Adjust Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Compound |
| Function: | Run |
| Casing Protection: | Protection Type |
| Number of Poles: | 8 |
| Samples: |
US$ 21.5/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Are gear motors suitable for both heavy-duty industrial applications and smaller-scale uses?
Yes, gear motors are suitable for both heavy-duty industrial applications and smaller-scale uses. Their versatility and ability to provide torque multiplication make them valuable in a wide range of applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of why gear motors are suitable for both types of applications:
1. Heavy-Duty Industrial Applications:
Gear motors are commonly used in heavy-duty industrial applications due to their robustness and ability to handle high loads. Here are the reasons why they are suitable for such applications:
- Torque Multiplication: Gear motors are designed to provide high torque output, making them ideal for applications that require substantial force to move or operate heavy machinery, conveyors, or equipment.
- Load Handling: Industrial settings often involve heavy loads and demanding operating conditions. Gear motors, with their ability to handle high loads, are well-suited for tasks such as lifting, pulling, pushing, or driving heavy materials or equipment.
- Durability: Heavy-duty industrial applications require components that can withstand harsh environments, frequent use, and demanding operating conditions. Gear motors are typically constructed with durable materials and designed to withstand heavy vibrations, shock loads, and temperature variations.
- Speed Reduction: Many industrial processes require the reduction of motor speed to achieve the desired output speed. Gear motors offer precise speed reduction capabilities through gear ratios, allowing for optimal control and operation of machinery and equipment.
2. Smaller-Scale Uses:
While gear motors excel in heavy-duty industrial applications, they are also suitable for smaller-scale uses across various industries and applications. Here’s why gear motors are well-suited for smaller-scale uses:
- Compact Size: Gear motors are available in compact sizes, making them suitable for applications with limited space or small-scale machinery, devices, or appliances.
- Torque and Power Control: Even in smaller-scale applications, there may be a need for torque multiplication or precise power control. Gear motors can provide the necessary torque and power output for tasks such as precise positioning, controlling speed, or driving small loads.
- Versatility: Gear motors come in various configurations, such as parallel shaft, planetary, or worm gear designs, offering flexibility to match specific requirements. They can be adapted to different applications, including robotics, medical devices, automotive systems, home automation, and more.
- Efficiency: Gear motors are designed to be efficient, converting the electrical input power into mechanical output power with minimal losses. This efficiency is advantageous for smaller-scale applications where energy conservation and battery life are critical.
Overall, gear motors are highly versatile and suitable for both heavy-duty industrial applications and smaller-scale uses. Their ability to provide torque multiplication, handle high loads, offer precise speed control, and accommodate various sizes and configurations makes them a reliable choice in a wide range of applications. Whether it’s powering large industrial machinery or driving small-scale automation systems, gear motors provide the necessary torque, control, and durability required for efficient operation.

What are some common challenges or issues associated with gear motors, and how can they be addressed?
Gear motors, like any mechanical system, can face certain challenges or issues that may affect their performance, reliability, or longevity. However, many of these challenges can be addressed through proper design, maintenance, and operational practices. Here are some common challenges associated with gear motors and potential solutions:
1. Gear Wear and Failure:
Over time, gears in a gear motor can experience wear, resulting in decreased performance or even failure. The following measures can address this challenge:
- Proper Lubrication: Regular lubrication with the appropriate lubricant can minimize friction and wear between gear teeth. It is essential to follow manufacturer recommendations for lubrication intervals and use high-quality lubricants suitable for the specific gear motor.
- Maintenance and Inspection: Routine maintenance and periodic inspections can help identify early signs of gear wear or damage. Timely replacement of worn gears or components can prevent further damage and ensure the gear motor’s optimal performance.
- Material Selection: Choosing gears made from durable and wear-resistant materials, such as hardened steel or specialized alloys, can increase their lifespan and resistance to wear.
2. Backlash and Inaccuracy:
Backlash, as discussed earlier, can introduce inaccuracies in gear motor systems. The following approaches can help address this issue:
- Anti-Backlash Gears: Using anti-backlash gears, which are designed to minimize or eliminate backlash, can significantly reduce inaccuracies caused by gear play.
- Tight Manufacturing Tolerances: Ensuring precise manufacturing tolerances during gear production helps minimize backlash and improve overall accuracy.
