Product Description
nema17 Planetary Gearbox Stepping Motor price on hot sale
General Specificati
| Housing Material | Metal |
| Bearing at Output | Ball Bearings |
| Max.Radial Load(12mm from flange) | ≤80N |
| Max.Shaft Axial Load | ≤30N |
| Radial Play of Shaft (near to Flange) | ≤0.06mm |
| Axial Play of Shaft | ≤0.3mm |
| Backlash at No-load | 1.5° |
Electrical Specification:
| Model No. | Step Angle | Motor Length | Current /Phase |
Resistance /Phase |
Inductance /Phase |
Holding Torque | # of Leads | Detent Torque | Rotor Inertia | Mass |
| ( °) | (L)mm | A | Ω | mH | kg.cm | No. | g.cm | g.cm | Kg | |
| JK42HS34-1334 | 1.8 | 34 | 1.33 | 2.1 | 2.5 | 2.2 | 4 | 120 | 34 | 0.22 |
| JK42HS34-0406 | 1.8 | 34 | 0.4 | 24 | 15 | 1.6 | 6 | 120 | 34 | 0.22 |
| JK42HS40-1684 | 1.8 | 40 | 1.68 | 1.65 | 3.2 | 3.6 | 4 | 150 | 54 | 0.28 |
| JK42HS40-1206 | 1.8 | 40 | 1.2 | 3 | 2.7 | 2.9 | 6 | 150 | 54 | 0.28 |
| JK42HS48-1684 | 1.8 | 48 | 1.68 | 1.65 | 2.8 | 4.4 | 4 | 260 | 68 | 0.35 |
| JK42HS48-1206 | 1.8 | 48 | 1.2 | 3.3 | 2.8 | 3.17 | 6 | 260 | 68 | 0.35 |
| JK42HS60-1704 | 1.8 | 60 | 1.7 | 3 | 6.2 | 7.3 | 4 | 280 | 102 | 0.5 |
| JK42HS60-1206 | 1.8 | 60 | 1.2 | 6 | 7 | 5.6 | 6 | 280 | 102 | 0.5 |
42HS Planetary Gearbox Specifications
| Reduction ratio | 3.71 | 5.18 | 13.76 | 19.2 | 26.8 | 51 | 71 | 99.5 | 139 |
| Number of gear trains | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||||
| Length(L2) mm | 27.3 | 35 | 42.7 | ||||||
| Max.rated torque kg.cm | 20 | 30 | 40 | ||||||
| Short time permissible torque kg.cm | 40 | 60 | 80 | ||||||
| Weight g | 350 | 450 | 550 | ||||||
Products of special request can be made according to the customer request !
company information:
our certification:
Our Company offers 3 major series of products:Hybrid Stepper motors, Brushless Dc motor and Dc Brush motor.
We are always continues develop new type models.If you need other kinds of parts, please don’t hesitate to contact us.
Amy Gao
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Household Appliances, Car, Power Tools |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Adjust Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Compound |
| Function: | Run |
| Casing Protection: | Protection Type |
| Number of Poles: | 8 |
| Samples: |
US$ 21.5/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Are gear motors suitable for both heavy-duty industrial applications and smaller-scale uses?
Yes, gear motors are suitable for both heavy-duty industrial applications and smaller-scale uses. Their versatility and ability to provide torque multiplication make them valuable in a wide range of applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of why gear motors are suitable for both types of applications:
1. Heavy-Duty Industrial Applications:
Gear motors are commonly used in heavy-duty industrial applications due to their robustness and ability to handle high loads. Here are the reasons why they are suitable for such applications:
- Torque Multiplication: Gear motors are designed to provide high torque output, making them ideal for applications that require substantial force to move or operate heavy machinery, conveyors, or equipment.
- Load Handling: Industrial settings often involve heavy loads and demanding operating conditions. Gear motors, with their ability to handle high loads, are well-suited for tasks such as lifting, pulling, pushing, or driving heavy materials or equipment.