- Backlash Compensation: Implementing control algorithms or mechanisms to compensate for backlash can help mitigate its effects and improve the accuracy of the gear motor.
3. Noise and Vibrations:
Gear motors can generate noise and vibrations during operation, which may be undesirable in certain applications. The following strategies can help mitigate this challenge:
- Noise Dampening: Incorporating noise-dampening features, such as vibration-absorbing materials or isolation mounts, can reduce noise and vibrations transmitted from the gear motor to the surrounding environment.
- Quality Gears and Bearings: Using high-quality gears and bearings can minimize vibrations and noise generation. Precision-machined gears and well-maintained bearings help ensure smooth operation and reduce unwanted noise.
- Proper Alignment: Ensuring accurate alignment of gears, shafts, and other components reduces the likelihood of noise and vibrations caused by misalignment. Regular inspections and adjustments can help maintain optimal alignment.
4. Overheating and Thermal Management:
Heat buildup can be a challenge in gear motors, especially during prolonged or heavy-duty operation. Effective thermal management techniques can address this issue:
- Adequate Ventilation: Providing proper ventilation and airflow around the gear motor helps dissipate heat. This can involve designing cooling fins, incorporating fans or blowers, or ensuring sufficient clearance for air circulation.
- Heat Dissipation Materials: Using heat-dissipating materials, such as aluminum or copper, in motor housings or heat sinks can improve heat dissipation and prevent overheating.
- Monitoring and Control: Implementing temperature sensors and thermal protection mechanisms allows for real-time monitoring of the gear motor’s temperature. If the temperature exceeds safe limits, the motor can be automatically shut down or adjusted to prevent damage.
5. Load Variations and Shock Loads:
Unexpected load variations or shock loads can impact the performance and durability of gear motors. The following measures can help address this challenge:
- Proper Sizing and Selection: Choosing gear motors with appropriate torque and load capacity ratings for the intended application helps ensure they can handle expected load variations and occasional shock loads without exceeding their limits.
- Shock Absorption: Incorporating shock-absorbing mechanisms, such as dampers or resilient couplings, can help mitigate the effects of sudden load changes or impacts on the gear motor.
- Load Monitoring: Implementing load monitoring systems or sensors allows for real-time monitoring of load variations. This information can be used to adjust operation or trigger protective measures when necessary.
By addressing these common challenges associated with gear motors through appropriate design considerations, regular maintenance, and operational practices, it is possible to enhance their performance, reliability, and longevity.

What is a gear motor, and how does it combine the functions of gears and a motor?
A gear motor is a type of motor that incorporates gears into its design to combine the functions of gears and a motor. It consists of a motor, which provides the mechanical power, and a set of gears, which transmit and modify this power to achieve specific output characteristics. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a gear motor is and how it combines the functions of gears and a motor:
A gear motor typically consists of two main components: the motor and the gear system. The motor is responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy, generating rotational motion. The gear system, on the other hand, consists of multiple gears with different sizes and tooth configurations. These gears are meshed together in a specific arrangement to transmit and modify the output torque and speed of the motor.
The gears in a gear motor serve several functions:
1. Torque Amplification:
One of the primary functions of the gear system in a gear motor is to amplify the torque output of the motor. By using gears with different sizes, the input torque can be effectively multiplied or reduced. This allows the gear motor to provide higher torque at lower speeds or lower torque at higher speeds, depending on the gear arrangement. This torque amplification is beneficial in applications where high torque is required, such as in heavy machinery or vehicles.
2. Speed Reduction or Increase:
The gear system in a gear motor can also be used to reduce or increase the rotational speed of the motor output. By utilizing gears with different numbers of teeth, the gear ratio can be adjusted to achieve the desired speed output. For example, a gear motor with a higher gear ratio will output lower speed but higher torque, whereas a gear motor with a lower gear ratio will output higher speed but lower torque. This speed control capability allows for precise matching of motor output to the requirements of specific applications.
3. Directional Control:
Gears in a gear motor can be used to control the direction of rotation of the motor output shaft. By employing different combinations of gears, such as spur gears, bevel gears, or worm gears, the rotational direction can be changed. This directional control is crucial in applications where bidirectional movement is required, such as in conveyor systems or robotic arms.
4. Load Distribution:
The gear system in a gear motor helps distribute the load evenly across multiple gears, which reduces the stress on individual gears and increases the overall durability and lifespan of the motor. By sharing the load among multiple gears, the gear motor can handle higher torque applications without putting excessive strain on any particular gear. This load distribution capability is especially important in heavy-duty applications that require continuous operation under demanding conditions.
By combining the functions of gears and a motor, gear motors offer several advantages. They provide torque amplification, speed control, directional control, and load distribution capabilities, making them suitable for various applications that require precise and controlled mechanical power. Gear motors are commonly used in industries such as robotics, automotive, manufacturing, and automation, where reliable and efficient power transmission is essential.


editor by CX 2024-03-28
China High Torque Micro NEMA17 Planetary Gear Reducer Stepper Motor for CNC Kit ac motor
Solution Description
Product Description
Planetary Equipment Stepping Motor :
Precision high-end upgrade with Nema8, Nema 11, Nema14, Nema 17, Nema23, Nema 24
stepper motor low noise, low vibration, firm and durable. Increase torque at low speed.
Reduction ratio:1:3.7 , 1:5.2 , 1:14 , 1:19 ,1:27 ,1:51 , 1:71 ,1:100 ,1:139 , 1:189 ,1:264 , 1:369 ,And 48 hours delivery , in stock .
Application:
Automation control, medical equipment, textile machinery,and packaging machinery fields. Not only in the field of the automation industry, it also has a good use status in the home. Products with low speed and inertia are often seen: electric curtains, electric shutters, etc
Solution Parameters
Planetary Gear Box Specification:
| Housing Substance | Steel |
| Bearing at Output | Ball Bearings |
| Max.Radial Load(10mm from flange) | 200N |
| Max.Shaft Axial Load | 100N |
| Radial Engage in of Shaft (around to Flange) | ≤0.06mm |
| Axial Play of Shaft | ≤0.3mm |
| Backlash at No-load | 1 stage≤1°,2stage≤1.2°,3stage≤1.5° |
42HS Hybrid Stepping Motor Technical specs:
| Model No. | Step Angle | Motor Size(L1) | Rated | Existing | Resistance | Inductance | Holding Torque | # of Leads | Rotor Inertia | Mass | Max.Equipment Ratio |
| Voltage | /Section | /Phase | /Period | ||||||||
| Solitary Shaft | ( °) | (L)mm | V | A | Ω | mH | mN.m | No. | g.cm2 | Kg | |
| 42HSC1409 | one.eight | 34 | two.ninety three | 1.33 | two.2 | three.five | 270 | four | 30 | .22 | ≤1:369 |
| 42HSC4409 | one.8 | 40 | 2.five | one.five | 1.sixty five | 3.three | 380 | four | forty | .3 | ≤1:369 |
| 42HSC1409 Planetary Gearbox Requirements: | ||||||||||||
| Reduction ratio | 3.71 | five.eighteen | fourteen | 19 | 27 | fifty one | seventy one | a hundred | 139 | 189 | 264 | 369 |
| Overall Top(L1+L2) (mm) | 65.five | 65.5 | seventy six.1 | seventy six.1 | 76.one | 86.five | 86.five | 86.5 | 86.five | 96.nine | 96.9 | ninety six.9 |
| Output torque ( mN.m) | 902 | 1259 | 3062 | 4155 | 5000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | ten thousand | 10000 |
| Complete Excess weight(g) | 428 | 428 | 510 | 510 | 510 | 592 | 592 | 592 | 592 | 674 | 674 | 674 |
| Variety of equipment trains | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||
| Reducer Size(L2) (mm) | 31.five | 42.1 | 52.five | 62.nine | ||||||||
| Efficiency | 90% | 81% | 73% | 66% | ||||||||
| 42HSC4409 Planetary Gearbox Specifications: | ||||||||||||
| Reduction ratio | 3.71 | five.eighteen | fourteen | 19 | 27 | fifty one | 71 | one hundred | 139 | 189 | 264 | 369 |
| Overall Peak(L1+L2) (mm) | seventy one.five | seventy one.five | eighty two.one | 82.1 | eighty two.1 | ninety two.five | 92.5 | 92.5 | 92.5 | 102.nine | 102.9 | 102.nine |
| Output torque ( mN.m) | 1269 | 1772 | 4309 | 5000 | 5000 | ten thousand | 10000 | ten thousand | ten thousand | ten thousand | 10000 | 10000 |
| Overall Fat(g) | 508 | 508 | 590 | 590 | 590 | 672 | 672 | 672 | 672 | 754 | 754 | 754 |
| Amount of equipment trains | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||
| Reducer Length(L2) (mm) | 31.five | 42.one | 52.5 | 62.9 | ||||||||
| Performance | 90% | 81% | 73% | 66% | ||||||||
Thorough Photographs
Company Profile
ZheJiang UMot Technological innovation Co., Ltd. specializes in R&D and sales of stepper motors, servo motors, linear modules and connected movement manage merchandise, customizing and creating large-top quality motor products for users with special needs close to the world, and delivering all round options for movement manage methods. Merchandise are exported to more than 30 nations around the world and regions such as the United States, Germany, France, Italy, Russia, and Switzerland. The firm’s major items and program layout have been commonly utilized in automation control, precision devices, health-related products, sensible property, 3D printing and a lot of other fields.