- Durability: Heavy-duty industrial applications require components that can withstand harsh environments, frequent use, and demanding operating conditions. Gear motors are typically constructed with durable materials and designed to withstand heavy vibrations, shock loads, and temperature variations.
- Speed Reduction: Many industrial processes require the reduction of motor speed to achieve the desired output speed. Gear motors offer precise speed reduction capabilities through gear ratios, allowing for optimal control and operation of machinery and equipment.
2. Smaller-Scale Uses:
While gear motors excel in heavy-duty industrial applications, they are also suitable for smaller-scale uses across various industries and applications. Here’s why gear motors are well-suited for smaller-scale uses:
- Compact Size: Gear motors are available in compact sizes, making them suitable for applications with limited space or small-scale machinery, devices, or appliances.
- Torque and Power Control: Even in smaller-scale applications, there may be a need for torque multiplication or precise power control. Gear motors can provide the necessary torque and power output for tasks such as precise positioning, controlling speed, or driving small loads.
- Versatility: Gear motors come in various configurations, such as parallel shaft, planetary, or worm gear designs, offering flexibility to match specific requirements. They can be adapted to different applications, including robotics, medical devices, automotive systems, home automation, and more.
- Efficiency: Gear motors are designed to be efficient, converting the electrical input power into mechanical output power with minimal losses. This efficiency is advantageous for smaller-scale applications where energy conservation and battery life are critical.
Overall, gear motors are highly versatile and suitable for both heavy-duty industrial applications and smaller-scale uses. Their ability to provide torque multiplication, handle high loads, offer precise speed control, and accommodate various sizes and configurations makes them a reliable choice in a wide range of applications. Whether it’s powering large industrial machinery or driving small-scale automation systems, gear motors provide the necessary torque, control, and durability required for efficient operation.

What are some common challenges or issues associated with gear motors, and how can they be addressed?
Gear motors, like any mechanical system, can face certain challenges or issues that may affect their performance, reliability, or longevity. However, many of these challenges can be addressed through proper design, maintenance, and operational practices. Here are some common challenges associated with gear motors and potential solutions:
1. Gear Wear and Failure:
Over time, gears in a gear motor can experience wear, resulting in decreased performance or even failure. The following measures can address this challenge:
- Proper Lubrication: Regular lubrication with the appropriate lubricant can minimize friction and wear between gear teeth. It is essential to follow manufacturer recommendations for lubrication intervals and use high-quality lubricants suitable for the specific gear motor.
- Maintenance and Inspection: Routine maintenance and periodic inspections can help identify early signs of gear wear or damage. Timely replacement of worn gears or components can prevent further damage and ensure the gear motor’s optimal performance.
- Material Selection: Choosing gears made from durable and wear-resistant materials, such as hardened steel or specialized alloys, can increase their lifespan and resistance to wear.
2. Backlash and Inaccuracy:
Backlash, as discussed earlier, can introduce inaccuracies in gear motor systems. The following approaches can help address this issue:
- Anti-Backlash Gears: Using anti-backlash gears, which are designed to minimize or eliminate backlash, can significantly reduce inaccuracies caused by gear play.
- Tight Manufacturing Tolerances: Ensuring precise manufacturing tolerances during gear production helps minimize backlash and improve overall accuracy.
- Backlash Compensation: Implementing control algorithms or mechanisms to compensate for backlash can help mitigate its effects and improve the accuracy of the gear motor.
3. Noise and Vibrations:
Gear motors can generate noise and vibrations during operation, which may be undesirable in certain applications. The following strategies can help mitigate this challenge:
- Noise Dampening: Incorporating noise-dampening features, such as vibration-absorbing materials or isolation mounts, can reduce noise and vibrations transmitted from the gear motor to the surrounding environment.
- Quality Gears and Bearings: Using high-quality gears and bearings can minimize vibrations and noise generation. Precision-machined gears and well-maintained bearings help ensure smooth operation and reduce unwanted noise.