Our organization has been recognized as a large-tech enterprise by appropriate departments, has a complete quality administration system, has acquired ISO9001, CE, RoHs and other relevant certifications, and holds a amount of electrical patent certificates. “Concentration, Professionalism, Focus” in the subject of automation of motor R&D and technique handle remedies is the firm’s business function. “Be your most trustworthy companion” is the firm’s provider philosophy. We have usually been aiming to “make first-course merchandise with expert technology”, maintain pace with the instances, innovate consistently, and supply a lot more end users with much better goods and solutions.
FAQ
1. Delivery method:
1)Worldwide Categorical supply DHL&FEDEX &UPS&TNT& 7-10days
two)Shipping and delivery by air 7-ten days
3)transport by sea, supply time relies upon on the spot port.
2. Complex Assist:
We can supply you with professional specialized assistance. And our products good quality promise is 6 months. Also, we accept items personalized.
three. Why must you acquire from us, not from other suppliers?
Expert one-to-1 motor customized. The world’s huge company of selection for high-quality suppliers. ISO9001:2008 good quality administration method certification, by way of the CE, ROHS certification.
4. How to decide on types?
Just before buying, make sure you get in touch with us to affirm product No. and requirements to steer clear of any misunderstanding.
5. Are you a manufacturing unit?
Yes, we are a factory, and we produce stepper motor/driver, Servo motor/driver.
|
US $31.2-54.68 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Robot |
|---|---|
| Speed: | Low Speed |
| Number of Stator: | Two-Phase |
| Excitation Mode: | HB-Hybrid |
| Function: | Control, Driving |
| Number of Poles: | 2 |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 42/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Housing Material | Metal |
| Bearing at Output | Ball Bearings |
| Max.Radial Load(10mm from flange) | 200N |
| Max.Shaft Axial Load | 100N |
| Radial Play of Shaft (near to Flange) | ≤0.06mm |
| Axial Play of Shaft | ≤0.3mm |
| Backlash at No-load | 1 stage≤1°,2stage≤1.2°,3stage≤1.5° |
###
| Model No. | Step Angle | Motor Length(L1) | Rated | Current | Resistance | Inductance | Holding Torque | # of Leads | Rotor Inertia | Mass | Max.Gear Ratio |
| Voltage | /Phase | /Phase | /Phase | ||||||||
| Single Shaft | ( °) | (L)mm | V | A | Ω | mH | mN.m | No. | g.cm2 | Kg | |
| 42HSC1409 | 1.8 | 34 | 2.93 | 1.33 | 2.2 | 3.5 | 270 | 4 | 30 | 0.22 | ≤1:369 |
| 42HSC4409 | 1.8 | 40 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1.65 | 3.3 | 380 | 4 | 40 | 0.3 | ≤1:369 |
###
| 42HSC1409 Planetary Gearbox Specifications: | ||||||||||||
| Reduction ratio | 3.71 | 5.18 | 14 | 19 | 27 | 51 | 71 | 100 | 139 | 189 | 264 | 369 |
| Total Height(L1+L2) (mm) | 65.5 | 65.5 | 76.1 | 76.1 | 76.1 | 86.5 | 86.5 | 86.5 | 86.5 | 96.9 | 96.9 | 96.9 |
| Output torque ( mN.m) | 902 | 1259 | 3062 | 4155 | 5000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 |
| Total Weight(g) | 428 | 428 | 510 | 510 | 510 | 592 | 592 | 592 | 592 | 674 | 674 | 674 |
| Number of gear trains | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||
| Reducer Length(L2) (mm) | 31.5 | 42.1 | 52.5 | 62.9 | ||||||||
| Efficiency | 90% | 81% | 73% | 66% | ||||||||
###
| 42HSC4409 Planetary Gearbox Specifications: | ||||||||||||
| Reduction ratio | 3.71 | 5.18 | 14 | 19 | 27 | 51 | 71 | 100 | 139 | 189 | 264 | 369 |