- Proper Alignment: Ensuring accurate alignment of gears, shafts, and other components reduces the likelihood of noise and vibrations caused by misalignment. Regular inspections and adjustments can help maintain optimal alignment.
4. Overheating and Thermal Management:
Heat buildup can be a challenge in gear motors, especially during prolonged or heavy-duty operation. Effective thermal management techniques can address this issue:
- Adequate Ventilation: Providing proper ventilation and airflow around the gear motor helps dissipate heat. This can involve designing cooling fins, incorporating fans or blowers, or ensuring sufficient clearance for air circulation.
- Heat Dissipation Materials: Using heat-dissipating materials, such as aluminum or copper, in motor housings or heat sinks can improve heat dissipation and prevent overheating.
- Monitoring and Control: Implementing temperature sensors and thermal protection mechanisms allows for real-time monitoring of the gear motor’s temperature. If the temperature exceeds safe limits, the motor can be automatically shut down or adjusted to prevent damage.
5. Load Variations and Shock Loads:
Unexpected load variations or shock loads can impact the performance and durability of gear motors. The following measures can help address this challenge:
- Proper Sizing and Selection: Choosing gear motors with appropriate torque and load capacity ratings for the intended application helps ensure they can handle expected load variations and occasional shock loads without exceeding their limits.
- Shock Absorption: Incorporating shock-absorbing mechanisms, such as dampers or resilient couplings, can help mitigate the effects of sudden load changes or impacts on the gear motor.
- Load Monitoring: Implementing load monitoring systems or sensors allows for real-time monitoring of load variations. This information can be used to adjust operation or trigger protective measures when necessary.
By addressing these common challenges associated with gear motors through appropriate design considerations, regular maintenance, and operational practices, it is possible to enhance their performance, reliability, and longevity.

What is a gear motor, and how does it combine the functions of gears and a motor?
A gear motor is a type of motor that incorporates gears into its design to combine the functions of gears and a motor. It consists of a motor, which provides the mechanical power, and a set of gears, which transmit and modify this power to achieve specific output characteristics. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a gear motor is and how it combines the functions of gears and a motor:
A gear motor typically consists of two main components: the motor and the gear system. The motor is responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy, generating rotational motion. The gear system, on the other hand, consists of multiple gears with different sizes and tooth configurations. These gears are meshed together in a specific arrangement to transmit and modify the output torque and speed of the motor.
The gears in a gear motor serve several functions:
1. Torque Amplification:
One of the primary functions of the gear system in a gear motor is to amplify the torque output of the motor. By using gears with different sizes, the input torque can be effectively multiplied or reduced. This allows the gear motor to provide higher torque at lower speeds or lower torque at higher speeds, depending on the gear arrangement. This torque amplification is beneficial in applications where high torque is required, such as in heavy machinery or vehicles.
2. Speed Reduction or Increase:
The gear system in a gear motor can also be used to reduce or increase the rotational speed of the motor output. By utilizing gears with different numbers of teeth, the gear ratio can be adjusted to achieve the desired speed output. For example, a gear motor with a higher gear ratio will output lower speed but higher torque, whereas a gear motor with a lower gear ratio will output higher speed but lower torque. This speed control capability allows for precise matching of motor output to the requirements of specific applications.
3. Directional Control:
Gears in a gear motor can be used to control the direction of rotation of the motor output shaft. By employing different combinations of gears, such as spur gears, bevel gears, or worm gears, the rotational direction can be changed. This directional control is crucial in applications where bidirectional movement is required, such as in conveyor systems or robotic arms.
4. Load Distribution:
The gear system in a gear motor helps distribute the load evenly across multiple gears, which reduces the stress on individual gears and increases the overall durability and lifespan of the motor. By sharing the load among multiple gears, the gear motor can handle higher torque applications without putting excessive strain on any particular gear. This load distribution capability is especially important in heavy-duty applications that require continuous operation under demanding conditions.
By combining the functions of gears and a motor, gear motors offer several advantages. They provide torque amplification, speed control, directional control, and load distribution capabilities, making them suitable for various applications that require precise and controlled mechanical power. Gear motors are commonly used in industries such as robotics, automotive, manufacturing, and automation, where reliable and efficient power transmission is essential.


editor by CX 2024-03-28
China High Torque 30W 50W 80W Planetary 12V 24V DC Electric Motor with Reduction Gear with Good quality
Merchandise Description
Glow Motors Solution Presentation
1. Features
1) 16 poles with 3 phases exterior rotor
two) Reduced torque ripple
three) Large inertia torque
four) Compact design and style
five) Insulation class B
six) Application: Health care, Automation
2. Efficiency parameters
| Item | Directions |
|
Star |
|
120 degree electrical angle |
|
±10% @20ºC |
|
±20% @1kHz |
|
-20ºC~+50ºC |
|
100MΩMin. ,500VDC |
|
500VAC for 1 minute |
|
.02Max. (450 g-load) |
|
.15Max. (450 g-load) |
|
Course B |
3. Mechanical Dimensions
four. Wiring recommendations
| Lead Color | Guide Gauge | Operate | Instructions |
| Crimson | UL1430 26AWG | Vcc | Corridor positive:+5V~+24V DC |
| BLUE | Hall A | ||
| Inexperienced | Hall B | ||
| WHITE | Corridor C | ||
| BLACK | GND | HALL unfavorable | |
| YELLOW | UL1430 20AWG | Period U | |
| Purple | Period V | ||
| BLACK | Phase W |
5. Shnmotor Prime Rated Merchandise
six. Package
1.FedEX / DHL / UPS / TNT for samples,Door to door services
two.By sea for batch merchandise
3.Customs specifying freight forwarders or negotiable shipping techniques
four.Supply Time:20-twenty five Times for samples30-35 Days for batch goods
5.Payment Phrases:T/T,L/C at sight,D/P etc.
seven. FAQ
Q1. When can I get the quotation?
We generally estimate inside of 24 hrs after we get your inquiry.
If you are urgent to get the price tag, you should deliver the message on and or phone us straight.
Q2. How can I get a sample to verify your good quality?
Right after cost verified, you can requiry for samples to verify top quality.
If you need the samples, we will demand for the sample cost.
But the sample value can be refundable when your quantity of 1st purchase is earlier mentioned the MOQ
Q3. Can you do OEM for us?
Sure, the merchandise packing can be made as you want.
Q4. How about MOQ?
1 pcs for carton box.
Q5. What is your main market?
Jap Europe, Southeast Asia, South The usa.
You should feel free to speak to us if you have any query.
|
US $5.5-50 / Piece | |
100 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated| Freight Cost Calculator |
|---|
###
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Household Appliances, Car, Power Tools |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Adjust Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Excited |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Item | Instructions |
|
Star |
|
120 degree electrical angle |
|
±10% @20ºC |
|
±20% @1kHz |
|
-20ºC~+50ºC |
|
100MΩMin. ,500VDC |
|
500VAC for one minute |
|
0.02Max. (450 g-load) |
|
0.15Max. (450 g-load) |
|
Class B |
###
| Lead Color | Lead Gauge | Function | Instructions |
| RED | UL1430 26AWG | Vcc | Hall positive:+5V~+24V DC |
| BLUE | HALL A | ||
| GREEN | HALL B | ||
| WHITE | HALL C | ||
| BLACK | GND | HALL negative | |
| YELLOW | UL1430 20AWG | PHASE U | |
| RED | PHASE V | ||
| BLACK | PHASE W |
|
US $5.5-50 / Piece | |
100 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated| Freight Cost Calculator |
|---|
###
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Household Appliances, Car, Power Tools |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Adjust Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Excited |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Item | Instructions |
|
Star |
|
120 degree electrical angle |
|
±10% @20ºC |
|
±20% @1kHz |
|
-20ºC~+50ºC |
|
100MΩMin. ,500VDC |
|
500VAC for one minute |
|
0.02Max. (450 g-load) |
|
0.15Max. (450 g-load) |
|
Class B |
###
| Lead Color | Lead Gauge | Function | Instructions |
| RED | UL1430 26AWG | Vcc | Hall positive:+5V~+24V DC |
| BLUE | HALL A | ||
| GREEN | HALL B | ||
| WHITE | HALL C | ||
| BLACK | GND | HALL negative | |
| YELLOW | UL1430 20AWG | PHASE U | |
| RED | PHASE V | ||
| BLACK | PHASE W |
What Is a Gear Motor?