| Total Height(L1+L2) (mm) | 71.5 | 71.5 | 82.1 | 82.1 | 82.1 | 92.5 | 92.5 | 92.5 | 92.5 | 102.9 | 102.9 | 102.9 |
| Output torque ( mN.m) | 1269 | 1772 | 4309 | 5000 | 5000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 |
| Total Weight(g) | 508 | 508 | 590 | 590 | 590 | 672 | 672 | 672 | 672 | 754 | 754 | 754 |
| Number of gear trains | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||
| Reducer Length(L2) (mm) | 31.5 | 42.1 | 52.5 | 62.9 | ||||||||
| Efficiency | 90% | 81% | 73% | 66% | ||||||||
|
US $31.2-54.68 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Robot |
|---|---|
| Speed: | Low Speed |
| Number of Stator: | Two-Phase |
| Excitation Mode: | HB-Hybrid |
| Function: | Control, Driving |
| Number of Poles: | 2 |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 42/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Housing Material | Metal |
| Bearing at Output | Ball Bearings |
| Max.Radial Load(10mm from flange) | 200N |
| Max.Shaft Axial Load | 100N |
| Radial Play of Shaft (near to Flange) | ≤0.06mm |
| Axial Play of Shaft | ≤0.3mm |
| Backlash at No-load | 1 stage≤1°,2stage≤1.2°,3stage≤1.5° |
###
| Model No. | Step Angle | Motor Length(L1) | Rated | Current | Resistance | Inductance | Holding Torque | # of Leads | Rotor Inertia | Mass | Max.Gear Ratio |
| Voltage | /Phase | /Phase | /Phase | ||||||||
| Single Shaft | ( °) | (L)mm | V | A | Ω | mH | mN.m | No. | g.cm2 | Kg | |
| 42HSC1409 | 1.8 | 34 | 2.93 | 1.33 | 2.2 | 3.5 | 270 | 4 | 30 | 0.22 | ≤1:369 |
| 42HSC4409 | 1.8 | 40 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1.65 | 3.3 | 380 | 4 | 40 | 0.3 | ≤1:369 |
###
| 42HSC1409 Planetary Gearbox Specifications: | ||||||||||||
| Reduction ratio | 3.71 | 5.18 | 14 | 19 | 27 | 51 | 71 | 100 | 139 | 189 | 264 | 369 |
| Total Height(L1+L2) (mm) | 65.5 | 65.5 | 76.1 | 76.1 | 76.1 | 86.5 | 86.5 | 86.5 | 86.5 | 96.9 | 96.9 | 96.9 |
| Output torque ( mN.m) | 902 | 1259 | 3062 | 4155 | 5000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 |
| Total Weight(g) | 428 | 428 | 510 | 510 | 510 | 592 | 592 | 592 | 592 | 674 | 674 | 674 |
| Number of gear trains | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||
| Reducer Length(L2) (mm) | 31.5 | 42.1 | 52.5 | 62.9 | ||||||||
| Efficiency | 90% | 81% | 73% | 66% | ||||||||
###
| 42HSC4409 Planetary Gearbox Specifications: | ||||||||||||
| Reduction ratio | 3.71 | 5.18 | 14 | 19 | 27 | 51 | 71 | 100 | 139 | 189 | 264 | 369 |
| Total Height(L1+L2) (mm) | 71.5 | 71.5 | 82.1 | 82.1 | 82.1 | 92.5 | 92.5 | 92.5 | 92.5 | 102.9 | 102.9 | 102.9 |
| Output torque ( mN.m) | 1269 | 1772 | 4309 | 5000 | 5000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 |
| Total Weight(g) | 508 | 508 | 590 | 590 | 590 | 672 | 672 | 672 | 672 | 754 | 754 | 754 |
| Number of gear trains | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||
| Reducer Length(L2) (mm) | 31.5 | 42.1 | 52.5 | 62.9 | ||||||||
| Efficiency | 90% | 81% | 73% | 66% | ||||||||
How to Assemble a Planetary Motor
A Planetary Motor uses multiple planetary surfaces to produce torque and rotational speed. The planetary system allows for a wide range of gear reductions. Planetary systems are particularly effective in applications where higher torques and torque density are needed. As such, they are a popular choice for electric vehicles and other applications where high-speed mobility is required. Nevertheless, there are many benefits associated with using a planetary motor. Read on to learn more about these motors.