A gear motor is an electric motor coupled with a gear train. It uses either DC or AC power to achieve its purpose. The primary benefit of a gear reducer is its ability to multiply torque while maintaining a compact size. The trade-off of this additional torque comes in the form of a reduced output shaft speed and overall efficiency. However, proper gear technology and ratios provide optimum output and speed profiles. This type of motor unlocks the full potential of OEM equipment.
Inertial load
Inertial load on a gear motor is the amount of force a rotating device produces due to its inverse square relationship with its inertia. The greater the inertia, the less torque can be produced by the gear motor. However, if the inertia is too high, it can cause problems with positioning, settling time, and controlling torque and velocity. Gear ratios should be selected for optimal power transfer.
The duration of acceleration and braking time of a gear motor depends on the type of driven load. An inertia load requires longer acceleration time whereas a friction load requires breakaway torque to start the load and maintain it at its desired speed. Too short a time period can cause excessive gear loading and may result in damaged gears. A safe approach is to disconnect the load when power is disconnected to prevent inertia from driving back through the output shaft.
Inertia is a fundamental concept in the design of motors and drive systems. The ratio of mass and inertia of a load to a motor determines how well the motor can control its speed during acceleration or deceleration. The mass moment of inertia, also called rotational inertia, is dependent on the mass, geometry, and center of mass of an object.
Applications
There are many applications of gear motors. They provide a powerful yet efficient means of speed and torque control. They can be either AC or DC, and the two most common motor types are the three-phase asynchronous and the permanent magnet synchronous servomotor. The type of motor used for a given application will determine its cost, reliability, and complexity. Gear motors are typically used in applications where high torque is required and space or power constraints are significant.
There are two types of gear motors. Depending on the ratio, each gear has an output shaft and an input shaft. Gear motors use hydraulic pressure to produce torque. The pressure builds on one side of the motor until it generates enough torque to power a rotating load. This type of motors is not recommended for applications where load reversals occur, as the holding torque will diminish with age and shaft vibration. However, it can be used for precision applications.
The market landscape shows the competitive environment of the gear motor industry. This report also highlights key items, income and value creation by region and country. The report also examines the competitive landscape by region, including the United States, China, India, the GCC, South Africa, Brazil, and the rest of the world. It is important to note that the report contains segment-specific information, so that readers can easily understand the market potential of the geared motors market.
Size
The safety factor, or SF, of a gear motor is an important consideration when selecting one for a particular application. It compensates for the stresses placed on the gearing and enables it to run at maximum efficiency. Manufacturers provide tables detailing typical applications, with multiplication factors for duty. A gear motor with a SF of three or more is suitable for difficult applications, while a gearmotor with a SF of one or two is suitable for relatively easy applications.