VPLite
If you’re looking to replace the original VP, the VPLite has a similar output shaft as the original. This means that you can mix and match your original gear sets, including the input and output shafts. You can even mix metal inputs with plastic outputs. Moreover, if you decide to replace the gearbox, you can easily disassemble the entire unit and replace it with a new one without losing any output torque.
Compared to a planetary motor, a spur gear motor uses fewer gears and is therefore cheaper to produce. However, the latter isn’t suitable for high-torque applications. The torque produced by a planetary gearmotor is evenly distributed, which makes it ideal for applications that require higher torque. However, you may have to compromise on the torque output if you’re looking for a lightweight option.
The VersaPlanetary Lite gearbox replaces the aluminum ring gear with a 30% glass-filled nylon gear. This gearbox is available in two sizes, which means you can mix and match parts to get a better gear ratio. The VPLite gearbox also has a female 5mm hex output shaft. You can mix and match different gearboxes and planetary gearboxes for maximum efficiency.
VersaPlanetary
The VersaPlanetary is a highly versatile planetary motor that can be mounted in a variety of ways. Its unique design includes a removable shaft coupler system that makes it simple to swap out the motor with another. This planetary motor mounts in any position where a CIM motor mounts. Here’s how to assemble the motor. First, remove the hex output shaft from the VersaPlanetary output stage. Its single ring clip holds it in place. You can use a drill press to drill a hole into the output shaft.
After mounting the gearbox, you can then mount the motor. The mounting hardware included with the VersaPlanetary Planetary Motor comes with four 10-32 threaded holes on a two-inch bolt circle. You can use these holes to mount your VersaPlanetary on a CIM motor or a CIM-compatible motor. Once assembled, the VersaPlanetary gearbox has 72 different gear ratios.
The VersaPlanetary gearbox is interchangeable with regular planetary gearboxes. However, it does require additional parts. You can purchase a gearbox without the motor but you’ll need a pinion. The pinion attaches to the shaft of the motor. The gearbox is very sturdy and durable, so you won’t have to worry about it breaking or wearing out.
Self-centering planetary gears
A planetary motor is a simple mechanical device that rotates around a axis, with the planets moving around the shaft in a radial direction. The planets are positioned so that they mesh with both the sun gear and the output gears. The carrier 48 is flexibly connected to the drive shaft and can move depending on the forces exerted by the planet gears. In this way, the planets can always be in the optimal mesh with the output gears and sun gear.
The first step in developing a planetary gear motor is to identify the number of teeth in each planet. The number of teeth should be an integer. The tooth diameters of the planets should mesh with each other and the ring. Typically, the teeth of one planet must mesh with each other, but the spacing between them must be equal or greater than the other. This can be achieved by considering the tooth count of each planet, as well as the spacing between planets.