The global gear motor market is highly fragmented, with numerous small players catering to various end-use industries. The report identifies various industry trends and provides comprehensive information on the market. It outlines historical data and offers valuable insights on the industry. The report also employs several methodologies and approaches to analyze the market. In addition to providing historical data, it includes detailed information by market segment. In-depth analysis of market segments is provided to help identify which technologies will be most suitable for which applications.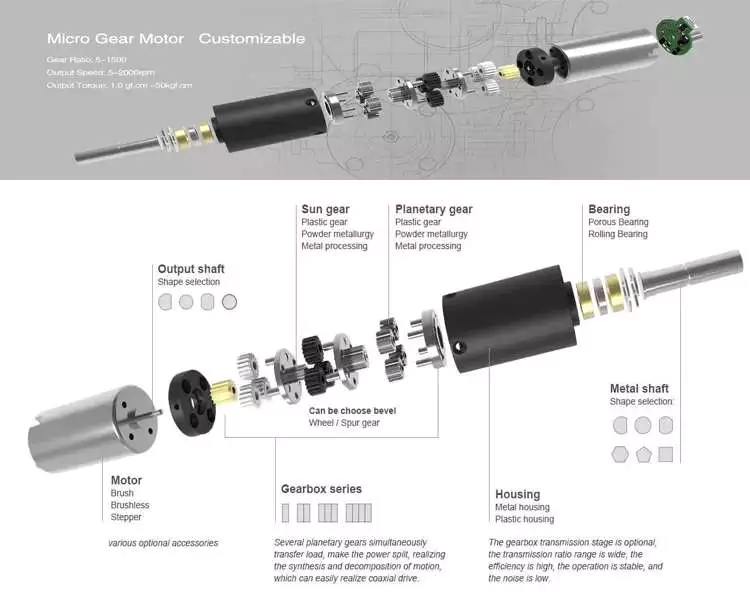
Cost
A gear motor is an electric motor that is paired with a gear train. They are available in AC or DC power systems. Compared to conventional motors, gear reducers can maximize torque while maintaining compact dimensions. But the trade-off is the reduced output shaft speed and overall efficiency. However, when used correctly, a gear motor can produce optimal output and mechanical fit. To understand how a gear motor works, let’s look at two types: right-angle geared motors and inline geared motors. The first two types are usually used in automation equipment and in agricultural and medical applications. The latter type is designed for rugged applications.
In addition to its efficiency, DC gear motors are space-saving and have low energy consumption. They can be used in a number of applications including money counters and printers. Automatic window machines and curtains, glass curtain walls, and banknote vending machines are some of the other major applications of these motors. They can cost up to 10 horsepower, which is a lot for an industrial machine. However, these are not all-out expensive.
Electric gear motors are versatile and widely used. However, they do not work well in applications requiring high shaft speed and torque. Examples of these include conveyor drives, frozen beverage machines, and medical tools. These applications require high shaft speed, so gear motors are not ideal for these applications. However, if noise and other problems are not a concern, a motor-only solution may be the better choice. This way, you can use a single motor for multiple applications.
Maintenance
Geared motors are among the most common equipment used for drive trains. Proper maintenance can prevent damage and maximize their efficiency. A guide to gear motor maintenance is available from WEG. To prevent further damage, follow these maintenance steps:
Regularly check electrical connections. Check for loose connections and torque them to the recommended values. Also, check the contacts and relays to make sure they are not tangled or damaged. Check the environment around the gear motor to prevent dust from clogging the passageway of electric current. A proper maintenance plan will help you identify problems and extend their life. The manual will also tell you about any problems with the gearmotor. However, this is not enough – it is important to check the condition of the gearbox and its parts.
Conduct visual inspection. The purpose of visual inspection is to note any irregularities that may indicate possible problems with the gear motor. A dirty motor may be an indication of a rough environment and a lot of problems. You can also perform a smell test. If you can smell a burned odor coming from the windings, there may be an overheating problem. Overheating can cause the windings to burn and damage.
Reactive maintenance is the most common method of motor maintenance. In this type of maintenance, you only perform repairs if the motor stops working due to a malfunction. Regular inspection is necessary to avoid unexpected motor failures. By using a logbook to document motor operations, you can determine when it is time to replace the gear motor. In contrast to preventive maintenance, reactive maintenance requires no regular tests or services. However, it is recommended to perform inspections every six months.


editor by czh 2023-01-17
in Vladivostok Russian Federation sales price shop near me near me shop factory supplier Step Stepping High Torque Hybrid Electric Reduction Stepper Planetary Gear Motor manufacturer best Cost Custom Cheap wholesaler

If you are interested in any of our items or would like to discuss a prospective buy, please really feel cost-free to speak to us. We have exported our goods to Korea, Turkey, Bulgaria, Romania, Russia, Italy, Norway, the Usa, Canada, and so forth. Our main goods are Needle Roller bearings, Cylindrical Roller Bearings, Rod end Bearings, Spherical basic bearings, Keep track of roller Bearings for Guideway, Roller Bearings, Mix Bearings for forklifts, Drinking water Pump Bearings, SNR Car Bearings and all types of Spherical Bearings. Action Stepping Large Torque Hybrid Electrical Reduction Stepper Equipment EPT
Features:
one. Placement mistake correction and never get rid of actions
2. Substantial torque at large speed
three. Quick reaction and excellent acceleration
4. EPT recent adjustment based on load, reduce temperature rising.
5. substantial dynamic overall performance at acceleration and deceleration, No vibration from high pace to zero velocity.
Product photo:
Specification:
| Merchandise Title | Electrical Stepper EPT |
| Dimensions | Nema 8(20mm), eleven(28mm), 14(35mm), sixteen(39mm), 17(42mm), 23(57mm), 24(60mm), 34(86mm) |
| Phase Angle | Diploma .nine, 1.two, 1.8(Optional or Customized) |
| Torque(oz.in) | Up to three.eleven, 5.7, seventeen, forty one, 56, 85, 113, 425 |
| Rated Current | .1A~10A (A/Phase) |
| Typical Purposes | Printers, Labeling EPT, Laser cutting EPT, SMT tools, EPT EPT, Dispensing EPT, Scorching stamping EPT, Manipulator, Robotic, Analytical and Medical Instruments, Textile EPT, Embroidery EPT, EPT Telescope Positioning Techniques, Substantial Velocity Dome Digicam |
FAQ
Q: Can you make the stepper motor with customization?
A: Indeed, we can customise for every your request, like EPT, voltage, speed, shaft measurement, wires, connectors, IP quality, and so on.
Q: Do you give samples?
A: Indeed. Sample is accessible for screening.
Q: What is your MOQ?
A: It is 10pcs for the commencing of our company.
Q: What is your guide time?
A: StXiHu (West Lake) Dis.Hu (West Lake) Dis.rd solution require 5-30days, a little bit EPTer for customized merchandise.
Q: Do you provide EPT assist?
A: Of course. Our company have design and deveXiHu (West Lake) Dis.Hu (West Lake) Dis.ment staff, we can give EPT help if you
require.
Q: How to ship to us?
A: It is available by air, or by sea, or by practice.
Q: How to shell out the cash?
A: T/T and L/C is chosen, with different forex, incXiHu (West Lake) Dis.Hu (West Lake) Dis. USD, EUR, RMB, etc.
Q: How can I know the item is suited for me?
A: gt1ST verify drawing and specification gt2nd check sample gt3rd start mass production.
Q: Can I occur to your business to go to?
A: Yes, you are welcome to check out us at any time.
Q: How shall we make contact with you?
A: You can send inquiry directly, and we will react within 24 hrs.


in Tirunelveli India sales price shop near me near me shop factory supplier Planetary Gearbox Gear Speed Reducer Motor Winch Track Wheel Drive System Reduction Transmission Epicyclic Inline Precision Precision NEMA 34 Gearbox manufacturer best Cost Custom Cheap wholesaler

Due to our wide product selection and abundant encounters in this business, Our merchandise are used in many fields. In addition, WE CAN Generate Custom-made VARIATORS, GEARED MOTORS, Electric MOTORS AND OTHER HYDRAULIC Merchandise In accordance TO CUSTOMERS’ DRAWINGS.
Planetary EPT equipment pace EPT motor winch keep track of wheel drive method reduction EPT epicyclic inline precision precision nema 34 EPT