A second step is to align the planet gears with the output gears. In a planetary motor, self-centering planetary gears must be aligned with both input and output gears to provide maximum torque. For this to be possible, the planet gears must be connected with the output shaft and the input shaft. Similarly, the output shaft should also be able to align with the input gear.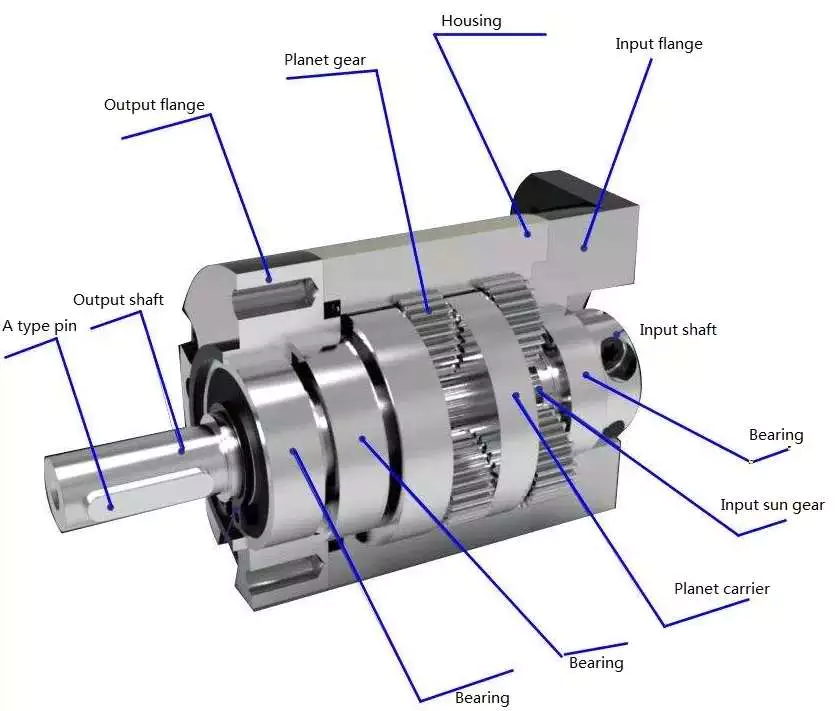
Encoders
A planetary geared motor is a DC motor with a planetary gearbox. The motor can be used to drive heavy loads and has a ratio of 104:1. The shaft speed is 116rpm when it is unloaded. A planetary gearbox has a low backlash and is often used in applications that need high torque. Planetary Motor encoders can help you keep track of your robot’s position or speed.
They are also able to control motor position and speed with precision. Most of them feature high resolution. A 0.18-degree resolution encoder will give you a minimum of 2000 transitions per rotation between outputs A and B. The encoder is built to industrial standards and has a sturdy gearbox to avoid damage. The encoder’s robust design means it will not stall when the motor reaches its maximum speed.
There are many advantages to a planetary motor encoder. A high-quality one will not lose its position or speed even if it’s subject to shocks. A good quality planetary motor will also last a long time. Planetary motors are great for resale or for your own project. If you’re considering buying a planetary motor, consider this information. It’ll help you decide if a particular model is right for your needs.
Cost
There are several advantages of planetary motors. One of the biggest is their cost, but they can also be used in many different applications. They can be combined with a variety of gearboxes, and are ideal for various types of robots, laboratory automation, and production applications. Planetary gearboxes are available in many different materials, and plastic planetary gearboxes are an economical alternative. Plastic gearboxes reduce noise at higher speeds, and steel input stage gears are available for high torques. A modified lubrication system can help with difficult operating conditions.
In addition to being more durable, planetary motors are much more efficient. They use fewer gears, which lowers the overall cost of production. Depending on the application, a planetary motor can be used to move a heavy object, but is generally less expensive than its counterpart. It is a better choice for situations where the load is relatively low and the motor is not used frequently. If you need a very high torque output, a planetary motor may be the better option.
Planetary gear units are a good choice for applications requiring high precision, high dynamics, and high torque density. They can be designed and built using TwinCAT and TC Motion Designer, and are delivered as complete motor and gear unit assemblies. In a few simple steps, you can calculate the torque required and compare the costs of different planetary gear units. You can then choose the best model for your application. And because planetary gear units are so efficient, they are a great option for high-end industrial applications.
Applications
There are several different applications of the planetary motor. One such application is in motion control. Planetary gearboxes have many benefits, including high torque, low backlash, and torsional stiffness. They also have an extremely compact design, and can be used for a variety of applications, from rack and pinion drives to delta robotics. In many cases, they are less expensive to manufacture and use than other types of motors.
Another application for planetary gear units is in rotary tables. These machines require high precision and low backlash for their precise positioning. Planetary gears are also necessary for noise reduction, which is a common feature in rotary tables. High precision planetary gears can make the height adjustment of OP tables a breeze. And because they are extremely durable and require low noise, they are a great choice for this application. In this case, the planetary gear is matched with an AM8000 series servomotor, which gives a wide range of choices.
The planetary gear transmission is also widely used in helicopters, automobiles, and marine applications. It is more advanced than a countershaft drive, and is capable of higher torque to weight ratios. Other advantages include its compact design and reduced noise. A key concern in the development of this type of transmission is to minimize vibration. If the output of a planetary gear transmission system is loud, the vibration caused by this type of drive system may be too loud for comfort.


editor by czh 2023-01-20